Abstract
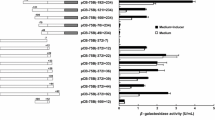
Bacillus pumilus SG2 is a chitinolytic bacterium that produces two chitinases, namely ChiS and ChiL. The chiS and chiL genes are consecutively expressed under a common promoter. Regulation of the chiS and chiL genes is under the control of carbon catabolite repression (CCR) in B. pumilus. This study aimed to investigate the cis-acting elements of the chitinase promoter. For this purpose, we transferred the chiS gene along with its specific promoter to Bacillus subtilis as a host. Primer extension analysis revealed two transcription start sites located 287 and 65 bp upstream of the chiS start codon. The distal promoter was highly compatible with the consensus sequence of the σA-type promoters in B. subtilis, whereas the proximal promoter sequence showed less similarity to the σA-type consensus sequence. A catabolite responsive element (cre), which is required for CCR in Bacillus species, was found to be 136 to 123 bp upstream of the chiS start codon. Interestingly, this cre site was located upstream of the −35 of the proximal promoter and downstream of the distal promoter. Deletion of this cre site sequence rendered the chiS expression constitutive.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadian G, Degrassi G, Venturi V, Zeigler DR, Soudi M, Zanguinejad P (2007) Bacillus pumilus SG2 isolated from saline conditions produces and secretes two chitinases. J Appl Microbiol 103:1081–1089
Anagnostopoulos C, Spizizen J (1961) Requirements for transformation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 81:741–746
Bathily H, Babana AH, Samaké F (2010) Bacillus pumilus, a new pathogen on potato tubers in storage in Mali. AJMR 4(20):2067–2071
Bhattacharya D, Nagpure A, Gupta RK (2007) Bacterial chitinases: properties and potential. Crit Rev Biotechnol 27:21–28
Brückner R, Titgemeyer F (2002) Carbon catabolite repression in bacteria: choice of the carbon source and rautoregulatory limitation of sugar utilization. FEMS Microbiol Lett 209:141–148
Chu HH, Hoang V, Hofemeister J, Schrempf H (2001) A Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ChbB protein binds beta- and alpha-chitin and has homologues in related strains. Microbiology 147:1793–1803
Delic I, Robbins PW, Westpheling J (1992) Direct repeat sequences are implicated in the regulation of two Streptomyces chitinase promoters that are subject to carbon catabolite control. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:1885–1889
Deutscher J, Francke C, Postma PW (2006) How phosphotransferase system-related protein phosphorylation regulates carbohydrate metabolism in bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 70:939–1031
Fischer SH, Sonenshein AL (1991) Control of carbon and nitrogen metabolism in Bacillus subtilis. Ann Rev Microbiol 45:107–135
Fujita Y (2009) Carbon catabolite control of the metabolic network in Bacillus subtilis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:245–259
Galal AA, El-Bana AA, Janse J (2006) Bacillus pumilus, a new pathogenon mango plants. Egypt J Phytopathol 34(1):17–29
Grundy FJ, Waters DA, Allen SHG, Henkin TM (1993) Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis acetate kinase gene by CcpA. J Bacteriol 175:7348–7355
Harwood CR, Cutting SM (1990) Molecular biological methods for Bacillus. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester
Harwood CR, Wipat A (1996) Sequencing and functional analysis of the genome of Bacillus subtilis strain 168. FEBS Lett 389:84–87
Hueck CJ, Hillen W (1995) Catabolite repression in Bacillus subtilis: a global regulatory mechanism for the Gram-positive bacteria. Mol Microbiol 15:395–401
Hueck CJ, Hillen W, Saier MH Jr (1994) Analysis of a cis-active sequence mediating catabolite repression in Gram-positive bacteria. Res Microbiol 145:503–518
Kim JH, Yang YK, Chambliss GH (2005) Evidence that Bacillus catabolite control protein CcpA interacts with RNA polymerase to inhibit transcription. Mol Microbiol 56:155–162
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Mach RL, Strauss J, Zeilinger S, Schindler M, Kubicek CP (1996) Carbon catabolite repression of xylanase I (xynI) gene expression in Trichoderma reesei. Mol Microbiol 21:1273–1281
Michel JF, Millet J (1970) Physiological studies on early-blocked sporulation mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Appl Bacteriol 33:220–227
