Abstract
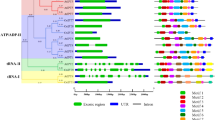
The High osmolarity glycerol (HOG) gene family plays crucial roles in various developmental and physiological processes in fungi, such as the permeability of cell membrane, chlamydospore formation and stress signaling. Although the function of HOG genes has been investigated in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and some filamentous fungi, a comprehensive analysis of HOG gene family has not been performed in Aspergillus oryzae, a fungi mainly used for the production of soy sauce. In this study, we identified and corrected a total of 90 HOG genes from the A. oryzae genome. According to the phylogenetic relationship, they were divided into four discrete groups (Group A–D) comprising of 16, 24, 30 and 20 proteins, respectively. Six conserved motifs and exon–intron structures were examined among all HOG proteins to reveal the diversity of AoHOG genes. Based on transcriptome technology, the expression patterns of AoHOG genes across all developmental stages was identified, suggesting that the AoHOG gene family mainly functions in the logarithmic phase of development. The expression profiles of AoHOG genes under different concentrations of salt stress indicated that AoHOG genes are extensively involved in salt stress response, with possibly different mechanisms. The genome-wide identification, evolutionary, gene structures and expression analyses of AoHOG genes provide a comprehensive overview of this gene family as well as their potential involvements in development and stress responses. Our results will facilitate further research on HOG gene family regarding their physiological and biochemical functions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altshuler I, Mcleod AM, Colbourne JK, Yan ND, Cristescu ME (2015) Synergistic interactions of biotic and abiotic environmental stressors on gene expression. Genome 58:99–109
Altwasser R, Baldin C, Weber J, Guthke R, Kniemeyer O, Brakhage AA, Linde J, Valiante V (2015) Network modeling reveals cross talk of MAP kinases during adaptation to caspofungin stress in Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS ONE 10:e0136932
Babazadeh R, Furukawa T, Hohmann S, Furukawa K (2014) Rewiring yeast osmostress signalling through the MAPK network reveals essential and non-essential roles of Hog1 in osmoadaptation. Sci Rep 4:4697
Bon E, Casaregola S, Blandin G, Llorente B, Neuveglise C, Munsterkotter M, Guldener U, Mewes HW, Van Helden J, Dujon B, Gaillardin C (2003) Molecular evolution of eukaryotic genomes: hemiascomycetous yeast spliceosomal introns. Nucleic Acids Res 31:1121–1135
Bondarenko VS, Gelfand MS (2016) Evolution of the exon-intron structure in ciliate genomes. PLoS ONE 11:e0161476
Chen RE, Thorner J (2007) Function and regulation in MAPK signaling pathways: lessons learned from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773:1311–1340
Cheng XJ, He B, Chen L, Xiao SQ, Fu J, Chen Y, Yu TQ, Cheng ZQ, Feng H (2016) Transcriptome analysis confers a complex disease resistance network in wild rice Oryza meyeriana against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Sci Rep 6:38215
Eisman B, Alonsomonge R, Román E, Arana D, Nombela C, Pla J (2006) The Cek1 and Hog1 mitogen-activated protein kinases play complementary roles in cell wall biogenesis and chlamydospore formation in the fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Eukaryot Cell 5:347
Fedorova ND, Khaldi N, Joardar VS, Maiti R, Amedeo P, Anderson MJ, Crabtree J, Silva JC, Badger JH, Albarraq A, Angiuoli S, Bussey H, Bowyer P, Cotty PJ, Dyer PS, Egan A, Galens K, Fraser-Liggett CM, Haas BJ, Inman JM, Kent R, Lemieux S, Malavazi I, Orvis J, Roemer T, Ronning CM, Sundaram JP, Sutton G, Turner G, Venter JC, White OR, Whitty BR, Youngman P, Wolfe KH, Goldman GH, Wortman JR, Jiang B, Denning DW, Nierman WC (2008) Genomic islands in the pathogenic filamentous fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS Genet 4:e1000046
Fitzgibbon GJ, Morozov IY, Jones MG, Caddick MX (2005) Genetic analysis of the TOR pathway in Aspergillus nidulans. Eukaryot Cell 4:1595–1598
Furukawa K, Yoshimi A, Furukawa T, Hoshi Y, Hagiwara D, Sato N, Fujioka T, Mizutani O, Mizuno T, Kobayashi T, Abe K (2007) Novel reporter gene expression systems for monitoring activation of the Aspergillus nidulans HOG pathway. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:1724–1730
Galagan JE, Calvo SE, Cuomo C, Ma LJ, Wortman JR, Batzoglou S, Lee SI, Baştürkmen M, Spevak CC, Clutterbuck J, Kapitonov V, Jurka J, Scazzocchio C, Farman M, Butler J, Purcell S, Harris S, Braus GH, Draht O, Busch S, D’Enfert C, Bouchier C, Goldman GH, Bell-Pedersen D, Griffiths-Jones S, Doonan JH, Yu J, Vienken K, Pain A, Freitag M, Selker EU, Archer DB, Peñalva MA, Oakley BR, Momany M, Tanaka T, Kumagai T, Asai K, Machida M, Nierman WC, Denning DW, Caddick M, Hynes M, Paoletti M, Fischer R, Miller B, Dyer P, Sachs MS, Osmani SA, Birren BW (2005) Sequencing of Aspergillus nidulans. and comparative analysis with A. fumigatus and A. oryzae. Nature 438:1105–1115
Gietz RD, Schiestl RH (2007) Quick and easy yeast transformation using the LiAc/SS carrier DNA/PEG method. Nat Protoc 2:35–37
Hagiwara D, Suzuki S, Kamei K, Gonoi T, Kawamoto S (2014) The role of AtfA and HOG MAPK pathway in stress tolerance in conidia of Aspergillus fumigatus. Fungal Genet Biol 73:138–149
