Abstract
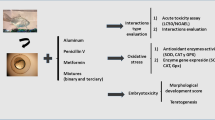
Aluminum, mercury, and iron have been found in high concentrations in various freshwater bodies around the world and have been shown to be very harmful contaminants to hydrobionts, causing metabolic dysfunction and damage at various levels. However, studies on mixtures of these pollutants are scarce, particularly in younger or developing organisms, which are more sensitive to damage. Therefore, the objective of this work was to evaluate the toxicity of Al, Fe, and Hg, in isolation and in mixture, on common carp embryos exposed to the maximum permissible limits described in the Mexican regulations for the protection of aquatic life, correlating the biomarkers of oxidative stress with the effects on embryonic development. For this purpose, the Cyprinus carpio embryos were exposed to iron (0.1 mg L−1), mercury (0.00001 mg L−1), aluminum (0.05 mg L−1), and their mixture, throughout their development and until hatching. The activity of the antioxidant enzymes (SOD, CAT, and GPx), the degree of lipoperoxidation, and the content of hydroperoxides and total proteins, as well as the morphological development of the embryos were evaluated at 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h, and 96 h of exposure. The results showed that the metals under study are toxic to C. carpio embryos and that their interaction modifies the toxic response. Thus, iron generates alterations in the activity of antioxidant enzymes and modification in embryonic development to a lesser extent than aluminum and the mixture of metals, while mercury exerts its toxicity on embryos by mechanisms other than oxidative stress, but the modification to the activity of antioxidant enzymes may contribute to the changes observed in embryonic development. The changes in the response of biomarkers of embryotoxicity and oxidative stress suggest that the combination of metals produces an antagonism-type interaction, so this study provides a precedent for future research to determine the type of interaction that a mixture of contaminants generates in developing aquatic organisms.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
Aba, L., Prasetyo, A., Sitti-Ilmawati, W. O., Ode-Ahmad, L., & Sahidin, L. O. (2019). Reduction of iron and manganese concentration in dug well water by using Moramo beach sand as filter media. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1153(9th International Conference on Physics and Its Applications), 012078.
Aceto, A., Amicarelli, F., Sacchetta, P., Dragani, B., Bucciarelli, T., Masciocco, L., et al. (1994). Developmental aspects of detoxifying enzymes in fish (Salmo iridaeus). Free Radical Research, 21(5), 285–294. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715769409056581
Ali, H., Khan, E., & Ilahi, I. (2019). Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. Journal of Chemistry, 2019, 14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6730305
Apostoli, P., & Catalani, S. (2011). Metal ions affecting reproduction and development. Metal Ions in Life Sciences, 8, 263–303.
Barabasz, W., Albinska, D., Jaskowska, M., & Lipiec, J. (2002). Ecotoxicology of aluminium. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 11(3), 199–203. http://www.pjoes.com/Ecotoxicology-of-Aluminium,87442,0,2.html. Accessed 29 June 2020
Beker van Woudenberg, A., Snel, C., Rijkmans, E., De Groot, D., Bouma, M., Hermsen, S., et al. (2014). Zebrafish embryotoxicity test for developmental (neuro)toxicity: Demo case of an integrated screening approach system using anti-epileptic drugs. Reproductive Toxicology, 49, 101–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2014.07.082
Bosch, C., Olivares, A., Faria, M., Navas, J. M., del Olmo, I., Grimalt, J. O., et al. (2009). Identification of water soluble and particle bound compounds causing sublethal toxic effects. A field study on sediments affected by a chlor-alkali industry. Aquatic Toxicology, 94(1), 16–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2009.05.011.
Boukadida, K., Cachot, J., Clérandeaux, C., Gourves, P. Y., & Banni, M. (2017). Early and efficient induction of antioxidant defense system in Mytilus galloprovincialis embryos exposed to metals and heat stress. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 138, 105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.12.021
Boveris, A. (1998). Biochemistry of free radicals: From electrons to tissues. Medicina (B Aires), 58(4), 350–356. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9816695/. Accessed 3 Sept 2020.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72(1–2), 248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Bridges, C. C., & Zalups, R. K. (2017). The aging kidney and the nephrotoxic effects of mercury. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health - Part B: Critical Reviews. Taylor and Francis Inc. https://doi.org/10.1080/10937404.2016.1243501.
