Abstract
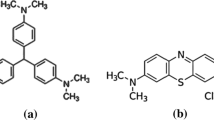
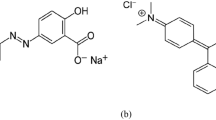
The potential to remove methylene blue (MB) basic dye and indigo carmine (IC) acidic dye, from wastewater treatment systems using corn stigmata through biosorption was investigated in batch experiments. The effects of contact time, solution pH, biosorbent dosage, initial dye concentration, salts, and temperature were sought. Results showed that the maximal uptakes of MB were 106.3 mg g−1 at pH = 7 and 63.7 mg g−1 for IC at pH = 2. In order to determine the properties and surface structure of the biomass physicochemical properties (pHpzc, elemental analysis, Boehm’s titration, and chemical composition), spectral (FTIR analysis) and morphological characteristics (SEM) were investigated. Random distribution of the active sites was described by the new biosorption fractal model of Brouers–Sotolongo. The thermodynamic study demonstrated the favorable character of the biosorption of MB and of IC, which was inhibited by the presence of salts. The elucidation of the biosorption mechanism showed that the biosorption of MB onto corn stigmata was mainly controlled by chemisorption and the biosorption of IC was described by physisorption.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah, R., & Taha, S. (2012). Biosorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution by nonviable Aspergillus fumigatus. Chemical Engineering Journal, 195–196, 69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.04.066.
Agarwal, S., Tyagi, I., Gupta, V. K., Ghasemi, N., Shahivand, M., & Ghasemi, M. (2016). Kinetics, equilibrium studies and thermodynamics of methylene blue adsorption on Ephedra strobilacea saw dust and modified using phosphoric acid and zinc chloride. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 218, 208–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.02.073.
Anastopoulos, I., & Kyzas, G. Z. (2015). Composts as biosorbents for decontamination of various pollutants: a review. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 226, 61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2345-2.
Àngels Olivella, M., Fiol, N., de la Torre, F., Poch, J., & Villaescusa, I. (2012). A mechanistic approach to methylene blue sorption on two vegetable wastes: cork bark and grape stalks. BioResources, 7(3), 3340–3354.
Balarak, D., Jaafari, J., Hassani, G., Mahdavi, Y., Tyagi, I., Agarwal, S., & Gupta, V. K. (2015). The use of low-cost adsorbent (Canola residues) for the adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution: isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Colloids and Interface Science Communications, 7, 16–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2015.11.004.
Balistrieri, L. S., & Murray, J. w. (1981). The surface chemistry of goethite (alpha FeOOH) in major ion seawater. American Journal of Sciences, 281, 788–806.
Hamissa, A. M. B., Brouers, F., Ncibi, M. C., & Seffen, M. (2013). Kinetic modeling study on methylene blue sorption onto Agave americana fibers: fractal kinetics and regeneration studies. Separation Science and Technology, 48, 2834–2842. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2013.809104.
Boehm, H. P. (1994). Some aspects of the surface chemistry of carbon blacks and other carbons. Carbon, 32(5), 759–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-6223(94)90031-0.
Boudechiche, N., Mokaddem, H., Sadaoui, Z., & Trari, M. (2016). Biosorption of cationic dye from aqueous solutions onto lignocellulosic biomass (Luffa cylindrica): characterization, equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. International Journal of Industrial Chemistry, 7, 167–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40090-015-0066-4.
Brouers, F., & Al-Musawi, T. J. (2015). On the optimal use of isotherm models for the characterization of biosorption of lead onto algae. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 212, 46–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.08.054.
Brouers, F., & Sotolongo-costa, O. (2006). Generalized fractal kinetics in complex systems (application to biophysics and biotechnology). Physica A, 368, 165–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2005.12.062.
Brouers, F., Sotolongo, O., Marquez, F., & Pirard, J. P. (2005). Microporous and heterogeneous surface adsorption isotherms arising from levy distributions. Physica A, 349, 271–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2004.10.032.
Chao, H.-P., & You, S.-J. (2017). Activated carbons from golden shower upon different chemical activation methods: synthesis and characterizations. Adsorption Science & Technology, 0(0),1–19. https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617416684837.