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Miwa Y, Nakata A, Ogiwara A, Yamamoto M, Fujita Y (2000) Evaluation and characterization of catabolite responsive elements (cre) of Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res 28:1206–1210
Ni X, Westpheling J (1997) Direct repeat sequences in the Streptomyces chitinase-63 promoter direct both glucose repression and chitin induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:13116–13121
Pan J, Huang Q, Zhang Y (2004) Gene cloning and expression of an alkaline serine protease with dehairing function from Bacillus pumilus. Curr Microbiol 49:165–169
Park JK, Okamoto T, Yamasaki Y, Tanaka K, Nakagawa T, Kawamukai M, Matsuda H (1997) Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequencing, and regulation of the chiA gene encoding one of chitinases from Enterobacter sp. G-1. J Ferment Bioeng 84:493–501
Poncet S, Mijakovic I, Nessler S, Gueguen-Chaignon V, Chaptal V, Galinier A, Boel G, Maze A, Deutscher J (2004) HPr kinase/phosphorylase, a Walker motif A-containing bifunctional sensor enzyme controlling catabolite repression in Gram-positive bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta 1697:123–135
Reizer J, Bergstedt U, Galinier A, Kuster E, Saier MH Jr, Hillen W, Steinmetz M, Deutscher J (1996) Catabolite repression resistance of gnt operon expression in Bacillus subtilis conferred by mutation of His-15, the site of phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphorylation of the phosphocarrier protein HPr. J Bacteriol 178:5480–5486
Reizer J, Hoischen C, Titgemeyer F, Rivolta C, Rabus R, Stülke J, Karamata D, Saier MH Jr, Hillen W (1998) A novel protein kinase that controls carbon catabolite repression in bacteria. Mol Microbiol 27:1157–1169
Roberts WK, Selitrennikoff CP (1988) Plant and bacterial chitinases differ in antifungal activity. J Gen Microbiol 134:169–176
Saier MH Jr (1998) Multiple mechanisms controlling carbon metabolism in bacteria. Biotechnol Bioeng 58:170–174
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbour, New York
Schumacher M, Allen G, Diel M, Seidel G, Hillen W, Brennan R (2004) Structural basis for allosteric control of the transcription regulator CcpA by the phosphoprotein HPr-Ser46-P. Cell 118:731–741
Shali A, Ghasemi SH, Ahmadian G, Ranjbar G, Dehestani A, Khalesi N, Motallebi E, Vahed M (2011) Bacillus pumilus SG2 chitinases induced and regulated by chitin, show inhibitory activity against Fusarium graminearum and Bipolaris sorokiniana. Phytoparasitica 38:141–147
Spizizen J (1958) Transformation of biochemically deficient strains of Bacillus subtilis by deoxyribonucleate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 44:1072–1078
Sun T, Altenbuchner J (2010) Characterization of a mannose utilization system in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 192:2128–2139
Weickert MJ, Chambliss GH (1990) Site-directed mutagenesis of a catabolite repression operator sequence in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:6238–6242
Xiao L, Liu C, Xie C, Cai J, Chen YH (2012) The direct repeat sequence upstream of Bacillus chitinase genes is cis-acting elements that negatively regulate heterologous expression in E. coli. Enzyme Microb Technol 50:280–286
Yamamoto H, Mori M, Sekiguchi J (1999) Transcription of genes near the sspE locus of the Bacillus subtilis genome. Microbiology 145:2171–2180
Yanisch-Perron C, Vieira J, Messing J (1985) Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33:103–119
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from National Institute of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (NIGEB) of Iran to project no; 377. Authors would like to thank Dr. J. Altenbuchner (Institut für Industrielle Genetik, Universität Stuttgart) and Prof. Dr. J.M. van Dijl (Faculty of Medical Sciences, Medical Microbiology, University of Groningen) for their comments and critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
K. Morabbi Heravi and A. Shali have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heravi, K.M., Shali, A., Naghibzadeh, N. et al. Characterization of cis-acting elements residing in the chitinase promoter of Bacillus pumilus SG2. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30, 1491–1499 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1569-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1569-9