Abstract
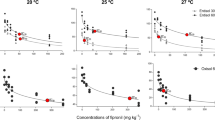
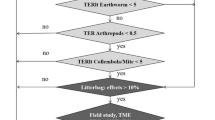
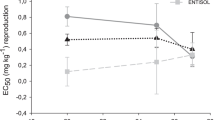
Widely used in agricultural fields, fipronil acts in the arthropods’ nervous systems. Although advances have been noticed, little is known about the effects of the insecticide to non-target soil organisms, especially considering specific parameters from tropical environments. This is the first study considering ecologically relevant tropical conditions to assess the environmental risk of fipronil to the terrestrial ecosystem. The present study aimed to estimate fipronil’s ecological risk to soil organisms through a tiered approach. At the screening level (TIER I) data were obtained from both the literature and laboratory experiments. For the intermediate level (TIER II), species sensitivity distributions (SSD) curves were generated based on ecotoxicological data from six species of soil invertebrates in two soil types. To estimate the risk, the Toxicity-Exposure Ratios (TER) were calculated at each tier considering the related toxicity data and the fipronil concentrations, which were measured and predicted in the field. Results showed that ecologically relevant concentrations of fipronil lead to a high risk for the edaphic community (above 100 times higher than the established safety value). The high risks were observed for both tiers, although at TIER II (SSD approach) it was at least 2.5 times higher than at TIER I. It was also discussed here that the pesticide mode of action is the factor most influencing toxicity; the estimated risk considering artificial soil was comparable to that with the natural soil; and estimating risk using only one species (as performed in the tropics) may underestimate the risk to the edaphic community.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors state that all data will be made available to readers upon reasonable request.
References
AGROFIT. Sistema de agrotóxicos fitossanitários. Disponível em:<https://agrofit.agricultura.gov.br/agrofit_cons/principal_agrofit_cons>. Access: June, 2021.
Alves, Paulo Roger L., Elke J.B.N. Cardoso, Alexandre M. Martines, José Paulo Sousa, E Amarildo Pasini (2014) “Seed Dressing Pesticides on Springtails in Two Ecotoxicological Laboratory Tests”. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 105: 65–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.04.010
Amorim, Mónica João de Barros, Jorg Römbke, Hans-Joachim Schallnaß, e Amadeu Mortágua Velho Maia Soares (2005) “Effect Of Soil Properties And Aging On The Toxicity Of Copper For Enchytraeus Albidus, Enchytraeus Luxuriosus, And Folsomia Candida”. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 24, no 8: 1875. https://doi.org/10.1897/04-505R.1
Amorim, Mónica João de Barros, Yannick Gansemans, Susana I. L. Gomes, Filip Van Nieuwerburgh, e Janeck J. Scott-Fordsmand (2021) “Annelid Genomes: Enchytraeus Crypticus, a Soil Model for the Innate (and Primed) Immune System”. Lab Animal 50, no 10: 285–94. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41684-021-00831-x.
ANVISA. Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária. F-43 FIPRONIL (2021) Available in: https://www.gov.br/anvisa/pt-br/setorregulado/regularizacao/agrotoxicos/monografias/monografias-autorizadas/f/4351json-file-1/view. Access: August, 2021.
Bandeira, Felipe Ogliari, Paulo Roger Lopes Alves, Thuanne Braúlio Hennig, Juliane Brancalione, Diego José Nogueira, e William Gerson Matias (2021) “Chronic Effects of Clothianidin to Non-Target Soil Invertebrates: Ecological Risk Assessment Using the Species Sensitivity Distribution (SSD) Approach”. Journal of Hazardous Materials 419: 126491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126491
Bandow, Cornelia, Anja Coors, Nora Karau, e Jörg Römbke (2014a) “Interactive Effects of Lambda-Cyhalothrin, Soil Moisture, and Temperature on Folsomia Candida and Sinella Curviseta (Collembola): Interaction of Chemical and Climatic Factors on Collembola”. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 33, no 3: 654–61. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2479
Bandow, Cornelia, Nora Karau, e Jörg Römbke (2014b) “Interactive Effects of Pyrimethanil, Soil Moisture and Temperature on Folsomia Candida and Sinella Curviseta (Collembola)”. Applied Soil Ecology 81: 22–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2014.04.010
BASF Regent 800 WG - Inseticida para Cana-de-Açúcar | Bula e Informações”. Access: April 28th, 2022. https://agriculture.basf.com/br/pt/protecao-de-cultivos-e-sementes/produtos/regent-800-wg.html
Bicho, Rita C., Susana I. L. Gomes, Amadeu M. V. M. Soares, e Mónica J. B. Amorim (2015) “Non-Avoidance Behaviour in Enchytraeids to Boric Acid Is Related to the GABAergic Mechanism”. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 22, no 9: 6898–6903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3921-5
Buch, Andressa Cristhy, Júlia Carina Niemeyer, Maria Elizabeth Fernandes Correia, e Emmanoel Vieira Silva-Filho (2016) “Ecotoxicity of Mercury to Folsomia Candida and Proisotoma Minuta (Collembola: Isotomidae) in Tropical Soils: Baseline for Ecological Risk Assessment”. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 127: 22–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.01.009.