Hagiwara D, Sakamoto K, Abe K, Gomi K (2016) Signaling pathways for stress responses and adaptation in Aspergillus species: stress biology in the post-genomic era. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 80:1–14
Han F, Pei H, Hu W, Zhang S, Han L, Ma G (2016) The feasibility of ultrasonic stimulation on microalgae for efficient lipid accumulation at the end of the logarithmic phase. Algal Res 16:189–194
He B, Gu YH, Tao X, Cheng XJ, Wei CH, Fu J, Cheng ZQ, Zhang YZ (2015) De novo transcriptome sequencing of Oryza officinalis Wall ex Watt to identify disease-resistance genes. Int J Mol Sci 16:29482–29495
He B, Ma L, Hu Z, Li H, Ai M, Long C, Zeng B (2017) Deep sequencing analysis of transcriptomes in Aspergillus oryzae in response to salinity stress. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 1–2:1–10
Hohmann S, Krantz M, Nordlander B (2007) Yeast osmoregulation. Method Enzymol 428:29
Ivashchenko AT, Tauasarova MI, Atambayeva SA (2009) Exon-intron structure of genes in complete fungal genomes. Mol Bio 43:24–31
Ji Y, Yang F, Ma D, Zhang J, Wan Z, Liu W, Li R (2012) HOG-MAPK signaling regulates the adaptive responses of Aspergillus fumigatus to thermal stress and other related stress. Mycopathologia 174:273–282
Kitamoto K (2015) Cell biology of the Koji mold Aspergillus oryzae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 79:1–7
Lee YH, Tominaga M, Hayashi R, Sakamoto K, Yamada O, Akita O (2006) Aspergillus oryzae strains with a large deletion of the aflatoxin biosynthetic homologous gene cluster differentiated by chromosomal breakage. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:339–345
Lee YM, Kim E, An J, Lee Y, Choi E, Choi W, Moon E, Kim W (2016) Dissection of the HOG pathway activated by hydrogen peroxide in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Environ Microbiol 19:584–597
Lenassi M, Vaupotic T, Gundecimerman N, Plemenitas A (2007) The MAP kinase HwHog1 from the halophilic black yeast Hortaea werneckii: coping with stresses in solar salterns. Aquat Biosyst 3:1–11
Liu B (2013) Characterizing the contributions of individual components to the dynamic properties of the HOG pathway in S. cerevisiae. Princeton: Princeton University
Liu Q, Xue Q (2007) Computational identification and phylogenetic analysis of the MAPK gene family in Oryza sativa. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:6
Loftus BJ et al (2005) The genome of the Basidiomycetous Yeast and Human Pathogen. Cryptococcus Neoformans Sci 307:1321
Machida M et al (2005) Genome sequencing and analysis of Aspergillus oryzae. Nature 438:1157–1161
Machida M, Yamada O, Gomi K (2008) Genomics of Aspergillus oryzae: learning from the history of Koji Mold and exploration of its future. DNA Res 15:173
Maeda H, Sano M, Maruyama Y, Tanno T, Akao T, Totsuka Y, Endo M, Sakurada R, Yamagata Y, Machida M, Akita O, Hasegawa F, Abe K, Gomi K, Nakajima T, Iguchi Y (2004) Transcriptional analysis of genes for energy catabolism and hydrolytic enzymes in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus oryzae using cDNA microarrays and expressed sequence tags. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:74–83
Mcguire AM, Pearson MD, Neafsey DE, Galagan JE (2008) Cross-kingdom patterns of alternative splicing and splice recognition. Genome Biol 9:R50
Nakazawa J, Terada S, Yamada M, Hikichi S (2013) The HOG signal transduction pathway in the halophilic fungus Wallemia ichthyophaga: identification and characterisation of MAP kinases WiHog1A and WiHog1B Extremophiles. Life Under Extreme Conditions 17:623–636
Payne GA et al (2009) Whole genome comparison of Aspergillus flavus. and A. oryzae. Med Mycol 44:S9–S11
Posas F, WurglerMurphy SM, Maeda T, Witten EA, Thai TC, Saito H (1996) Yeast HOG1 MAP kinase cascade is regulated by a multistep phosphorelay mechanism in the SLN1-YPD1-SSK1 “two-component” osmosensor. Cell 86:865–875
Solé C, Nadalribelles M, Kraft C, Peter M, Posas F, Nadal ED (2011) Control of Ubp3 ubiquitin protease activity by the Hog1 SAPK modulates transcription upon osmostress. Embo J 30:3274–3284
Wang D, Zheng ZY, Feng J, Zhan XB, Zhang LM, Wu JR, Lin CC (2013) A high salt tolerant neutral protease from Aspergillus oryzae: purification, characterization and kinetic properties. Appl Biochem Microbiol 49:378–385
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant Nos. 31171731 and 31460447), International S&T Cooperation Project of Jiangxi Provincial (Grant No. 20142BDH80003), General Science and Technology Project of Nanchang City (Grant No. 3000035402), “555 Talent Project” of Jiangxi Province and Science, the Science Funds of Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20114BAB205039) and Technology Research Project of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education (Grant Nos. GJJ160765, GJJ160795 and GJJ160794).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Research involving animal and human rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Bin He and Yayi Tu have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, B., Tu, Y., Hu, Z. et al. Genome-wide identification and expression profile analysis of the HOG gene family in Aspergillus oryzae. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34, 35 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-018-2419-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-018-2419-6