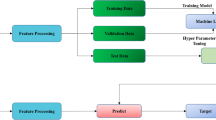
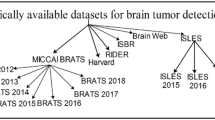
Abstract
A brain stroke, commonly called as a cerebral vascular accident (CVA) is one of the deadliest diseases across the globe and may lead to various physical impairments or even death. Therefore, timely detection, diagnosis, and treatment of said medical emergency are urgent requirements to minimize life loss, which is not affordable in any sense. Nowadays, with the advancements in Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning, these techniques are popularly used in the domain of medical image analysis in general, and brain stroke imaging in particular, to automate image analysis more accurately and less human error-prone. The aim of this state-of-the-art study is to explore the latest computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) techniques to detect, classify, and segment cerebral strokes. Available methods or techniques, and tools used for analysis have been presented and compared with their attained results. In this study, available open-access datasets in the domain of brain stroke analysis have been explored and presented. Moreover, the research also includes the major challenges and provides researchers with applicable future directions.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing does not apply to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
The Central Nervous System: Structure and Function - Per Brodal - Google Books. https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=WdATFQ0YUrMC&oi=fnd&pg=PR7&dq=brain+structure+and+nervous+system&ots=TVt9ofJzVV&sig=fjPE2T798Jbr07ksqNluorZXGlw&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false. Accessed 3 Nov 2022
Calhoun V (2022) Data-driven approaches for identifying links between brain structure and function in health and disease. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 20:87–100. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2018.20.2/VCALHOUN
Casillo SM, Luy DD, Goldschmidt E (2020) A History of the Lobes of the Brain. World Neurosurg 134:353–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WNEU.2019.10.155
Bontempi D, Benini S, Signoroni A et al (2020) CEREBRUM: a fast and fully-volumetric Convolutional Encoder-decodeR for weakly-supervised sEgmentation of BRain strUctures from out-of-the-scanner MRI. Med Image Anal 62:101688. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEDIA.2020.101688
King M, Hernandez-Castillo CR, Poldrack RA et al (2019) (2019) Functional boundaries in the human cerebellum revealed by a multi-domain task battery. Nat Neurosci 228(22):1371–1378. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-019-0436-x
Sclocco R, Beissner F, Bianciardi M et al (2018) Challenges and opportunities for brainstem neuroimaging with ultrahigh field MRI. Neuroimage 168:412–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NEUROIMAGE.2017.02.052
Brain Structure And Function | Brain Injury | British Columbia. https://www.nbia.ca/brain-structure-function/. Accessed 11 Dec 2022
Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI et al (2022) Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2022 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 145:E153–E639
World Health Organization (2014) The top 10 causes of death. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death. Accessed 17 Oct 2022
Inamdar MA, Raghavendra U, Gudigar A et al (2021) A Review on Computer Aided Diagnosis of Acute Brain Stroke. Sensors 21(8507):21–8507. https://doi.org/10.3390/S21248507
Vilela P, Rowley HA (2017) Brain ischemia: CT and MRI techniques in acute ischemic stroke. Eur J Radiol 96:162–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EJRAD.2017.08.014
Karthik R, Menaka R (2017) Computer-aided detection and characterization of stroke lesion – a short review on the current state-of-the art methods. Imaging Sci J 66:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/13682199.2017.1370879
Demeestere J, Wouters A, Christensen S, et al (2020) Review of Perfusion Imaging in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 1017–1024https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.028337
Meijs M, Meijer FJA, Prokop M et al (2020) Image-level detection of arterial occlusions in 4D-CTA of acute stroke patients using deep learning. Med Image Anal 66:101810. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEDIA.2020.101810
Karthik R, Menaka R, Johnson A, Anand S (2020) Neuroimaging and deep learning for brain stroke detection - A review of recent advancements and future prospects. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 197:105728. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CMPB.2020.105728
Macellari F, Paciaroni M, Agnelli G, Caso V (2014) Neuroimaging in intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 45:903–908
ISLES: Ischemic Stroke Lesion Segmentation Challenge 2022. http://www.isles-challenge.org/. Accessed 17 Oct 2022