Carniel, Leticia Scopel Camargo. Novel Approaches And Future Directions For Pesticide Ecological Risk Assessment To In-Soil Fauna. 2019. 197 f. Tese (Doutorado) - Universidade do Estado de Santa Catarina, Lages, Sc, (2019). Disponível em: https://estudogeral.uc.pt/bitstream/10316/91061/1/Thesis_Leticia%20Scopel%20Camargo%20Carniel_final.pdf. Access: August 5th, 2021.
Carniel, Letícia Scopel Camargo, Julia Carina Niemeyer, Luís Carlos Iuñes de Oliveira Filho, Douglas Alexandre, Luciano Gebler, e Osmar Klauberg-Filho (2019) “The Fungicide Mancozeb Affects Soil Invertebrates in Two Subtropical Brazilian Soils”. Chemosphere 232: 180–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.179.
Chagnon, Madeleine, David Kreutzweiser, Edward A.D. Mitchell, Christy A. Morrissey, Dominique A. Noome, e Jeroen P. Van der Sluijs (2015) “Risks of Large-Scale Use of Systemic Insecticides to Ecosystem Functioning and Services”. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 22, no 1: 119–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3277-x
Christofoletti, C.A., Pereira, C., Ansoar, Y. (2017) “O emprego de agrotóxicos na cultura de cana-de-açúcar, in: Fontanetti, C.S., Bueno, O.C. (Eds.), Cana-de-Açúcar e Seus Impactos: Uma Visão Acadêmica. Canal6, Rio Claro, pp. 51–61.
Daam, Michiel A., Sara Leitão, Maria José Cerejeira, e J. Paulo Sousa (2011) “Comparing the Sensitivity of Soil Invertebrates to Pesticides with That of Eisenia Fetida”. Chemosphere 85, no 6: 1040–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.07.032
Daam, Michiel A., Sónia Chelinho, Júlia C. Niemeyer, Olugbenga J. Owojori, P. Mangala C. S. De Silva, Jóse Paulo Sousa, Cornelis A. M. van Gestel, e Jörg Römbke (2019) “Environmental Risk Assessment of Pesticides in Tropical Terrestrial Ecosystems: Test Procedures, Current Status, and Future Perspectives”. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 181,: 534–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.06.038
de Menezes Oliveira, V. B., de Oliveira Bianchi, M., & Espíndola, E. L. G. (2018). Hazard assessment of the pesticides KRAFT 36 EC and SCORE in a tropical natural soil using an ecotoxicological test battery. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 37(11), 2919–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4056
ECHA European Chemicals Agency. e Ramboll. Topical Scientific Workshop on Soil Risk Assessment: Workshop Proceedings : Helsinki, 7 8 (October 2015). LU: Publications Office, 2016. https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2823/785130
EFSA Panel on Plant Protection Products and their Residues (PPR) PPR panel (2013) “Guidance on Tiered Risk Assessment for Plant Protection Products for Aquatic Organisms in Edge-of-Field Surface Waters | EFSA”. Access: June 9th, 2022. https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/3290.
EFSA Panel on Plant Protection Products and their Residues (PPR), Colin Ockleford, Paulien Adriaanse, Philippe Berny, Theodorus Brock, Sabine Duquesne, Sandro Grilli, et al. (2017) “Scientific Opinion Addressing the State of the Science on Risk Assessment of Plant Protection Products for In‐soil Organisms”. EFSA Journal 15, no 2. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2017.4690
European Commission, Joint Research Centre, Johnson, N., Scheu, S., Ramirez, K., et al. (2016). In N. Johnson, S. Scheu, K. Ramirez, P. Lemanceau, P. Eggleton, A. Jones, F. Moreira, E. Barrios, G. De Deyn, M. Briones, N. Kaneko, E. Kandeler, D. Wall, J. Six, N. Fierer, S. Jeffery, P. Lavelle, W. Putten, B. Singh, … L. Montanarella (Eds.), Global soil biodiversity atlas. Publications Office. https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2788/2613.