Buege, J. A., & Aust, S. D. (1978). Biomembranes - Part C: Biological oxidations. Methods in Enzymology, 52, 302–310.
Bury, N., & Grosell, M. (2003). Iron acquisition by teleost fish. In Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology - C Toxicology and Pharmacology (Vol. 135, pp. 97–105). Elsevier Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1532-0456(03)00021-8
Capriello, T., Monteiro, S., Félix, L., Dozinetti, A., Aliperti, V., & Ferrandino, I. (2021a). Apoptosis, oxidative stress and genotoxicity in developing zebrafish after aluminium exposure. Aquatic Toxicology, 23(2021), 105872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2021.105872
Capriello, T., Grimaldi, M. C., Cofone, R., D’Aniello, S., & Ferrandino, I. (2019). Effects of aluminium and cadmium on hatching and swimming ability in developing zebrafish. Chemosphere, 222, 243–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.140
Capriello, T., Monteiro, S. M., Félix, L. M., Donizetti, A., Aliperti, V., & Ferrandino, I. (2021b). Apoptosis, oxidative stress and genotoxicity in developing zebrafish after aluminium exposure. Aquatic Toxicology, 236, 105872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2021.105872
Carrasco, L., Barata, C., García-Berthou, E., Tobias, A., Bayona, J. M., & Díez, S. (2011). Patterns of mercury and methylmercury bioaccumulation in fish species downstream of a long-term mercury-contaminated site in the lower Ebro River (NE Spain). Chemosphere, 84(11), 1642–1649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.05.022
Chang, Y., Lee, W. Y., Lin, Y. J., & Hsu, T. (2017). Mercury (II) impairs nucleotide excision repair (NER) in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos by targeting primarily at the stage of DNA incision. Aquatic Toxicology, 192, 97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.09.001
Chen, P. J., Wu, W. L., & Wu, K. C. W. (2013). The zerovalent iron nanoparticle causes higher developmental toxicity than its oxidation products in early life stages of medaka fish. Water Research, 47(12), 3899–3909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.12.043
Choi, J., Bae, S., Lim, H., Lim, J. A., Lee, Y. H., Ha, M., & Kwon, H. J. (2017). Mercury exposure in association with decrease of liver function in adults: A longitudinal study. Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, 50(6), 377–385. https://doi.org/10.3961/jpmph.17.099
Cobbina, S. J., Chen, Y., Zhou, Z., Wu, X., Zhao, T., Zhang, Z., et al. (2015). Toxicity assessment due to sub-chronic exposure to individual and mixtures of four toxic heavy metals. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 294, 109–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.03.057
Cunha Gemaque, T., Pereira da Costa, D., Vaz Pereira, L., & Miranda Filho, K. C. (2019). Evaluation of iron toxicity in the tropical fish Leporinus friderici. Biomed J Sci & Tech Res, 18(2), 13436–13441. https://doi.org/10.26717/BJSTR.2019.18.003127.
