Abstract
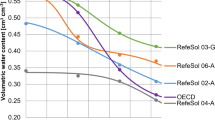
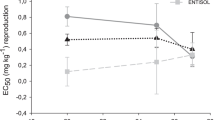
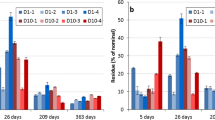
The aim of this study was to assess the effect of temperature on the toxicity of fipronil toward earthworms (Eisenia andrei) in two Brazilian soils (Entisol and Oxisol) with contrasting textures. In the case of Entisol, the influence of soil moisture content on toxicity was also investigated. Earthworms were exposed for 56 days to soils spiked with increasing concentrations of fipronil (8.95, 19.48, 38.22, 155.61, and 237.81 mg kg−1 for Entisol; 12.99, 27.94, 48.42, 204.67, and 374.29 mg kg−1 for Oxisol) under scenarios with different combinations of temperature (20, 25 and 27 °C) and soil moisture content (60 and 30% of water holding capacity (WHC) for Entisol and 60% WHC for Oxisol). The number of juveniles produced was taken as the endpoint, and a risk assessment was performed based on the hazard quotient (HQ). In Entisol, at 60% WHC the fipronil toxicity decreased at 27 °C compared with the other temperatures tested (EC50 = 52.58, 48.48, and 110 mg kg−1 for 20, 25, and 27 °C, respectively). In the case of Oxisol at 60% WHC, the fipronil toxicity increased at 27 °C compared with other temperatures (EC50 = 277.57, 312.87, and 39.89 mg kg−1 at 20, 25, and 27 °C, respectively). An increase in fipronil toxicity was also observed with a decrease in soil moisture content in Entisol at 27 °C (EC50 = 27.95 and 110 mg kg−1 for 30% and 60% WHC, respectively). The risk of fipronil was only significant at 27 °C in Entisol and Oxisol with water contents of 30% and 60% WHC, respectively, revealing that higher temperatures are able to increase the risk of fipronil toxicity toward earthworms depending on soil type and soil moisture content. The results reported herein show that soil properties associated with climatic shifts could enhance the ecotoxicological effects and risk of fipronil for earthworms, depending on the type of soil.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves PRL, Cardoso EJBN, Martines AM, Sousa JP, Pasini A (2013) Earthworm ecotoxicological assessments of pesticides used to treat seeds under tropical conditions. Chemosphere 90:2674–2682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.11.046
Alves PRL, Cardoso EJBN, Martines AM, Sousa JP, Pasini A (2014) Seed dressing pesticides on springtails in two ecotoxicological laboratory tests. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 105:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.04.010
Bandeira FO, Alves PRL, Hennig TB, Toniolo T, Natal-da-Luz T, Baretta D (2020) Effect of temperature on the toxicity of imidacloprid to Eisenia andrei and Folsomia candida in tropical soils. Environ Pollut 267:115565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115565
Belfroid A, Meiling J, Sijm D, Hermens J, Seinen W, van Gestel K (1994) Uptake of hydrophobic halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons from food by earthworms (Eisenia andrei). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 27:260–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00214272
Chelinho S, Domene X, Campana P, Andrés P, Römbke J, Sousa JP (2014) Toxicity of phenmedipham and carbendazim to Enchytraeus crypticus and Eisenia andrei (Oligochaeta) in Mediterranean soils. J Soils Sediments 14:584–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0818-8
Chopra I, Chauhan R, Kumari B, Dahiya KK (2011) Fate of fipronil in cotton and soil under tropical climatic conditions. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 86:242–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-010-0180-0
Coleman DC, Crossley DA, Hendrix PF (2004) Fundamentals of soil ecology, 2nd edn. Georgia, Elsevier Inc, Athens, p 502p
Daam MA, Chelinho S, Niemeyer JC, Owojori OJ, De Silva PMCS, Sousa JP, van Gestel CAM, Römbke J (2019) Environmental risk assessment of pesticides in tropical terrestrial ecosystems: test procedures, current status and future perspectives. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 181:534–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.06.038
Da Silva KMD, Rezende LCSH, Bergamasco R, Da Silva CA, Gonçalves DS (2012). Caracterização Físico - Química Da Fibra De Coco Verde Para a Adsorção De Metais Pesados Em Efluente De Indústria De Tintas Engevista 15 43 https://doi.org/10.22409/engevista.v15i1.387