Dick S (2019) Artificial Intelligence. Harvard Data Sci Rev 1:. https://doi.org/10.1162/99608F92.92FE150C
Alzubi JA, Kumar A, Alzubi OA, Manikandan R (2019) Efficient approaches for prediction of brain tumor using machine learning techniques. Indian J Public Heal Res Dev 10:267–272. https://doi.org/10.5958/0976-5506.2019.00298.5
de Bruijne M (2016) Machine learning approaches in medical image analysis: From detection to diagnosis. Med Image Anal 33:94–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEDIA.2016.06.032
Erickson BJ, Korfiatis P, Akkus Z, Kline TL (2017) Machine Learning for Medical Imaging. Radiographics 37:505. https://doi.org/10.1148/RG.2017160130
Libbrecht MW (2015) Noble WS (2015) Machine learning applications in genetics and genomics. Nat Rev Genet 166(16):321–332. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3920
Noble WS (2006) What is a support vector machine? Nat Biotechnol 24:1565–1567
Schober P, Vetter TR (2021) Logistic Regression in Medical Research. Anesth Analg 132:365. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000005247
Alzubi OA, Alzubi JA, Alweshah M et al (2020) An optimal pruning algorithm of classifier ensembles: dynamic programming approach. Neural Comput Appl 32:16091–16107. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00521-020-04761-6
Chen T, Shang C, Su P et al (2021) A Decision Tree-Initialised Neuro-fuzzy Approach for Clinical Decision Support. Artif Intell Med 111:101986. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ARTMED.2020.101986
Wickramasinghe I, Kalutarage H (2021) Naive Bayes: applications, variations and vulnerabilities: a review of literature with code snippets for implementation. Soft Comput 25:2277–2293. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00500-020-05297-6/FIGURES/2
Thayumanavan M, Ramasamy A (2021) An efficient approach for brain tumor detection and segmentation in MR brain images using random forest classifier, 266–274https://doi.org/10.1177/1063293X211010542
Movassagh AA, Alzubi JA, Gheisari M et al (2023) Artificial neural networks training algorithm integrating invasive weed optimization with differential evolutionary model. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 14:6017–6025. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02623-6
Shahid N, Rappon T, Berta W (2019) Applications of artificial neural networks in health care organizational decision-making: A scoping review. PLoS ONE 14:e0212356
Mutasa S, Sun S, Ha R (2021) Understanding artificial intelligence based radiology studies: CNN architecture. Clin Imaging 80:72–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CLINIMAG.2021.06.033
Chen M, Shi X, Zhang Y et al (2017) Deep Feature Learning for Medical Image Analysis with Convolutional Autoencoder Neural Network. IEEE Trans Big Data 7:750–758. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBDATA.2017.2717439
Yi X, Walia E, Babyn P (2019) Generative adversarial network in medical imaging: A review. Med Image Anal 58:101552. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEDIA.2019.101552
Alzubi OA, Alzubi JAA, Tedmori S, Rashaideh H, Almomani O (2018) Consensus-based combining method for classifier ensembles. Int Arab J Inf Technol 15(1):76–86
Rebouças Filho PP, Sarmento RM, Holanda GB, de Alencar LD (2017) New approach to detect and classify stroke in skull CT images via analysis of brain tissue densities. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 148:27–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2017.06.011
Karthik R, Menaka R (2017) A multi-scale approach for detection of ischemic stroke from brain MR images using discrete curvelet transformation. Meas J Int Meas Confed 100:223–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2017.01.001
Subudhi A, Acharya UR, Dash M et al (2018) Automated approach for detection of ischemic stroke using Delaunay Triangulation in brain MRI images. Comput Biol Med 103:116–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.10.016
Rajendra Acharya U, Meiburger KM, Faust O et al (2019) Automatic detection of ischemic stroke using higher order spectra features in brain MRI images. Cogn Syst Res 58:134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsys.2019.05.005
Dourado CMJM, da Silva SPP, da Nóbrega RVM et al (2019) Deep learning IoT system for online stroke detection in skull computed tomography images. Comput Networks 152:25–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMNET.2019.01.019
Patel A, Van De Leemput SC, Prokop M et al (2019) Image Level Training and Prediction: Intracranial Hemorrhage Identification in 3D Non-Contrast CT. IEEE Access 7:92355–92364. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2927792
Ho KC, Speier W, Zhang H et al (2019) A Machine Learning Approach for Classifying Ischemic Stroke Onset Time from Imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38:1666–1676. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2019.2901445