de Oliveira, L. F., Santos, C., Risso, W. E., & dos Reis Martinez, C. B. (2018). Triple-mixture of Zn, Mn, and Fe increases bioaccumulation and causes oxidative stress in freshwater neotropical fish. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 37(6), 1749–1756. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4133
DOF. (1989). ACUERDO por el que se establecen los Criterios Ecológicos de Calidad del Agua. México: Diario Oficia de la Federación. dof.gob.mx/index.php?year=1989&month=12&day=13
Domagalski, J. (1998). Occurrence and transport of total mercury and methyl mercury in the Sacramento River Basin, California. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 64(1–3–3 pt 1), 277–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0375-6742(98)00038-7
Driscoll, C. T., Mason, R. P., Man Chan, H., Jacob, D. J., & Pirrone, N. (2013). Mercury as a global pollutant: Sources, pathways, and effects terms of use. Environmental Science and Technology, 47, 4983. https://doi.org/10.1021/es305071v
Ercal, N., Gurer-Orhan, H., & Aykin-Burns, N. (2001). Toxic metals and oxidative stress part I: Mechanisms involved in metal-induced oxidative damage. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 1(6), 529–539. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026013394831
Exley, C. (2004). The pro-oxidant activity of aluminum. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 36(3), 380–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2003.11.017
Feng, J., Gao, Y., Ji, Y., & Zhu, L. (2018). Quantifying the interactions among metal mixtures in toxicodynamic process with generalized linear model. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 345, 97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.11.013
Fent, K., Weston, A. A., & Caminada, D. (2006, February 10). Ecotoxicology of human pharmaceuticals. Aquatic Toxicology. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2005.09.009
Fernandes-Azevedo, B., Barros-Furieri, L., Maciel-Peçanha, F., Wiggers, G. A., Frizera-Vassallo, P., Ronacher-Simões, M., et al. (2012). Toxic effects of mercury on the cardiovascular and central nervous systems. Journal of Biomedicine & Biotechnology, 2012, 11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/949048
García-Medina, S., Razo-Estrada, A. C., Gómez-Oliván, L. M., Amaya-Chávez, A., Madrigal-Bujaidar, E., & Galar-Martínez, M. (2010). Aluminum-induced oxidative stress in lymphocytes of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 36(4), 875–882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-009-9363-1
González, P. M., Abele, D., & Puntarulo, S. (2010). Exposure to excess dissolved iron in vivo affects oxidative status in the bivalve Mya arenaria. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology - C Toxicology and Pharmacology, 152(2), 167–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2010.04.006
Green, A. J., & Planchart, A. (2018). The neurological toxicity of heavy metals: A fish perspective. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part - c: Toxicology and Pharmacology, 208, 12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2017.11.008
Guibaud, G., & Gauthier, C. (2003). Study of aluminium concentration and speciation of surface water in four catchments in the Limousin region (France). In Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry (Vol. 97, pp. 16–25). Elsevier Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0162-0134(03)00254-X
Herkovits, J., Castañaga, L. A., D’Eramo, J. L., & Jourani, V. P. (2015). Living organisms influence on environmental conditions: PH modulation by amphibian embryos versus aluminum toxicity. Chemosphere, 139, 210–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.05.025
Hermsen, S. A. B., van den Brandhof, E. J., van der Ven, L. T. M., & Piersma, A. H. (2011). Relative embryotoxicity of two classes of chemicals in a modified zebrafish embryotoxicity test and comparison with their in vivo potencies. Toxicology in Vitro, 25(3), 745–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2011.01.005
Hernández, A. F., Gil, F., & Lacasaña, M. (2017, October 1). Toxicological interactions of pesticide mixtures: An update. Archives of Toxicology. Springer Verlag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-017-2043-5
Hertzberg, R. C., & Teuschler, L. K. (2002, December 1). Evaluating quantitative formulas for dose-response assessment of chemical mixtures. Environmental Health Perspectives. Public Health Services, US Dept of Health and Human Services. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.02110s6965
Ho, N. Y., Yang, L., Legradi, J., Armant, O., Takamiya, M., Rastegar, S., & Strähle, U. (2013). Gene responses in the central nervous system of zebrafish embryos exposed to the neurotoxicant methyl mercury. Environmental Science and Technology, 47(7), 3316–3325. https://doi.org/10.1021/es3050967
Ismail, A., & Yusof, S. (2011). Effect of mercury and cadmium on early life stages of Java medaka (Oryzias javanicus): A potential tropical test fish. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 63(5–12), 347–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.02.014