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). (2006). Conclusion regarding the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance fipronil. EFSA Journal, 4(5), RN-65, 110 pp. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2006.65r
FAO. (2017). Soil Organic Carbon: the hidden potential. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Rome.
FAO, (2020). ITPS. State of Knowledge of Soil Biodiversity - Status, Challenges and Potentialities: Report 2020. Rome, Italy: FAO, 2020. https://doi.org/10.4060/cb1928en
Feitosa, Ingrid Ruanna dos Santos, Nívea Cristina Guedes Munina, Bianca Veloso Goulart e Cassiana Carolina Montagner (2023) “Ocorrência de agrotóxicos em solos argilosos e arenosos após aplicação em pastagens e cana-de-açúcar”. Química Nova (accepted article: december 2022). https://doi.org/10.21577/0100-4042.20230025
Filizola, H. F. (2006). In H. F. Filizola, M. A. F. Gomes, & M. D. de Souza (Eds.), Manual de procedimentos de coleta de amostras em áreas agrícolas para análise da qualidade ambiental: solo, água e sedimentos (p. 169). Jaguariúna: Embrapa Meio Ambiente.
FOCUS. Soil Persistence Models and EU Registration, European Commission, 1996. Document No. 7617/VI/96. URL:https://esdac.jrc.ec.europa.eu/public_path/u891/Soil%20persistence%20models%20and%20EU%20registration%E2%80%99%20%281997%29.pdf
Forbes, Valery E., Peter Calow, e Richard M. Sibly (2001) “Are Current Species Extrapolation Models a Good Basis for Ecological Risk Assessment?” Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 20, no 2: 442–47. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620200227
Fox, D.R., R.A. Dam, R. Fisher, G.E. Batley, A.R. Tillmanns, J. Thorley, C.J. Schwarz, D.J. Spry, e K. McTavish (2021) “Recent Developments in Species Sensitivity Distribution Modeling”. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 40, no 2: 293–308. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4925
Frampton, Geoff K., Stephan Jänsch, Janeck J. Scott-Fordsmand, Jörg Römbke, e Paul J. van den Brink (2006) “Effects of Pesticides on Soil Invertebrates in Laboratory Studies: A Review and Analysis Using Species Sensitivity Distributions”. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 25, no 9: 2480–89. https://doi.org/10.1897/05-438R.1
Garcia, M. (2004). Effects of pesticides on soil fauna: development of ecotoxicological test methods for tropical regions. Universidade de Bonn.
Goulart, Bianca Veloso, Beatriz De Caroli Vizioli, Evaldo Luiz Gaeta Espindola, e Cassiana Carolina Montagner (2020) “Matrix Effect Challenges to Quantify 2,4-D and Fipronil in Aquatic Systems”. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 192, no 12: 797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08776-3
Goulart, B. V., Vizioli, B. C., Espindola, E. L. G., & Montagner, C. C. (2023). Influence of the Soil Composition on the Determination of 2, 4-D and Fipronil in Environmental Samples by SLE-LC-MS/MS. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 34, 1717–1725. https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20230126
Gredelj, Andrea, Alberto Barausse, Laura Grechi, e Luca Palmeri (2018) “Deriving Predicted No-Effect Concentrations (PNECs) for Emerging Contaminants in the River Po, Italy, Using Three Approaches: Assessment Factor, Species Sensitivity Distribution and AQUATOX Ecosystem Modelling”. Environment International 119: 66–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.06.017
Gunasekara, Amrith S., Tresca Truong, Kean S. Goh, Frank Spurlock, e Ronald S. Tjeerdema (2007) “Environmental Fate and Toxicology of Fipronil”. Journal of Pesticide Science 32, no 3: 189–99. https://doi.org/10.1584/jpestics.R07-02
Huguier, Pierre, Nicolas Manier, Olugbenga John Owojori, Pascale Bauda, Pascal Pandard, e Jörg Römbke (2015) “The Use of Soil Mites in Ecotoxicology: A Review”. Ecotoxicology 24, no 1: 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1363-y
IBAMA (1996) Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis, 1996. Portaria normativa IBAMA nº 84. Available in: https://servicos.ibama.gov.br/ctf/manual/html/Portaria_84.pdf
IEA (2022) Instituto de Economia Agrícola. Relação de trocas entre defensivos e produtos agrícolas. Disponível em http://ciagri.iea.sp.gov.br/nia1/RelaTrocaDefensivos.aspx?cod_sis=20
ISO (International Standardization and Organization. (2014). ISO 11267 - Soil quality: inhibition of reproduction of Collembola (Folsomia candida) by soil pollutants. https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/sist/cb9279bd-e43b-4d02-b44e-8d594e1713a0/iso-11267-2014
