Abstract
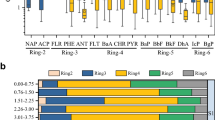
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) can form nonextractable residues in soil, significantly impacting their environmental behavior and fate. Although considerable research has been conducted on the formation of nonextractable residues of PAHs in soil through spiked experiments using representative PAH compounds, limited research has been given to the nonextractable residues of 16 priority PAHs in historically polluted soils. This study aimed to investigate the concentrations and compositions of the nonextractable residues for parent PAHs in five historically polluted soils and their biodegradation in three soils. The results indicated that the average contents of total nonextractable residues ranged from 183–2922 μg∙kg−1 in the five soils, with 4-ring PAHs (42.1 ± 4.2%) being the predominant component in the PAH compositions. The ratios of nonextractable residues for total PAHs ranged from 4.0% to 39.4% among the five soils, showing significant positive correlations with soil specific surface area, micropore area and volume, as well as clay content (p < 0.01). Furthermore, the mean ratios of the nonextractable residues for PAHs with different ring numbers generally decreased as the ring numbers increased. The average biodegradation rates of nonextractable residues for total PAHs ranged from 4.1% to 60.8% during a 30-day incubation period in the three soils, with the organic carbon and calcium contents identified as the key factors influencing the biodegradation among the three soils. This study highlights the significant impact of soil and PAH properties on the formation and biodegradation of nonextractable residues in historically polluted soils.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper and its Supplementary Information files. Should any raw data files be needed in another format they are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abo-State, M. A. M., Osman, M. E., Khattab, O. H., El-Kelani, T. A., & Abdel-Rahman, Z. M. (2021). Degradative pathways of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) by Phanerochaete chrysosporium under optimum conditions. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences, 14(1), 507–520. https://doi.org/10.1080/16878507.2021.2001247
Anasonye, F., Tammeorg, P., Parshintsev, J., Riekkola, M. L., & Tuomela, M. (2018). Role of biochar and fungi on PAH sorption to soil rich in organic matter. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 229, 49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3708-2
Barbosa, F., Jr., Rocha, B. A., Souza, M. C. O., Bocato, M. Z., Azevedo, L. F., Adeyemi, J. A., Santana, A., & Campiglia, A. D. (2023). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): Updated aspects of their determination, kinetics in the human body, and toxicity. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part B, 26, 28–65. https://doi.org/10.1080/10937404.2022.2164390
Barraclough, D., Kearney, T., & Croxford, A. (2005). Bound residues: Environmental solution or future problem? Environmental Pollution, 133(1), 85–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.04.016
Birdwell, J. E., & Thibodeaux, L. J. (2009). PAH repartitioning in field-contaminated sediment following removal of the labile chemical fraction. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(21), 8092–8097. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9016798
Chorom, M., Rengasamy, P., & Murray, R. S. (1994). Clay dispersion as influenced by pH and net particle charge of sodic soils. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 32(6), 1243–1252. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR9941243
Cornelissen, G., Gustafsson, O., Bucheli, T., Jonker, M., Koelmans, A., & Van Noort, P. (2005). Extensive sorption of organic compounds to black carbon, coal, and kerogen in sediments and soils: Mechanisms and consequences for distribution, bioaccumulation, and biodegradation. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(18), 6881–6895. https://doi.org/10.1021/es050191b
Dinadayalane, T. C., Hassan, A., & Leszczynski, J. (2012). A theoretical study of cation-π interactions: Li+, Na+, K+, Be2+, Mg2+ and Ca2+ complexation with mono-and bicyclic ring-fused benzene derivatives. Theoretical Chemistry Accounts, 131, 1131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00214-012-1131-0
Ding, Y., Li, Li., Wania, F., Zhang, Y., Huang, H., Liao, T., Liu, J., & Qi, S. (2020). Formation of non-extractable residues as a potentially dominant process in the fate of PAHs in soil: Insights from a combined field and modeling study on the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Environmental Pollution, 267, 115383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115383
Galbán-Malagón, C. J., Zapata, J., Perez-Venegas, D. J., Vargas, R., Latorre-Padilla, N., Luarte, T., Ahrendt, C., Hirmas-Olivares, A., Gómez-Aburto, V., Tapia, P., Isamit, V., Arce, P., Sánchez, C., & Pozo, K. (2023). Occurrence, source estimation, and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in coastal seawaters from the Quintero Industrial Complex (Valparaíso, Chile). Science of the Total Environment, 878, 162957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162957
Gao, Y., Wang, Y., Zeng, Y., & Zhu, X. (2013). Phytoavailability and rhizospheric gradient distribution of bound-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon residues in soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 77(5), 1572–1583. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2013.04.0128