Ismail, T., Lee, H. K., Kim, C., Kim, Y., Lee, H., Kim, J. H., et al. (2019). Comparative analysis of the developmental toxicity in Xenopus laevis and Danio rerio induced by Al2O3 nanoparticle exposure. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 38(12), 2672–2681. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4584
Isuev, A. R., Ismailova, S. I., & Ozernyuk, N. D. (2008). Comparative study of superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase activity in embryos and skeletal muscles of adult fish. Biology Bulletin, 35(5), 494–498. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359008050105
Jaishankar, M., Tseten, T., Anbalagan, N., Mathew, B. B., & Beeregowda, K. N. (2014). Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdisciplinary Toxicology. Slovak Toxicology Society. https://doi.org/10.2478/intox-2014-0009
Kim, M. J., Kim, C. H., An, M. J., Shin, G. S., Lee, H. M., Kim, J. Y., et al. (2020). Exposure to mercury induced early apoptotic signals in human placental BeWo cells through alteration of cell cycle regulation. Molecular and Cellular Toxicology, 16(4), 419–429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-020-00098-2
Kimmel, C. B., Ballard, W. W., Kimmel, S. R., Ullmann, B., & Schilling, T. F. (1995). Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Developmental Dynamics, 203(3), 253–310. https://doi.org/10.1002/aja.1002030302
Kumar, V., & Gill, K. D. (2014). Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in aluminium neurotoxicity and its amelioration: A review. Neurotoxicology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2014.02.004
Kumolu-Johnson, C. A., Ndimele, P. E., Akintola, S. L., & Jibuike, C. C. (2010). Copper, zinc and iron concentrations in water, sediment and Cynothrissa mento (Regan 1917) from Ologe Lagoon, Lagos, Nigeria: A preliminary survey. African Journal of Aquatic Science, 35(1), 87–94. https://doi.org/10.2989/16085914.2010.466588
Lee, J. Y., & Han, M. (2012). Iron removal using adsorptive filtration treatment for low iron concentration water from urban industrial region. International Journal of Urban Sciences, 16(1), 115–121. https://doi.org/10.1080/12265934.2012.662587
Levine, R. L., Williams, J. A., Stadtman, E. P., & Shacter, E. (1994). Carbonyl assays for determination of oxidatively modified proteins. Methods in Enzymology, 233(C), 346–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(94)33040-9
Li, H., Zhou, Q., Wu, Y., Fu, J., Wang, T., & Jiang, G. (2009). Effects of waterborne nano-iron on medaka (Oryzias latipes): Antioxidant enzymatic activity, lipid peroxidation and histopathology. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 72(3), 684–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.09.027
Logan, D. W., Burn, S. F., & Jackson, I. J. (2006). Regulation of pigmentation in zebrafish melanophores. Pigment Cell Research, 19(3), 206–213. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0749.2006.00307.x
Lubick, N. (2010). Mercury alters immune system response in artisanal gold miners. Environmental health perspectives. National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.118-a243
Lushchak, V. I. (2016, April 1). Contaminant-induced oxidative stress in fish: A mechanistic approach. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry. Springer Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0171-5
Malczyk, E. A., & Branfireun, B. A. (2015). Mercury in sediment, water, and fish in a managed tropical wetland-lake ecosystem. Science of the Total Environment, 524–525, 260–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.04.015
Mujika, J. I., Rezabal, E., Mercero, J. M., Ruipérez, F., Costa, D., Ugalde, J. M., & Lopez, X. (2014). Aluminium in biological environments: A computational approach. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal. https://doi.org/10.5936/csbj.201403002
Norwood, W. P., Borgmann, U., Dixon, D. G., & Wallace, A. (2003). Effects of metal mixtures on aquatic biota: A review of observations and methods. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment. Taylor and Francis Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1080/713610010
Nourooz-Zadeh, J., Tajaddini-Sarmadi, J., & Wolff, S. P. (1994). Measurement of plasma hydroperoxide concentrations by the ferrous oxidation-xylenol orange assay in conjunction with triphenylphosphine. Analytical Biochemistry, 220(2), 403–409. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1994.1357
Pal, P. B., Pal, S., Das, J., & Sil, P. C. (2012). Modulation of mercury-induced mitochondria-dependent apoptosis by glycine in hepatocytes. Amino Acids, 42(5), 1669–1683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0869-3
Papanikolaou, G., & Pantopoulos, K. (2005, January 15). Iron metabolism and toxicity. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2004.06.021
Patrick, L. (2002). Mercury toxicity and antioxidants: Part I: Role of glutathione and alpha-lipoic acid in the treatment of mercury toxicity. Alternative Medicine Review, 7(6), 456–471.
