Abstract
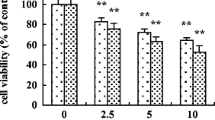
Mercury (Hg) is one of the universal environmental pollutants and is responsible for various organ pathophysiology including oxidative stress-induced hepatic disorders. In the present study, we aimed to explore the protective role of glycine in Hg-induced cytotoxicity and cell death in murine hepatocytes. Exposure of mercury (20 μM), in the form HgCl2 for 1 h, significantly enhanced the ALT and ALP leakage, increased reactive oxygen species production, reduced cell viability and distorted the antioxidant status of hepatocytes. Flow cytometric analyses shows that Hg-induced apoptotic death in hepatocytes. Mechanism of this pathophysiology involves reduced mitochondrial membrane potential, variations in Bcl-2/Bad proteins, activation of caspases and cleavage of PARP protein. In addition, Hg distinctly increased NF-κB phosphorylation in association with IKKα phosphorylation and IκBα degradation. Concurrent treatment with glycine (45 mM), however, reduced Hg-induced oxidative stress, attenuated the changes in NF-κB phosphorylation and protects hepatocytes from Hg-induced apoptotic death. Hg also distinctly increased the phosphorylation of p38, JNK and ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPKs). Glycine treatment suppressed these apoptotic events, signifying its protective role in Hg-induced hepatocyte apoptosis as referred by reduction of p38, JNK and ERK MAPK signaling pathways. Results suggest that glycine can modulate Hg-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in hepatocytes probably because of its antioxidant activity and functioning via mitochondria-dependent pathways and could be a beneficial agent in oxidative stress-mediated liver diseases.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALP:
-
Alkaline phosphatase
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotranferase
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified eagle’s medium
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulphoxide
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- GSSG:
-
Glutathione disulfide
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GST:
-
Glutathione S-transferase
- GR:
-
Glutathione reductase
- HgCl2 :
-
Mercuric chloride
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- PARP:
-
Poly ADP ribose polymerase
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- ERK:
-
Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase
References
Addaya S, Chakravarti K, Basu A, Santra M, Haldar S, Chatterjee GC (1984) Effects of mercuric chloride on several scavenging enzymes in rat kidney and influence of vitamin E supplementation. Acta Vitaminol Enzymol 6:103–107
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chang SI, Jin B, Youn P, Park C, Park JD, Ryu DY (2007) Arsenic-induced toxicity and the protective role of ascorbic acid in mouse testis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 218:196–203
Choi CH, Bark H, Chung JM, Park EK, Kim SH (2006) Elevated reactive oxygen species but not glutathione regulate mercury resistance to AML-2/DX100 cells. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 28:545–555
Coccine Y, Randin G, Candura S, Nappi R, Prockop L, Luigi M (2000) Low level exposure of methyl mercury modifies muscarinic cholinergic receptor binding characteristic in rat brain and lymphocyte: physiologic implication and new opportunities in biological monitoring. Environ Health Perspect 108:29
Das J, Ghosh J, Manna P, Sil PC (2010) Protective role of taurine against arsenic-induced mitochondria-dependent hepatic apoptosis via the inhibition of PKCδ-JNK pathway. PLoS One 5:e12602; 1–19
Das J, Ghosh J, Manna P, Sinha M, Sil PC (2009a) Taurine protects rat testes against NaAsO(2)-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis via mitochondrial dependent and independent pathways. Toxicol Lett 187:201–210
Das J, Ghosh J, Manna P, Sinha M, Sil PC (2009b) Arsenic-induced oxidative cerebral disorders: Protection by taurine. Drug Chem Toxicol 32:93–102
Das J, Ghosh J, Manna P, Sil PC (2010b) Acetaminophen induced acute liver failure via oxidative stress and JNK activation: protective role of taurine by the suppression of cytochrome P450 2E1. Free Radic Res 44:340–355
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulphydryl group. Arch Biochem Biophy 82:70–77
