Abstract
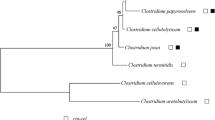
Cytophaga hutchinsonii is an important Gram-negative bacterium belonging to the Bacteroides phylum that can efficiently degrade cellulose. But the promoter that mediates the initiation of gene transcription has been unknown for a long time. In this study, we determined the transcription start site (TSS) of C. hutchinsonii by 5′ rapid amplification of cDNA ends (5′RACE). The promoter structure was first identified as TAAT and TATTG which are located -5 and -31 bp upstream of TSS, respectively. The function of -5 and -31 regions and the spacer length of the promoter Pchu_1284 were explored by site directed ligase-independent mutagenesis (SLIM). The results showed that the promoter activities were sharply decreased when the TTG motif was mutated into guanine (G) or cytosine (C). Interestingly, we found that the strong promoter was accompanied with many TTTG motifs which could enhance the promoter activities within certain copies. These characteristics were different from other promoters of Bacteriodes species. Furthermore, we carried out genome scanning analysis for C. hutchinsonii and another Bacteroides species by Perl6.0. The results indicated that the promoter structure of C. hutchinsonii possessed more unique features than other species. Also, the screened inducible promoter Pchu_2268 was used to overexpress protein CHU_2196 with a molecular weight of 120 kDa in C. hutchinsonii. The present study enriched the promoter structure of Bacteroidetes species and also provided a novel method for the highly expressed large protein (cellulase) in vivo, which was helpful to elucidate the unique cellulose degradation mechanism of C. hutchinsonii.
Key points
• The conserved structure of strong promoter of C. hutchinsonii was elucidated.
• Two novel regulation motifs of TTTG and AATTATG in the promoter were discovered.
• A new method for induced expression of cellulase in vivo was established.
• Helpful for explained the unique cellulose degradation mechanism of C. hutchinsonii.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available in the article and supplementary information files.
References
Alvarez B, Secades P, McBride MJ, Guijarro JA (2004) Development of genetic techniques for the psychrotrophic fish pathogen Flavobacterium psychrophilum. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(1):581–587. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.1.581-587.2004
Bayer EA, Belaich JP, Shoham Y, Lamed R (2004) The cellulosomes: multienzyme machines for degradation of plant cell wall polysaccharides. Annu Rev Microbiol 58:521–554. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.57.030502.091022
Bayer EA, Lamed R, White BA, Flint HJ (2008) From cellulosomes to cellulosomics. Chem Rec 8(6):364–377. https://doi.org/10.1002/tcr.20160
Bayley DP, Rocha ER, Smith CJ (2000) Analysis of cepA and other Bacteroides fragilis genes reveals a unique promoter structure. Fems Microbiol Lett 193(1):149–154. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09417.x
Bolshoy A, Nevo E (2000) Ecologic genomics of DNA: upstream bending in prokaryotic promoters. Genome Res 10(8):1185–1193. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.10.8.1185
Chen S, Bagdasarian M, Kaufman MG, Walker ED (2007) Characterization of strong promoters from an environmental Flavobacterium hibernum strain by using a green fluorescent protein-based reporter system. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(4):1089–1100. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01577-06
Chiu J, March PE, Lee R, Tillett D (2004) Site-directed, ligase-independent mutagenesis (SLIM): a single-tube methodology approaching 100% efficiency in 4 h. Nucleic Acids Res 32(21):e174. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gnh172
Cottrell MT, Kirchman DL (2000) Natural assemblages of marine proteobacteria and members of the Cytophaga-Flavobacter cluster consuming low- and high-molecular-weight dissolved organic matter. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(4):1692–1697. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.66.4.1692-1697.2000
Doree SM, Mulks MH (2001) Identification of an Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae consensus promoter structure. J Bacteriol 183(6):1983–1989. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.183.6.1983-1989.2001
Estrem ST, Gaal T, Ross W, Gourse RL (1998) Identification of an UP element consensus sequence for bacterial promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(17):9761–9766. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.17.9761
Gabrielian AE, Landsman D, Bolshoy A (1999) Curved DNA in promoter sequences. In Silico Biol 1(4):183–196
Gao L, Guan Z, Gao P, Zhang W, Qi Q, Lu X (2020) Cytophaga hutchinsonii gldN, encoding a core component of the type IX secretion system, is essential for ion assimilation, cellulose degradation, and cell motility. Appl Environ Microbiol 86(11):e00242-e320. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00242-20
Gao L, Tan Y, Zhang W, Qi Q, Lu X (2021) Cytophaga hutchinsonii SprA and SprT are essential components of the type IX secretion system required for Ca2+ acquisition, cellulose degradation, and cell motility. Front Microbiol 12:628555. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.628555