Pereira, S., Cavalie, I., Camilleri, V., Gilbin, R., & Adam-Guillermin, C. (2013). Comparative genotoxicity of aluminium and cadmium in embryonic zebrafish cells. Mutation Research, 750, 19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2012.07.007
Pérez-Coyotl, I., Galar-Martínez, M., García-Medina, S., Gómez-Oliván, L. M., Gasca-Pérez, E., Martínez-Galero, E., et al. (2019). Polluted water from an urban reservoir (Madín dam, México) induces toxicity and oxidative stress in Cyprinus carpio embryos. Environmental Pollution, 510–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.04.095
Pérez-Coyotl, I., Martínez-Vieyra, C., Galar-Martínez, M., Gómez-Oliván, L. M., García-Medina, S., Islas-Flores, H., et al. (2017). DNA damage and cytotoxicity induced on common carp by pollutants in water from an urban reservoir. Madín reservoir, a case study. Chemosphere, 185, 789–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.07.072
Perry, D., Weis, J., & Weis, P. (1988). Cytogenetic effects of methylmercury in embryos of the killifish Fundulus Heteroclitus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol, 17(5), 569–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055824
Quiroga-Santos, E. H., Galar-Martínez, M., García-Medina, S., Gasca-Pérez, E., Cano-Viveros, S., Ruíz-Lara, K., et al. (2021). Geno-cytotoxicity and congenital malformations produced by relevant environmental concentrations of aluminum, diclofenac and their mixture on Cyprinus carpio. An interactions study. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 82, 103555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2020.103555
Radi, R., Turrens, J. F., Chang, L. Y., Bush, K. M., Crapo, J. D., & Freeman, B. A. (1991). Detection of catalase in rat heart mitochondria. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 266(32), 22028–22034.
Ravenscroft, J., Roy, A., Queirolo, E. I., Mañay, N., Martínez, G., Peregalli, F., & Kordas, K. (2018). Drinking water lead, iron and zinc concentrations as predictors of blood lead levels and urinary lead excretion in school children from Montevideo, Uruguay. Chemosphere, 212, 694–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.07.154
Rayburn, J. R., & Aladdin, R. K. (2003). Developmental toxicity of copper, chromium, and aluminum using the shrimp embryo teratogenesis assay: Palaemonid with artificial seawater. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 71(3), 481–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-003-8741-0
Roy, B., & Bhadra, S. (2014). Effects of toxic levels of aluminium on seedling parameters of rice under hydroponic culture. Rice Science, 21(4), 217–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-6308(13)60182-1
Sadeq, S. A., & Beckerman, A. P. (2020). Evaluating additive versus interactive effects of copper and cadmium on Daphnia pulex life history. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(2), 2015–2026. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06622-9
Schmidt, S., Busch, W., Altenburger, R., & Küster, E. (2016). Mixture toxicity of water contaminants-effect analysis using the zebrafish embryo assay (Danio rerio). Chemosphere, 152, 503–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.006
Sevcikova, M., Modrá, H., Slaninova, A., & Svobodova, Z. (2011). Metals as a cause of oxidative stress in fish: A review. Veterinarni Medicina, 56(11), 537–546.
Sexton, K., & Hattis, D. (2007). Assessing cumulative health risks from exposure to environmental mixtures - Three fundamental questions. Environmental Health Perspectives, 115(5), 825–832. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.9333
Shi, Q., Sun, N., Kou, H., Wang, H., & Zhao, H. (2018). Chronic effects of mercury on Bufo gargarizans larvae: Thyroid disruption, liver damage, oxidative stress and lipid metabolism disorder. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 164, 500–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.058
Silva Pinheiro, J. P., Bertacini de Assis, C., Sanches, E. A., & Moreira, R. G. (2020). Aluminum, at an environmental concentration, associated with acidic pH and high water temperature, causes impairment of sperm quality in the freshwater teleost Astyanax altiparanae (Teleostei: Characidae). Environmental Pollution, 262, 114252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114252
Singh, M., Barman, A. S., Devi, A. L., Devi, A. G., & Pandey, P. K. (2019). Iron mediated hematological, oxidative and histological alterations in freshwater fish Labeo rohita. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 170, 87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.11.129
Sinha, K., Das, J., Pal, P. B., & Sil, P. C. (2013). Oxidative stress: The mitochondria-dependent and mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Archives of Toxicology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-013-1034-4
Slaninova, A., Machova, J., & Svobodova, Z. (2014). Fish kill caused by aluminium and iron contamination in a natural pond used for fish rearing: A case report. Veterinarni Medicina (Vol. 59).