Esterbauer H, Cheeseman KH (1990) Determination of aldehydic lipid peroxidation products: Malonaldehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal. Method Enzymol 186:407–421
Feuerstein GZ, Young PR (2000) Apoptosis in cardiac diseases: stress- and mitogen activated signaling pathways. Cardiovasc Res 45:560–569
Ghosh J, Das J, Manna P, Sil PC (2010a) Protective effect of the fruits of Terminalia arjuna against cadmium-induced oxidant stress and hepatic cell injury via MAPK activation and mitochondria dependent pathway. Food Chem 123:1062–1075
Ghosh J, Das J, Manna P, Sil PC (2008) Cytoprotective effect of arjunalic acid in response to sodium fluoride mediated oxidative stress and cell death via necrotic pathway. Toxicol in Vitro 22:1918–1926
Ghosh J, Das J, Manna P, Sil PC (2009a) Taurine prevents arsenic-induced cardiac oxidative stress and apoptotic damage: Role of NF-κB, p38 and JNK MAPK pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharm 240:73–87
Ghosh J, Das J, Manna P, Sil PC (2009b) Arjunolic acid, a triterpenoid saponin, prevents acetaminophen (APAP)-induced liver and hepatocyte injury via the inhibition of APAP bioactivation and JNK-mediated mitochondrial protection. Free Radical Biol Med 48:535–553
Ghosh J, Das J, Manna P, Sil PC (2010b) Acetaminophen induced renal injury via oxidative stress and TNF-alpha production: Therapeutic potential of arjunolic acid. Toxicology 268:8–18
Ghosh A, Sil PC (2008) A Protein from Cajanus indicus Spreng Protects Liver and Kidney against Mercuric Chloride-Induced Oxidative Stress. Biol Pharm Bull 31:1651–1658
Ghosh A, Sil PC (2009) Protection of acetaminophen induced mitochondrial dysfunctions and hepatic necrosis via Akt-NF-kappaB pathway: role of a novel plant protein. Chem Biol Interact 177:96–106
Green DR, Kroemer G (2004) The pathophysiology of mitochondrial cell death. Science 305:626–629
Green DR, Reed JC (1998) Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 281:1309–1312
Hansen JM, Zhang H, Hones DP (2006) Differential oxidation of thioredoxin-1, thioredoxin-2, and glutathione by metal ions. Free Radic Biol Med 40:138–145
Hissin PJ, Hilf RA (1976) A fluorometric method for determination of oxidized and reduced glutathione in tissues. Anal Biochem 74:214–226
Jezek P, Hlavata L (2005) Mitochondria in homeostasis of reactive oxygen species in cell, tissues, and organism. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:2478–2503
Kaur P, Aschner M, Syversen T (2006) Glutathione modulation influences methyl mercury induced neurotoxicity in primary cell cultures of neurons and astrocytes. Neurotoxicology 27:492–500
Korashy MH, El-Kadi AOS (2008) The role of redox-sensitive transcription factors NF-κB and AP-1 in the modulation of the Cyp1a1 gene by mercury, lead, and copper. Free Radic Biol Med 44:795–806
Lee S, Cha M, Kang C, Sohn ET, Lee H, Munawir A, Kim JS, Kim E (2009) Mutual synergistic toxicity between environmental toxicants: a study of mercury chloride and 4-nonylphenol. Environ Toxicol pharmacol 27:90–95
Madesh M, Balasubramanian KA (1997) A microlitre plate assay for superoxide using MTT reduction method. Indian J Biochem Biophys 34:535–539
Manna P, Sinha M, Sil PC (2007a) Arjunolic acid, a triterpenoid saponin, ameliorates arsenic-induced cyto-toxicity in hepatocytes. Chem Biol Interact 170:187–200
Manna P, Sinha M, Sil PC (2007b) Protection of arsenic-induced hepatic disorder by arjunolic acid. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 101:333–338
Manna P, Sinha M, Sil PC (2008a) Protection of arsenic-induced testicular oxidative stress by arjunolic acid. Redox Report 13:67–77
Manna P, Sinha M, Sil PC (2008b) Arsenic induced oxidative myocardial injury: protective role of arjunolic acid. Arch Toxicol 82:137–149
Manna P, Sinha M, Sil PC (2009a) Prophylactic role of arjunolic acid in response to streptozotocin mediated diabetic renal injury: activation of polyol pathway and oxidative stress responsive signaling cascades. Chem Biol Interact 181:297–308
Manna P, Sinha M, Sil PC (2009b) Protective role of arjunolic acid in response to streptozotocin-induced type-I diabetes via the mitochondrial dependent and independent pathways. Toxicology 257:53–63
Manna P, Ghosh J, Das J, Sil PC (2010a) Contribution of type 1 diabetes to rat liver dysfunction and cellular damage via activation of NOS, PARP, IκBα/NF-κB, MAPKs, and mitochondria-dependent prophylactic role of arjunolic acid. Free Radic Biol Med 48:1465–1484