Anbumozhi S (2020) Computer aided detection and diagnosis methodology for brain stroke using adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system classifier. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 30:196–202. https://doi.org/10.1002/ima.22380
Gautam A, Raman B (2020) Local gradient of gradient pattern: a robust image descriptor for the classification of brain strokes from computed tomography images. Pattern Anal Appl 23:797–817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-019-00838-8
Vasconcelos FFX, Sarmento RM, Rebouças Filho PP, de Albuquerque VHC (2020) Artificial intelligence techniques empowered edge-cloud architecture for brain CT image analysis. Eng Appl Artif Intell 91:103585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2020.103585
Herzog L, Murina E, Dürr O et al (2020) Integrating uncertainty in deep neural networks for MRI based stroke analysis. Med Image Anal 65:101790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2020.101790
Anupama CSS, Sivaram M, Lydia EL et al (2022) Synergic deep learning model–based automated detection and classification of brain intracranial hemorrhage images in wearable networks. Pers Ubiquitous Comput 26:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-020-01492-2
Gautam A, Raman B (2021) Towards effective classification of brain hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke using CNN. Biomed Signal Process Control 63:102178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102178
Cetinoglu YK, Koska IO, Uluc ME, Gelal MF (2021) Detection and vascular territorial classification of stroke on diffusion-weighted MRI by deep learning. Eur J Radiol 145:110050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.110050
Xu Y, Holanda G, Souza LFDF et al (2021) Deep Learning-Enhanced Internet of Medical Things to Analyze Brain CT Scans of Hemorrhagic Stroke Patients: A New Approach. IEEE Sens J 21:24941–24951. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2020.3032897
Gautam A, Raman B (2021) Brain strokes classification by extracting quantum information from CT scans. Multimed Tools Appl 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11342-9
Neethi AS, Niyas S, Kannath SK et al (2022) Stroke classification from computed tomography scans using 3D convolutional neural network. Biomed Signal Process Control 76:103720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2022.103720
Dogan S, Barua PD, Baygin M et al (2022) Novel multiple pooling and local phase quantization stable feature extraction techniques for automated classification of brain infarcts. Biocybern Biomed Eng 42:815–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2022.06.004
Chen YT, Chen YL, Chen YY et al (2022) Deep Learning-Based Brain Computed Tomography Image Classification with Hyperparameter Optimization through Transfer Learning for Stroke. Diagnostics 12:807. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040807
Tasci B, Tasci I (2022) Deep feature extraction based brain image classification model using preprocessed images: PDRNet. Biomed Signal Process Control 78:103948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2022.103948
Din MS, Gurbuz S, Akbal E et al (2022) Exemplar deep and hand-modeled features based automated and accurate cerebral hemorrhage classification method. Med Eng Phys 105:103819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2022.103819
Altuve M, Pérez A (2022) Intracerebral hemorrhage detection on computed tomography images using a residual neural network. Phys Medica 99:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2022.05.015
Deepa B, Murugappan M, Sumithra MG et al (2022) Pattern Descriptors Orientation and MAP Firefly Algorithm Based Brain Pathology Classification Using Hybridized Machine Learning Algorithm. IEEE Access 10:3848–3863. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3100549
Sivakumar P, Ganeshkumar P (2017) An efficient automated methodology for detecting and segmenting the ischemic stroke in brain MRI images. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 27:265–272. https://doi.org/10.1002/ima.22231
Zhang R, Zhao L, Lou W et al (2018) Automatic Segmentation of Acute Ischemic Stroke From DWI Using 3-D Fully Convolutional DenseNets. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 37:2149–2160. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2018.2821244
Gautam A, Raman B (2019) Segmentation of ischemic stroke lesion from 3d mr images using random forest. Multimed Tools Appl 78:6559–6579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6418-2
Deepa B, Sumithra MG (2019) An intensity factorized thresholding based segmentation technique with gradient discrete wavelet fusion for diagnosing stroke and tumor in brain MRI. Multidimens Syst Signal Process 30:2081–2112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-019-00642-x