Small, C. D., el-Khoury, M., Deslongchamps, G., Benfey, T. J., & Crawford, B. D. (2020). Matrix metalloproteinase 13 activity is required for normal and hypoxia-induced precocious hatching in zebrafish embryos. Journal of Developmental Biology, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/JDB8010003
Stankovic, S., Kalaba, P., & Stankovic, A. R. (2014, March 9). Biota as toxic metal indicators. Environmental Chemistry Letters. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-013-0430-6
Surai, P. F. (1999). Tissue-specific changes in the activities of antioxidant enzymes during the development of the chicken embryo. British Poultry Science, 40, 397–405. https://doi.org/10.1080/00071669987511
Szyczewski, P., Siepak, J., Niedzielski, P., & Sobczyński, T. (2009). Research on heavy metals in Poland. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 18(5).
Torres-Osorio, V., Urrego, R., Julián Echeverri-Zuluaga, J., & López-Herrera, A. (2019). Oxidative stress and antioxidant use during in vitro mammal embryo production. Review. Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Pecuarias, 10(2), 433–459. https://doi.org/10.22319/rmcp.v10i2.4652
Valavanidis, A., Vlahogianni, T., Dassenakis, M., & Scoullos, M. (2006). Molecular biomarkers of oxidative stress in aquatic organisms in relation to toxic environmental pollutants. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 64(2), 178–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.03.013
Valerio-García, R. C., Carbajal-Hernández, A. L., Martínez-Ruíz, E. B., Jarquín-Díaz, V. H., Haro-Pérez, C., & Martínez-Jerónimo, F. (2017). Exposure to silver nanoparticles produces oxidative stress and affects macromolecular and metabolic biomarkers in the goodeid fish Chapalichthys pardalis. Science of the Total Environment, 583, 308–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.070
Vijver, M. G., Elliott, E. G., Peijnenburg, W. J. G. M., & de Snoo, G. R. (2011). Response predictions for organisms water-exposed to metal mixtures: A meta-analysis. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 30(6), 1482–1487. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.499
Zengin, H., Yilmaz, Ö., Demir, E., & Gökce, Z. (2015). Antioxidant enzymatic defences during embryogenesis of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum 1792). Turkish Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 15, 437–446. https://doi.org/10.4194/1303-2712-v15_2_30
Zhang, Q. F., Li, Y. W., Liu, Z. H., & Chen, Q. L. (2016). Exposure to mercuric chloride induces developmental damage, oxidative stress and immunotoxicity in zebrafish embryos-larvae. Aquatic Toxicology, 181, 76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.10.029
Zhou, Q., Yang, N., Li, Y., Ren, B., Ding, X., Bian, H., & Yao, X. (2020). Total concentrations and sources of heavy metal pollution in global river and lake water bodies from 1972 to 2017. Global Ecology and Conservation, 22, e00925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2020.e00925
Acknowledgements
We give thanks to Biologist Gerardo Ontiveros at the Centro Carpícola Tiacaque for supplying the test specimens and giving advice on their care and maintenance.
Funding
This study was made possible by the financial support from the Secretaría de Investigación y Posgrado of the Instituto Politécnico Nacional (SIP-IPN, project 20180699).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
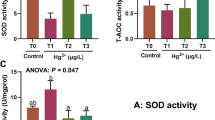
1. Common carps embryos exposed to concentrations equivalent to the maximum permissible limit for the protection of aquatic life of Al and Hg exhibit modifications to the activity of antioxidant enzymes, but only Al produces oxidative damage.
2. Al and Hg produce modifications to common carp embryonic development at concentrations equivalent to the maximum permissible limit for the protection of aquatic life.
3. Fe at concentrations equivalent to the maximum permissible limit for the protection of aquatic life, produces neither oxidative stress nor modifications to the embryonic development of C. carpio.
4. The toxicity of Fe, Al and Hg is modified by the interaction of the three toxicants
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cano-Viveros, S., Galar-Martínez, M., Gasca-Pérez, E. et al. The Relationship Between Embryotoxicity and Oxidative Stress Produced by Aluminum, Iron, Mercury, and Their Mixture on Cyprinus carpio. Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 376 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05312-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05312-y