Gao, Y., Yuan, X., Lin, X., Sun, B., & Zhao, Z. (2015). Low-molecular-weight organic acids enhance the release of bound PAH residues in soils. Soil & Tillage Research, 145, 103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2014.09.008
Gao, Y., Hu, X., Zhou, Z., Zhang, W., Wang, Y., & Sun, B. (2017). Phytoavailability and mechanism of bound PAH residues in field contaminated soils. Environmental Pollution, 222, 465–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.11.076
Guerin, W. F., & Boyd, S. A. (1992). Differential bioavailability of soil-sorbed naphthalene to two bacterial species. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 58(4), 1142–1152. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.58.4.1142-1152.1992
Guo, J. Y., Chen, J. A., Wang, J. F., & Wu, F. C. (2017). Bound PAHs in sediment and related environmental significance. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 72(4), 530–539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-017-0393-x
Haritash, A. K., & Kaushik, C. P. (2009). Biodegradation aspects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 169(1–3), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.03.137
He, L., Song, J., & Peng, P. (2008). Characterization of extractable and non-extractable polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils and sediments from the Pearl River Delta, China. Environmental Pollution, 156, 769–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.06.003
Kaewmano, C., Kheoruenromne, I., Suddhiprakarn, A., & Gilkes, R. J. (2009). Aggregate stability of salt-affected kaolinitic soils on the North-east Plateau Thailand. Soil Research, 47(7), 697–706. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR08248
Kästner, M., Nowak, K. M., Miltner, A., Trapp, S., & Schäffer, A. (2014). Classification and modelling of nonextractable residue (NER) formation of xenobiotics in soil – a synthesis. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 44, 2107–2171. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2013.828270
Laor, Y., Strom, P. F., & Farmer, W. J. (1999). Bioavailability of phenanthrene sorbed to mineral-associated humic acid. Water Research, 33(7), 1719–1729. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00378-9
Leboeuf, E. J., & Weber, W. J. (1997). A distributed reactivity model for sorption by soils and sediments. 8. sorbent organic domains: discovery of a humic acid glass transition and an argument for a polymer-based model. Environmental Science & Technology, 31(6), 1697–1702.
Li, X., Zhang, X., Li, L., Lin, C., Dong, W., Shen, W., Yong, X., Jia, H., Wu, X., & Zhou, J. (2020). Anaerobic biodegradation of pyrene by Klebsiella sp LZ6 and its proposed metabolic pathway. Environmental Technology, 41(16), 2130–2139. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1556348
Li, W., Park, R., Alexandrou, N., Dryfhout-Clark, H., Brice, K., & Hung, H. (2021). Multi-year analyses reveal different trends, sources, and implications for source-related human health risks of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Canadian Great Lakes Basin. Environmental Science & Technology, 55(4), 2254–2264. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c07079
Liang, L., Song, X., Kong, J., Shen, C., Huang, T., & Hu, Z. (2014). Anaerobic biodegradation of high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by a facultative anaerobe Pseudomonas sp. JP1. Biodegradation, 25, 825–833. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-014-9702-5
Ling, W., Zeng, Y., Gao, Y., Dang, H., & Zhu, X. (2010). Availability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aging soils. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 10, 799–807. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-010-0187-5
Loiseau, L., & Barriuso, E. (2002). Characterization of the atrazine’s bound (nonextractable) residues using fractionation techniques for soil organic matter. Environmental Science & Technology, 36(4), 683–689. https://doi.org/10.1021/es010146d
Marchal, G., Smith, K. E. C., Rein, A., Winding, A., Trapp, S., & Karlson, U. G. (2013). Comparing the desorption and biodegradation of low concentrations of phenanthrene sorbed to activated carbon, biochar and compost. Chemosphere, 90(6), 1767–1778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.07.048
Meng, F., Yang, X., Duan, L., Naidu, R., Nuruzzaman, M., & Semple, K. T. (2019). Influence of pH, electrical conductivity and ageing on the extractability of benzo[a]pyrene in two contrasting soils. Science of the Total Environment, 690, 647–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.445
Mordaunt, C. J., Gevao, B., Jones, K. C., & Semple, K. T. (2005). Formation of non-extractable pesticide residues: Observations on compound differences, measurement and regulatory issues. Environmental Pollution, 133(1), 25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.04.018
Nam, K., Kim, J. Y., & Oh, D. I. (2003). Effect of soil aggregation on the biodegradation of phenanthrene aged in soil. Environmental Pollution, 121, 147–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00181-1
Northcott, G. L., & Jones, K. C. (2001). Partitioning, extractability, and formation of nonextractable PAH residues in soil. 1. compound differences in aging and sequestration. Environmental Science & Technology, 35(6), 1103–1110.