Liu L, Chen S, Zhang F et al (2020) Deep convolutional neural network for automatically segmenting acute ischemic stroke lesion in multi-modality MRI. Neural Comput Appl 32:6545–6558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04096-x
Nishio M, Koyasu S, Noguchi S et al (2020) Automatic detection of acute ischemic stroke using non-contrast computed tomography and two-stage deep learning model. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 196:105711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105711
Nazari-Farsani S, Nyman M, Karjalainen T et al (2020) Automated segmentation of acute stroke lesions using a data-driven anomaly detection on diffusion weighted MRI. J Neurosci Methods 333:108575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2019.108575
Li L, Wei M, Liu B et al (2021) Deep Learning for Hemorrhagic Lesion Detection and Segmentation on Brain CT Images. IEEE J Biomed Heal Inform 25:1646–1659. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2020.3028243
Zhang L, Zhu C, Wu YW et al (2021) SFCN: Symmetric feature comparison network for detecting ischemic stroke lesions on CT images. IET Image Process 15:2818–2832. https://doi.org/10.1049/ipr2.12267
Shin H, Agyeman R, Rafiq M et al (2022) Automated segmentation of chronic stroke lesion using efficient U-Net architecture. Biocybern Biomed Eng 42:285–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2022.01.002
Wang S, Chen Z, You S et al (2022) Brain stroke lesion segmentation using consistent perception generative adversarial network. Neural Comput Appl 34:8657–8669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06816-8
Tomasetti L, Hollesli LJ, Engan K et al (2022) Machine Learning Algorithms Versus Thresholding to Segment Ischemic Regions in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. IEEE J Biomed Heal Informatics 26:660–672. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2021.3097591
Bao Q, Mi S, Gang B et al (2022) MDAN: Mirror Difference Aware Network for Brain Stroke Lesion Segmentation. IEEE J Biomed Heal Inform 26:1628–1639. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2021.3113460
ITK-SNAP Home. http://www.itksnap.org/pmwiki/pmwiki.php. Accessed 1 Aug 2023
Subudhi A, Dash M, Sabut S (2020) Automated segmentation and classification of brain stroke using expectation-maximization and random forest classifier. Biocybern Biomed Eng 40:277–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2019.04.004
Yalçın S, Vural H (2022) Brain stroke classification and segmentation using encoder-decoder based deep convolutional neural networks. Comput Biol Med 149:105941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105941
BraTS - V7 Open Datasets. https://www.v7labs.com/open-datasets/brats. Accessed 22 Oct 2022
OpenNeuro. https://openneuro.org/. Accessed 22 Oct 2022
PhysioNet. https://physionet.org/. Accessed 22 Oct 2022
ISLES: Ischemic Stroke Lesion Segmentation Challenge 2022. https://www.isles-challenge.org/. Accessed 22 Oct 2022
Anatomical Tracings of Lesions After Stroke (ATLAS). https://www.fcon_1000.projects.nitrc.org/indi/retro/atlas.html. Accessed 22 Oct 2022
ADNI | Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. https://www.adni.loni.usc.edu/. Accessed 22 Oct 2022
OASIS Brains - Open Access Series of Imaging Studies. https://www.oasis-brains.org/. Accessed 22 Oct 2022
Naser MZ, Alavi A (2020) Insights into Performance Fitness and Error Metrics for Machine Learning. Archit Struct Constr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s44150-021-00015-8
Shamir RR, Duchin Y, Kim J, et al (2019) Continuous Dice Coefficient: a Method for Evaluating Probabilistic Segmentations. https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.1906.11031
Yeghiazaryan V, Voiculescu I (2018) Family of boundary overlap metrics for the evaluation of medical image segmentation. J Med Imaging 5:1. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JMI.5.1.015006
Karimi D, Salcudean SE (2020) Reducing the Hausdorff Distance in Medical Image Segmentation with Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39:499–513. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2019.2930068
Rezatofighi H, Tsoi N, Gwak J, Sadeghian A, Reid I, Savarese S (2019) Generalized intersection over union: A metric and a loss for bounding box regression. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, pp 658–666
Funding
No funding has been received from any person or organization to carry out this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests
There is no conflict of interest related to this research.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, G.K., Kumar, S., Ranga, V. et al. Artificial intelligence in cerebral stroke images classification and segmentation: A comprehensive study. Multimed Tools Appl 83, 43539–43575 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-17324-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-17324-3