Manna P, Ghosh J, Das J, Sil PC (2010b) Streptozotocin induced activation of oxidative stress responsive splenic cell signaling pathways: protective role of arjunolic acid. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 244:114–129
Mingatto FE, Rodrigues T, Pigoso AA, Uyemura SA, Curti C, Santos AC (2003) The critical role of mitochondrial energetic impairment in the toxicity of nimesulide to hepatocytes. J Pharm Exp Therap 303:601–607
Pourahmad J, O’Brien PJ, Jokar F, Daraei B (2003) Carcinogenic metal induced sites of reactive oxygen species formation in hepatocytes. Toxicol Vitro 17:808–810
Roy A, Manna P, Sil PC (2009) Prophylactic role of taurine on arsenic mediated oxidative renal dysfunction via MAPKs/ NF-kappaB and mitochondria dependent pathways. Free Radic Res 43:995–1007
Sarkar K, Sil PC (2006) A 43 kDa protein from the herb Cajanus indicus L. protects thioacetamide induced cytotoxicity in hepatocytes. Toxicol In Vitro 20:634–640
Sarkar K, Ghosh A, Kinter M, Mazumder B, Sil PC (2006) Purification and characterization of a 43kD hepatoprotective protein from the herb Cajanus indicus L. Protein J 25:411–421
Sarkar K, Sil PC (2007) Attenuation of acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in vivo and in vitro by a 43 kD protein from the herb Cajanus indicus L. Toxicol Mech Methods 17:305–315
Sarkar MK, Kinter M, Mazumder B, Sil PC (2009) Purification and characterization of a novel antioxidant protein molecule from Phyllanthus niruri. Food Chem 114:1405–1412
Sarkar MK, Sil PC (2010) Prevention of tertiary butyl hydroperoxide induced oxidative impairment and cell death by a novel antioxidant protein molecule isolated from the herb, Phyllanthus niruri. Toxicol In Vitro 24:1711–1719
Schulze-Osthoff K, Ferrari D, Riehemann K, Wesselborg S (1997) Regulation of NF-κB activation by MAP kinase cascades. Immunobiology 198:35–49
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH (1968) Estimation of total, protein-bound, and non protein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal Biochem 24(25):192–205
Singh V, Joshi D, Shrivastava S, Shukla S (2007) Effect of monothiol along with antioxidant against mercury-induced oxidative stress in rat. Indian J Expt Biol 45:1037–1044
Sinha M, Manna P, Sil PC (2007a) Taurine, a conditionally essential amino acid, ameliorates arsenic-induced cytotoxicity in murine hepatocytes. Toxicol In Vitro 21:1419–1428
Sinha M, Manna P, Sil PC (2007b) Attenuation of cadmium chloride induced cytotoxicity in murine hepatocytes by a protein isolated from the leaves of the herb Cajanus indicus L. Arch Toxicol 81:397–406
Sinha M, Manna P, Sil PC (2008) Protective effect of arjunolic acid against arsenic-induced oxidative stress in mouse brain. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 22:15–26
Uchida K, Stadtman ER (1993) Covalent attachment of 4-hydroxynonenal to glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 268:6388–6393
Wheeler MD, Ikejema K, Enomoto N, Stacklewitz RF, Seabra V, Zhong Z (1999) Glycine: a new anti-inflammatory immunonutrient. Cell Mol Life Sci 56(9–10):843–856
Yamauchi H, Aminaka Y, Yoshida K, Sun G, Pi J, Waalkes MP (2004) Evaluation of DNA damage in patients with arsenic poisoning: urinary 8-hydroxydeoxyguanine. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 198:291–296
Yamanaka K, Hesegwa A, Sawamuna R, Okada S (1991) Cellular response to oxidative damage in lung induced by the administration of dimethylarsinic acid, a major metabolite of inorganic arsenics, in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 108:205–213
Zhong Z, Jones S, Thurman RG (1996) Glycine minimizes reperfusion injury in a low-flow, reflow liver perfusion model in the rat. Am J Physiol 270:G332–G338
Zhu H, Bannenberg GL, Moldéus P, Shertzer HG (1994) Oxidation pathways for the intracellular probe 2’, 7’-dichlorofluorescein. Arch Toxicol 68:582–587
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Mr. Prasanta Pal for excellent technical assistance for the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pal, P.B., Pal, S., Das, J. et al. Modulation of mercury-induced mitochondria-dependent apoptosis by glycine in hepatocytes. Amino Acids 42, 1669–1683 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0869-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0869-3