Donker MH, Abdel-Lateif HM, Khalil MA, Bayoumi BM, Van Straalen NM (1998) Temperature, physiological time, and zinc toxicity in the isopod Porcellio scaber. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:1558–1563. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620170817
Doran G, Eberbach P, Helliwell S (2006) The sorption and degradation of the rice pesticides fipronil and thiobencarb on two Australian rice-growing soils. Aust J Soil Res 44:599–610. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR05173
EC - European Commission (2002) SANCO/10329/2002 - Final guidance document on terrestrial ecotoxicology under council directive 91/414/EEC. European Commission Health & Consumer Protection Directorate General. E1-Plant Health
Edwards CA, Bohlen PJ (1996). Biology and ecology of earthworm, 3rd ed. – Chapman and Hall, London: 426
EFSA - European Food Safety Authority (2006) Conclusion regarding the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance metazachlor. EFSA J 6:1–110. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2008.145r
EMBRAPA - Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária (1988). Recomendações técnicas para o cultivo da soja. Circular técnica 16. Unidade de execução de pesquisa de âmbito estadual de Dourados MS. Dourados
Environment Canada (2004) Biological test method: tests for toxicity of contaminated soil to earthworms. Environmental Protection Series, EPS 1/RM/43 Ottawa, ON, Canada
Environment Canada (2007) Guidance document on statistical methods for environmental toxicity test. Environmental Protection Series, EPS 1/RM/46, 2005 with 2007 updates. Environmental Canada, Ottawa
EPPO - European and Mediterranean plant protection organization (2003) Environmental risk assessment scheme for plant protection products. Chapter 4: Soil OEPP EPP0 Bull 33:151–162
ESCAPE (2013). ESCAPE 2.0v: Estimation of soil concentrations after pesticide applications. Aachen, Germany: Fraunhofer IME
Gebrehiwot WH, Erkmen C, Uslu B (2019) A novel HPLC-DAD method with dilute-and-shoot sample preparation technique for the determination of buprofezin, dinobuton and chlorothalonil in food, environmental and biological samples. Int J Environ Anal Chem 99:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2019.1702169
González-Alcaraz MN, Van Gestel CAM (2016a) Metal/metalloid (As, Cd and Zn) bioaccumulation in the earthworm Eisenia andrei under different scenarios of climate change. Environ Pollut 215:178–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.05.012
González-Alcaraz MN, Van Gestel CAM (2016b) Toxicity of a metal(loid)-polluted agricultural soil to Enchytraeus crypticus changes under a global warming perspective: variations in air temperature and soil moisture content. Sci Total Environ 573:203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.061
González-Alcaraz MN, Tsitsiou E, Wieldraaijer R, Verweij RA, van Gestel CAM (2015) Effects of climate change on the toxicity of soils polluted by metal mine wastes to Enchytraeus crypticus. Environ Toxicol Chem 34:346–354. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2807
Hackenberger DK, Palijan G, Lončarić Ž, Glavaš OJ, Hackenberger BK (2018) Influence of soil temperature and moisture on biochemical biomarkers in earthworm and microbial activity after exposure to propiconazole and chlorantraniliprole. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:480–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.10.072
Hennig TB, Alves PRL, Toniolo T, Bandeira FO, Santos WE, Cabrera LC, Gilson IK, Baretta D (2021) Toxicity of fipronil to Folsomia candida in contrasting tropical soils and soil moisture contents: effects on the reproduction and growth. Ecotoxicol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-021-02490-7
Hennig TB, Lopes Alves PR, Schiehl A, De Araújo RF, Cabrera LC, Morelato RR, Baretta D (2022) Can the increase in atmospheric temperature enhance the toxicity and risk of fipronil for collembolans in tropical soils? Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18349-7
IBAMA (2019). Boletim de Comercialização de Agrotóxicos e Afins. Brasília, 2019. http://www.ibama.gov.br/agrotoxicos/relatorios-de-comercializacao-de-agrotoxicos . Accessed 26 October 2020.