Pignatello, J. J., & Xing, B. S. (1996). Mechanisms of slow sorption of organic chemicals to natural particles. Environmental Science & Technology, 30(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1021/es940683g
Regelink, I. C., Stoof, C. R., Rousseva, S., Weng, L., Lair, G. J., Kram, P., Nikolaidis, N. P., Kercheva, M., Banwart, S., & Comans, R. N. B. (2015). Linkages between aggregate formation, porosity and soil chemical properties. Geoderma, 247–248, 24–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.01.022
Stephenson, G. R., Ferris, I. G., Holland, P. T., & Nordberg, M. (2006). Glossary of terms relating to pesticides (IUPAC Recommendations 2006). Pure and Applied Chemistry, 78(11), 2075–2154. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac200678112075
Sun, J., Pan, L., Tsang, D. C., Zhan, Y., Zhu, L., & Li, X. (2018). Organic contamination and remediation in the agricultural soils of China: A critical review. Science of the Total Environment, 615, 724–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.271
Sun, S. S., Wei, R., Hu, S. Y., Yang, M. Y., & Ni, J. Z. (2024). Isolation and characterization of distinctive pyrene-degrading bacteria from an uncontaminated soil. Biodegradation. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-023-10065-y
Tanić, M. N., Dinić, D., Kartalović, B., Mihaljev, Ž, Stupar, S., Ćujić, M., & Onjia, A. (2023). Occurrence, source apportionment, and health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil of urban parks in a mid-sized city. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 234, 484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06504-4
Umeh, A. C., Duan, L., Naidu, R., & Semple, K. T. (2018). Time-dependent remobilisation of non-extractable benzo[a]pyrene residues in contrasting soils: Effects of aging, spiked concentration, and soil properties. Environmental Science & Technology, 52(21), 12295–12305. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b03008
Umeh, A. C., Duan, L., Naidu, R., & Semple, K. T. (2019a). Extremely small amounts of B[a]P residues remobilised in long-term contaminated soils: A strong case for greater focus on readily available and not total-extractable fractions in risk assessment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 368(15), 72–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.01.030
Umeh, A. C., Duan, L., Naidu, R., Esposito, M., & Semple, K. T. (2019b). In vitro gastrointestinal mobilization and oral bioaccessibility of PAHs in contrasting soils and associated cancer risks: Focus on PAH nonextractable residues. Environment International, 133, 105186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105186
Wang, Y., Xu, J., Shan, J., Ma, Y., & Ji, R. (2017). Fate of phenanthrene and mineralization of its non-extractable residues in an oxic soil. Environmental Pollution, 224, 377–383. https://doi.org/10.1021/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.02.017
Wei, R., Ni, J. Z., Li, X. Y., Chen, W. F., & Yang, Y. S. (2017). Dissipation and phytoremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in freshly spiked and long-term field-contaminated soils. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 7994–8003. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8459-x
Wei, R., Wei, S. T., Yao, C., Chen, W. F., Yang, L. M., & Ni, J. Z. (2023). Distribution and biodegradation of nonextractable polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in particle-size aggregates of field-contaminated soils. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 23, 3748–3760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03578-9
Wilcke, W. (2007). Global patterns of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soil. Geoderma, 141(3–4), 157–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.07.007
Xu, M., Wu, M., Zhang, Y., Zhang, H., & Guo, L. (2022). Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) by bacterial mixture. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 19(5), 3833–3844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03284-4
Zhao, N., Tan, Y., Zhang, X., Zhen, Z., Song, Q., Ju, F., & Ling, H. (2023). Molecular insights on the adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on soil clay minerals. Environmental Engineering Science, 40(3), 105–113. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2022.0190
Zhou, Y., Sun, F., Sun, F., Wu, X., Cao, S., Guo, X., Wang, Q., Wang, Y., & Ji, R. (2022). Formation and nature of non-extractable residues of emerging organic contaminants in humic acids catalyzed by laccase. The Science of the Total Environment, 829, 154300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154300
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42077130) and the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (2020J01189 and 2020J01140).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ran Wei, Weifeng Chen and Jinzhi Ni designed the research. Meiyu Yang, Cheng Yao, and Liuming Yang performed the research. Ran Wei and Jinzhi Ni analyzed the data and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The study is exempt from review by any Ethics Committee, and this type of research is nonhuman subject study, and waived the need for informed consent.
Consent to Participate and Publish
All of the authors have read and approved the paper and it has not been published previously nor is it being considered by any other peer-reviewed journal. All of the authors agreed with the content and that all gave explicit consent to submit the paper.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, R., Yang, M., Yao, C. et al. Characteristics and Biodegradation of Nonextractable Residues of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Historically Polluted Soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 235, 300 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-07115-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-07115-3