Gourse RL, Ross W, Gaal T (2000) UPs and downs in bacterial transcription initiation: the role of the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase in promoter recognition. Mol Microbiol 37(4):687–695. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01972.x
Jackson CA, Hoffmann B, Slakeski N, Cleal S, Hendtlass AJ, Reynolds EC (2000) A consensus Porphyromonas gingivalis promoter sequence. Fems Microbiol Lett 186(1):133–138. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09094.x
Ji X, Wang Y, Zhang C, Bai X, Zhang W, Lu X (2014) Novel outer membrane protein involved in cellulose and cellooligosaccharide degradation by Cytophaga hutchinsonii. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(15):4511–4518. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00687-14
Kanhere A, Bansal M (2005) A novel method for prokaryotic promoter prediction based on DNA stability. BMC Bioinformatics 6:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-6-1
Kelly JJ, Bansal A, Winkelman J, Janus LR, Hell S, Wencel M, Belt P, Kuehn KA, Rier ST, Tuchman NC (2010) Alteration of microbial communities colonizing leaf litter in a temperate woodland stream by growth of trees under conditions of elevated atmospheric CO2. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(15):4950–4959. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00221-10
Kibe R, Sakamoto M, Yokota H, Benno Y (2007) Characterization of the inhabitancy of mouse intestinal bacteria (MIB) in rodents and humans by real-time PCR with group-specific primers. Microbiol Immunol 51(4):349–357. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1348-0421.2007.tb03916.x
Kisand V, Cuadros R, Wikner J (2002) Phylogeny of culturable estuarine bacteria catabolizing riverine organic matter in the northern Baltic Sea. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(1):379–388. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.68.1.379-388.2002
Koo HS, Wu HM, Crothers DM (1986) DNA bending at adenine. thymine tracts. Nature 320(6062):501–506. https://doi.org/10.1038/320501a0
Kozakai T, Izumi A, Horigome A, Odamaki T, Xiao JZ, Nomura I, Suzuki T (2020) Structure of a core promoter in Bifidobacterium longum NCC2705. J Bacteriol 202(7):e00540-e619. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00540-19
Kumar D, Patro S, Ghosh J, Das A, Maiti IB, Dey N (2012) Development of a salicylic acid inducible minimal sub-genomic transcript promoter from Figwort mosaic virus with enhanced root- and leaf-activity using TGACG motif rearrangement. Gene 503(1):36–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2012.04.053
Liu M, Tolstorukov M, Zhurkin V, Garges S, Adhya S (2004) A mutant spacer sequence between -35 and -10 elements makes the Plac promoter hyperactive and cAMP receptor protein-independent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(18):6911–6916. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0401929101
MacLellan SR, MacLean AM, Finan TM (2006) Promoter Prediction in the Rhizobia. Microbiology (reading) 152(Pt 6):1751–1763. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.28743-0
Manz W, Amann R, Ludwig W, Vancanneyt M, Schleifer KH (1996) Application of a suite of 16S rRNA-specific oligonucleotide probes designed to investigate bacteria of the phylum cytophaga-flavobacter-bacteroides in the natural environment. Microbiology (reading) 142(Pt 5):1097–1106. https://doi.org/10.1099/13500872-142-5-1097
Matteau D, Rodrigue S (2015) Precise Identification of genome-wide transcription start sites in bacteria by 5’-rapid amplification of cDNA ends (5’-RACE). Methods Mol Biol 1334:143–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2877-4_9
McBride MJ, Braun TF, Brust JL (2003) Flavobacterium johnsoniae GldH is a lipoprotein that is required for gliding motility and chitin utilization. J Bacteriol 185(22):6648–6657. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.185.22.6648-6657.2003
McBride MJ, Kempf MJ (1996) Development of techniques for the genetic manipulation of the gliding bacterium Cytophaga johnsonae. J Bacteriol 178(3):583–590. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.178.3.583-590.1996
Olivieri A, Silvestrini F, Sanchez M, Alano P (2008) A 140-bp AT-rich sequence mediates positive and negative transcriptional control of a Plasmodium falciparum developmentally regulated promoter. Int J Parasitol 38(3–4):299–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2007.08.014
Owen-Hughes TA, Pavitt GD, Santos DS, Sidebotham JM, Hulton CS, Hinton JC, Higgins CF (1992) The chromatin-associated protein H-NS interacts with curved DNA to influence DNA topology and gene expression. Cell 71(2):255–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(92)90354-f
Puente JL, Bieber D, Ramer SW, Murray W, Schoolnik GK (1996) The bundle-forming pili of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli: transcriptional regulation by environmental signals. Mol Microbiol 20(1):87–100. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.1996.tb02491.x
Rangannan V, Bansal M (2009) Relative stability of DNA as a generic criterion for promoter prediction: whole genome annotation of microbial genomes with varying nucleotide base composition. Mol Biosyst 5(12):1758–1769. https://doi.org/10.1039/B906535K
Rio DC, Ares MJ, Hannon GJ (2010) Nilsen TW (2010) Purification of RNA using TRIzol (TRI reagent). Cold Spring Harb Protoc 6:pdb.prot5439. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot5439