IPCC (2021). Climate Change 2021: The physical science basis. Contribution of working group i to the sixth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S. L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M. I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J. B. R. Matthews, T. K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press In Press. IPCC
ISO - International Organization for Standardization (2012) 11268:2 Soil quality - effects of pollutants on earthworms – Part 2: Determination of effects on reproduction of Eisenia fetida/Eisenia andrei. ISO, Geneva
ISO - International Organization for Standardization (2014) 11267 Soil quality: inhibition of reproduction of Collembola (Folsomia candida) by soil contaminants. ISO, Geneva
Jackson D, Cornell CB, Luukinen B, Buhl K, Stone D (2009). Fipronil technical fact sheet; National Pesticide Information Center, Oregon State University Extension Services. http://npic.orst.edu/factsheets/archive/fiptech.html
Johnston MR, Herrick BM (2019) Cocoon heat tolerance of pheretimoid earthworms Amynthas tokioensis and Amynthas agrestis. Midland Nat 181:299–309. https://doi.org/10.1674/0003-0031-181.2.299
Li M, Li P, Wang L, Feng M, Han L (2015) Determination and dissipation of fipronil and its metabolites in peanut and soil. J Agric Food Chem 63:4435–4443. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf5054589
Lima MPR, Soares AMVM, Loureiro S (2011) Combined effects of soil moisture and carbaryl to earthworms and plants: simulation of flood and drought scenarios. Environ Pollut 159:1844–1851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.03.029
Lima MPR, Cardoso DN, Soares AMVM, Loureiro S (2015) Carbaryl toxicity prediction to soil organisms under high and low temperature regimes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 114:263–272
Lisbôa RM, Storck TR, Silveira AO, Wolff D, Tiecher TL, Brunetto G, Clasen B (2021) Ecotoxicological responses of Eisenia andrei exposed in field-contaminated soils by sanitary sewage. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 214:112049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112049
Long SM, Reichenberg F, Lister LJ, Hankard PK, Townsend J, Mayer P, Wright J, Holmstrup M, Svendsen C, Spurgeon DJ (2008) combined chemical (fluoranthene) and drought effects on Lumbricus rubellus demonstrate the applicability of the independent action model for multiple stressor assessment. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:629. https://doi.org/10.1897/08-187.1
Mandal K, Singh B (2013) Persistence of fipronil and its metabolites in sandy loam and clay loam soils under laboratory conditions. Chemosphere 91:1596–1603
Millican DS, Lutterschmidt WI (2007) Comparative seasonal observations of soil temperature and moisture and the occurrence of two earthworms inhabiting prairie and deciduous woodland sites. Southwest Nat 52:468–474. https://doi.org/10.1894/0038-4909(2007)52[468:CSOOST]2.0.CO;2
Mostert MA, Schoeman AS, Van Der Merwe M (2002) The relative toxicities of insecticides to earthworms of the Pheretima group (Oligochaeta). Pest Manage Sci 58:446–450. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.473
Natal-da-Luz T, Ojeda G, Pratas J, Van Gestel CAM, Sousa JP (2011) Toxicity to Eisenia andrei and Folsomia candida of a metal mixture applied to soil directly or via an organic matrix. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 76:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.05.017
Navarro S, Barba A, Cámara MA, Navarro S (1992) Persistencia de los plaguicidas en los suelos agrícolas. Secretariado de publicaciones e intercambio científico, Universidad de Murcia, Spain, Procesos y factores condicionantes, p 105
Noyes PD, McElwee MK, Miller HD, Clark BC, Van Tiem LA, Walcott KC, Erwin KN, Levin ED (2009) The toxicology of climate change: environmental contaminants in a warming world. Environ Int 35:971–986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2009.02.006
OECD – Organization for economic cooperation and development (2016). Test No. 222: Earthworm reproduction test (Eisenia fetida/andrei), OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals OECD Publishing Paris https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264264496-en.