Jager, Tjalling, Roel H. L. J. Fleuren, Elbert A. Hogendoorn, e Gert de Korte (2003) “Elucidating the Routes of Exposure for Organic Chemicals in the Earthworm, Eisenia Andrei (Oligochaeta)”. Environmental Science & Technology 37, nº 15: 3399–3404. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0340578
Joimel, S., Chassain, J., Artru, M., & Faburé, J. (2022). Collembola is Among the Most Pesticide-Sensitive Soil Fauna Groups: A Meta-Analysis. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 41(10), 2333–2341. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5428
Kamoun, Ikram Jaabiri, Olukayode O Jegede, Olugbenga J Owojori, Jalel Bouzid, Radhia Gargouri, e Jörg Römbke (2018) “Effects of Deltamethrin, Dimethoate, and Chlorpyrifos on Survival and Reproduction of the Collembolan Folsomia Candida and the Predatory Mite Hypoaspis Aculeifer in Two African and Two European Soils: Effects of Three Pesticides on Two Arthropods in Four Soils”. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management 14, no 1,: 92–104. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.1966
Klein, M. (2008). Calculation of PECsoil Including Plateau Concentrations for Pesticides Dependent on FOCUS Degradation Kinetics, FKZ: 360 03 037. Umweltbundesamt Dessau-Roßlau.
Kwok, Kevin WH, Kenneth MY Leung, Gilbert SG Lui, Vincent KH Chu, Paul KS Lam, David Morritt, Lorraine Maltby, et al. (2009) “Comparison of Tropical and Temperate Freshwater Animal Species’ Acute Sensitivities to Chemicals: Implications for Deriving Safe Extrapolation Factors: Tropical versus Temperate Species Sensitivity”. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management 3, no 1: 49–67. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.5630030105
Lavelle, P., T. Decaëns, M. Aubert, S. Barot, M. Blouin, F. Bureau, P. Margerie, P. Mora, e J.-P. Rossi (2006) “Soil Invertebrates and Ecosystem Services”. European Journal of Soil Biology 42: S3–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2006.10.002
Lima e Silva, Cláudia de, Claire van Haren, Giulia Mainardi, Winona de Rooij, Michella Ligtelijn, Nico M. van Straalen, e Cornelis A. M. van Gestel (2021) “Bringing Ecology into Toxicology: Life-Cycle Toxicity of Two Neonicotinoids to Four Different Species of Springtails in LUFA 2.2 Natural Soil”. Chemosphere 263: 128245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128245
MAPA (2021) Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento. Available in: < https://www.gov.br/agricultura/pt-br/assuntos/insumos-agropecuarios/insumos-pecuarios/produtos-veterinarios/listas/Lista_produtos_vigentes_abril2014.pdf/view>. Access: June, 2021.
Natal-da-Luz, T., Gevaert, T., Pereira, C., Alves, D., Arena, M., & Sousa, J. P. (2019). Should oral exposure in Hypoaspis aculeifer tests be considered in order to keep them in Tier I test battery for ecological risk assessment of PPPs? Environmental Pollution, 244, 871–876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.113
Niva, Cintia Carla, Julia Carina Niemeyer, Flávio Manoel Rodrigues Da Silva Júnior, Maria Edna Tenório Nunes, Danilo Lourenço De Sousa, Clara Wandenkolck Silva Aragão, Klaus Dieter Sautter, Evaldo Gaeta Espindola, José Paulo Sousa, e Jörg Römbke (2016) “Soil Ecotoxicology in Brazil Is Taking Its Course”. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 23, no 11: 11363–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6597-1
OECD (2016) Test No. 226: Predatory Mite (Hypoaspis (Geolaelaps) Aculeifer) Reproduction Test in Soil. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2. OECD, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264264557-en
Oliveira Filho, Luís Carlos Iuñes, e Dilmar Baretta (2016) “Por que devemos nos importar com os colêmbolos edáficos?” Scientia Agraria 17, no 2: 21. https://doi.org/10.5380/rsa.v17i2.48242
Rohr, Jason R., Christopher J. Salice, e Roger M. Nisbet (2016) “The pros and cons of ecological risk assessment based on data from different levels of biological organization”. Critical Reviews in Toxicology 46, no 9: 756–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408444.2016.1190685
Santo, Fernanda Benedet de, Naiara Guerra, Monica Santana Vianna, João Paulo Machado Torres, Cesar Augusto Marchioro, e Júlia Carina Niemeyer (2019) “Laboratory and Field Tests for Risk Assessment of Metsulfuron-Methyl-Based Herbicides for Soil Fauna”. Chemosphere 222: 645–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.145