Ross W, Gourse RL (2005) Sequence-independent upstream DNA-alphaCTD interactions strongly stimulate Escherichia coli RNA polymerase-lacUV5 promoter association. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(2):291–296. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0405814102
Ross W, Schneider DA, Paul BJ, Mertens A, Gourse RL (2003) An intersubunit contact stimulating transcription initiation by E coli RNA polymerase: interaction of the alpha C-terminal domain and sigma region 4. Genes Dev 17(10):1293–1307. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1079403
Rouch DA, Brown NL (1997) Copper-inducible transcriptional regulation at two promoters in the Escherichia coli copper resistance determinant pco. Microbiology (reading) 143(Pt 4):1191–1202. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-143-4-1191
Shen A, Higgins DE, Panne D (2009) Recognition of AT-rich DNA binding sites by the MogR repressor. Structure 17(5):769–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2009.02.018
Smale ST (2010) Beta-galactosidase assay. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2010(5):pdb.prot 5423. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot5423
Song Y, Liu C, Lee J, Bolanos M, Vaisanen ML, Finegold SM (2005) “Bacteroides goldsteinii sp. nov.” isolated from clinical specimens of human intestinal origin. J Clin Microbiol 43(9):4522–4527. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.43.9.4522-4527.2005
Stanier RY (1942) The Cytophaga group: a contribution to the biology of Myxobacteria. Bacteriol Rev 6(3):143–196. https://doi.org/10.1128/br.6.3.143-196.1942
Wang S, Zhao D, Bai X, Zhang W, Lu X (2017) Identification and characterization of a large protein essential for degradation of the crystalline region of cellulose by Cytophaga hutchinsonii. Appl Environ Microbiol 83(1):e02270-e2316. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02270-16
Wang X, Zheng ZM (2016) Construction of a transcription map for Papillomaviruses using RACE, RNase protection, and primer extension assays. Curr Protoc Microbiol 40:14B.6.1-16B.6.29. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780471729259.mc14b06s40
Wang Y, Wang Z, Cao J, Guan Z, Lu X (2014) FLP-FRT-based method to obtain unmarked deletions of CHU_3237 (porU) and large genomic fragments of Cytophaga hutchinsonii. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(19):6037–6045. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01785-14
Warne SE, DeHaseth PL (1993) Promoter recognition by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Effects of single base pair deletions and insertions in the spacer DNA separating the -10 and -35 regions are dependent on spacer DNA sequence. Biochemistry 32(24):6134–6140. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00075a003
Xie G, Bruce DC, Challacombe JF, Chertkov O, Detter JC, Gilna P, Han CS, Lucas S, Misra M, Myers GL, Richardson P, Tapia R, Thayer N, Thompson LS, Brettin TS, Henrissat B, Wilson DB, McBride MJ (2007) Genome sequence of the cellulolytic gliding bacterium Cytophaga hutchinsonii. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(11):3536–3546. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00225-07
Xie H, Lamont RJ (1999) Promoter architecture of the Porphyromonas gingivalis fimbrillin gene. Infect Immun 67(7):3227–3235. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.67.7.3227-3235.1999
Zhao D, Wang Y, Wang S, Zhang W, Qi Q, Lu X (2020) A disulfide oxidoreductase (CHU_1165) is essential for cellulose degradation by affecting outer membrane proteins in Cytophaga hutchinsonii. Appl Environ Microbiol 86(8):e02789-e2819. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02789-19
Zhu Y, McBride MJ (2014) Deletion of the Cytophaga hutchinsonii type IX secretion system gene sprP results in defects in gliding motility and cellulose utilization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(2):763–775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5355-2
Zhu Y, Zhang P, Zhang J, Xu W, Wang X, Wu L, Sheng D, Ma W, Cao G, Chen XL, Lu Y, Zhang YZ, Pang X (2019) The developmental regulator MtrA binds GlnR boxes and represses nitrogen metabolism genes in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 112(1):29–46. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.14252
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank Professor Mark J McBride (University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, Milwaukee, WI) for providing the C. hutchinsonii ATCC 33406 strains. We thank Dr. Yizhao Chang (State Key Laboratory of Microbial Technology, Microbial Technology Institute, Shandong University, Qingdao, China) for the bioinformatic analysis. We also give thanks to Dr. Edward C. Mignot (Shandong University) for the linguistic advice.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers 31770080 and 31371262).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XM L and GQ F developed the article initial concepts. GQ F and WX S performed the experiments under the supervision of XM L. GQ F, WX S, ZW G, and WC Z analyzed the results and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, G., Song, W., Guan, Z. et al. Some novel features of strong promoters discovered in Cytophaga hutchinsonii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 106, 2529–2540 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-11869-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-11869-3