Peijnenburg W, Capri E, Kula C, Liess M, Luttik R, Montforts M (2012) Evaluation of exposure metrics for effect assessment of soil invertebrates. Crit Rev Env Sci Tec 42:1862–1893. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2011.574100
Qin F, Gao Y, Xu P, Guo B, Li J, Wang H (2014) Enantioselective bioaccumulation and toxic effects of fipronil in the earthworm Eisenia foetida following soil exposure. Pest Manag Sci 71:553–561. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.3841
Qu H, Wang P, Ma R, Qiu X, Xu P, Zhou Z, Liu D (2014) Enantioselective toxicity, bioaccumulation and degradation of the chiral insecticide fipronil in earthworms (Eisenia foetida). Sci Total Environ 485:415–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.03.054
San Miguel A, Raveton M, Lempérière G, Ravanel P (2008) Phenylpyrazoles impact on Folsomia candida (Collembola). Soil Biol Biochem 40:2351–2357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.05.014
Scorza Júnior RP, Franco AA (2013) A temperatura e umidade na degradação de fipronil em dois solos de Mato Grosso do Sul. Ciência Rural 43:1203–1209
Shuai X, Chen J, Ray C (2012) Adsorption, transport and degradation of fipronil termiticide in three Hawaii soils. Pest Manag Sci 68:731–739. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.2320
Singh J, Schädler M, Demetrio W, Brown GG, Eisenhauer N (2019) Climate change effects on earthworms - a review. Soil Organisms 3:113–137. https://doi.org/10.25674/so91iss3pp114
Spomer NA, Kamble ST (2009) Sorption and desorption of fipronil in Midwestern soils. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84:264–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9915-1
Šustr V, Pižl V (2010) Temperature dependence and ontogenetic changes of metabolic rate of an endemic earthworm Dendrobaena mrazeki. Biologia 65:289–293. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-010-0019-5
Tedesco MJ, Gianello C, Bissani CA, Bohnen H, Volkweiss SJ (1995). Análise de solo, plantas e outros materiais, 2nd edn. Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, p 147 (Boletim Técnico, 5)
TIBCO Data Science (2013). STATISTICA 13.5.0.17.v: Data analysis software system [Software]. Palo Alto, CA: TIBCO Software.
Tingle CC, Rother JA, Dewhust CF, Lauer S, King WJ (2003) Fipronil: environmental fate, ecotoxicology, and human health concerns. In: Colin C (ed) Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 176. Springer, New York, pp 1–66
Waichman AV, Eve E, Nina NCS (2007) Do farmers understand the information displayed on pesticide product labels? A key question to reduce pesticides exposure and risk of poisoning in the Brazilian Amazon. J Crop Prot 26:576–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2006.05.011
Ying GG, Kookana RS (2006) Persistence and movement of fipronil termiticide with under-slab and trenching treatments. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2045–2050. https://doi.org/10.1897/05-652R.1
Zortéa T, dos Reis TR, Serafini S, de Sousa JP, da Silva AS, Baretta D (2018) Ecotoxicological effect of fipronil and its metabolites on Folsomia candida in tropical soils. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 62:203–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2018.07.011
Zortéa T, da Silva AS, dos Reis TR, Segat JC, Paulino AT, Sousa JP, Baretta D (2018) Ecotoxicological effects of fipronil, neem cake and neem extract in edaphic organisms from tropical soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 166:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.061
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was supported by the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) for the research grant (Project 407170/2016–2). DB received support from CNPq by Research Productivity Grant (CNPq 305939/2018–1). FOB and TBH received support from Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) by their master grants (process numbers 1735590 and 88882.447285/2019–01, respectively).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Author contribution
TBH: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, writing – original draft. PRLA: conceptualization, formal analysis, funding acquisition, investigation, project administration, resources, supervision, writing – review and editing. FOB: investigation, data curation, formal analysis. LCC: investigation, data curation, formal analysis. JSD: investigation. MATS: supervision and data curation. DB: resources, supervision, writing – review and editing.
Ethics approval and consent to participate: All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted (Brazilian regimentation for the scientific use of animals – Law no. 11.794). Consent to participate and publication is not applicable.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available and should be requested by e-mail.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Chris Lowe
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hennig, T.B., Alves, P.R.L., Bandeira, F.O. et al. Role of climatic factors in the toxicity of fipronil toward earthworms in two tropical soils: effects of increased temperature and reduced soil moisture content. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 56370–56378 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19813-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19813-8