Simon-Delso, N., Amaral-Rogers, V., Belzunces, L. P., Bonmatin, J. M., Chagnon, M., Downs, C., Furlan, L., et al. (2015). Systemic Insecticides (Neonicotinoids and Fipronil): Trends, Uses, Mode of Action and Metabolites. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(1), 5–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3470-y
Sluijs, J. P. van der, V. Amaral-Rogers, L. P. Belzunces, M. F. I. J. Bijleveld van Lexmond, J-M. Bonmatin, M. Chagnon, C. A. Downs, et al. (2015) “Conclusions of the Worldwide Integrated Assessment on the Risks of Neonicotinoids and Fipronil to Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning”. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 22, no 1: 148–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3229-5
SYSTAT SOFTWARE (2008) SigmaPlot for Windows Version 11.0. Developer: Systat Software Inc
Triques, Maria Carolina, Dayane Oliveira, Bianca Veloso Goulart, Cassiana Carolina Montagner, Evaldo Luiz Gaeta Espíndola, e Vanessa Bezerra de Menezes-Oliveira (2021) “Assessing Single Effects of Sugarcane Pesticides Fipronil and 2,4-D on Plants and Soil Organisms”. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 208: 111622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111622
Turbé, A., De Toni, A., Benito, P., Lavelle, P., Lavelle, P., et al. (2010). Soil biodiversity: functions, threats and tools for policy makers. https://hal-bioemco.ccsd.cnrs.fr/bioemco-00560420
USEPA, 2005 USEPA SSD Generator (ver. 1). (2005).https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2017-10/ssd_generator_v1.xlsm
Van Vlaardingen, P., Traas, T. P., Wintersen, A. M., & Aldenberg (2004) T.ETX 2.0. A program to calculate hazardous concentrations and fraction affected, based on normally distributed toxicity data (RIVM Report No.601501028/2004). National Institute for Public Health and the Environment. http://rivm.openrepository.com/handle/10029/256981
Zortéa, Talyta, Tamires Rodrigues dos Reis, Suélen Serafini, José Paulo de Sousa, Aleksandro Schafer da Silva, e Dilmar Baretta (2018b) “Ecotoxicological Effect of Fipronil and Its Metabolites on Folsomia candida in Tropical Soils”. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology 62: 203–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2018.07.011
Zortéa, Talyta, Julia C. Segat, Ana Paula Maccari, José Paulo Sousa, Aleksandro S. Da Silva, e Dilmar Baretta (2017) “Toxicity of Four Veterinary Pharmaceuticals on the Survival and Reproduction of Folsomia Candida in Tropical Soils”. Chemosphere 173: 460–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.069
Zortéa, Talyta, Aleksandro Schafer da Silva, Tamires Rodrigues dos Reis, Julia Corá Segat, Alexandre Tadeu Paulino, José Paulo Sousa, e Dilmar Baretta (2018a) “Ecotoxicological Effects of Fipronil, Neem Cake and Neem Extract in Edaphic Organisms from Tropical Soil”. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 166: 207–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.20ISO18.09.061
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Brazilian Coordination of Superior Level Staff Improvement (CAPES) for the Ph.D. degree scholarship conceded and the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) for the financial support conceded via the thematic project “Environmental effects of the pasture-sugarcane conversion and pasture intensification” (Process: 2015/187903) and the post-doctoral grant (Process PDJ: 2017/04858-0).
Funding
This work was supported by the Brazilian Coordination of Superior Level Staff Improvement (CAPES) through a Ph.D. degree scholarship conceded to Dayane de Oliveira, by the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) through financial support conceded via the thematic project “Environmental effects of the pasture-sugarcane conversion and pasture intensification” (Process: 2015/187903) and the post-doctoral grant (Process PDJ: 2017/04858–0) conceded to Vanessa Bezerra de Menezes-Oliveira.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira, D., Tadei, R., Triques, M.C. et al. Fipronil Risk Assessment in Tropical Soils: Relevant Concentrations Cause High Risk to the Edaphic Community. Water Air Soil Pollut 235, 123 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-06925-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-06925-9