Daneshvar, E., Vazirzadeh, A., Niazi, A., Sillanpä ä, M., & Bhatnagar, A. (2017). A comparative study of methylene blue biosorption using different modified brown, red and green macroalgae—effect of pretreatment. Chemical Engineering Journal, 307, 435–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.093.
de Almeida, E. J. R., & Corso, C. R. (2016). Acid blue 161: decolorization and toxicity analysis after microbiological treatment. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 227, 468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3042-5.
de Oliveira Brito, S. M., Andrade, H. M. C., Soares, L. F., & de Azevedo, R. P. (2010). Brazil nut shells as a new biosorbent to remove methylene blue and indigo carmine from aqueous solutions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 174, 84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.020.
Foo, K. Y. (2016). Value-added utilization of maize cobs waste as an environmental friendly solution for the innovative treatment of carbofuran. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 100, 295–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2016.01.020.
Freundlich, H. M. (1906). Über die adsorption in losungen. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 57, 385–471.
Fu, J., Chen, Z., Wang, M., Liu, S., Zhang, J., Zhang, J., et al. (2015). Adsorption of methylene blue by a high-efficiency adsorbent (polydopamine microspheres): kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics and mechanism analysis. Chemical Engineering Journal, 259, 53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.101.
Garcia-Jaldon, C. (1992). Caractérisation morphologique et chimique du chanvre (Cannabis sativa)/Prétraitement à la vapeur et valorization, Thesis,(Grenoble I University).
Ghaedi, M., Nasab, A. G., Khodadoust, S., Rajabi, M., & Azizian, S. (2014). Application of activated carbon as adsorbents for efficient removal of methylene blue: kinetics and equilibrium study. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 20, 2317–2324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.10.007.
Gupta, T. B., & Lataye, D. H. (2017). Adsorption of indigo carmine dye onto Acacia nilotica ( Babool ) sawdust activated carbon. Journal of Hazardous,Toxic ,and Radioactive Waste, 21(4), 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HZ.2153-5515.0000365.
Gupta, V. K., Pathania, D., Sharma, S., Agarwal, S., & Singh, P. (2013). Remediation of noxious chromium (VI) utilizing acrylic acid grafted lignocellulosic adsorbent. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 177, 343–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2012.10.017.
Ho, Y. S., & Mckay, G. (1998). Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chemical Engineering, 70, 115–124.
Hosni, K., & Srasra, E. (2010). Evaluation of phosphate removal from water by calcined-LDH synthesized from the dolomite. Colloid Journal, 72(3), 423–431. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061933X10030178.
Ilayaraja, M., Krishnan, N. P., & Kannan, R. S. (2013). Adsorption of rhodamine-B and Congo red dye from aqueous solution using activated carbon: kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics. IOSR Journal Of Environmental Science, Toxicology And Food Technology, 5(5), 79–89.
Indah, S., Helard, D., & Sasmita, A. (2016). Utilization of maize husk (Zea mays L.) as low-cost adsorbent in removal of iron from aqueous solution. Water Science and Technology, 73(12), 2929–2935. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.154.
Kankılıc, G. B., Metin, A. Ü., & Tüzün, I. (2016). Phragmites australis: an alternative biosorbent for basic dye removal. Ecological Engineering, 86, 85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.10.024.
Kesraoui, A., Mabrouk, A., & Seffen, M. (2017). Valuation of biomaterial: Phragmites australis in the retention of metal-complexed dyes. American Journal of Environmental Sciences, 13(3), 266–276. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajessp.2017.266.276.
Kesraoui, A., Moussa, A., Ali, G. B., & Seffen, M. (2015). Biosorption of alpacide blue from aqueous solution by lignocellulosic biomass: Luffa cylindrica fibers. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(16), 15832–15840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5262-4.
Kesraoui, A., Selmi, T., Seffen, M., & Brouers, F. (2016). Influence of alternating current on the adsorption of indigo carmine. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(11), 9940–9950. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7201-4.
Kristanti, R. A., & Hadibarata, T. (2016). Treatability of methylene blue solution by adsorption process using Neobalanocarpus hepmii and Capsicum annuum. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 227, 134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2834-y.
Lagergren, S. K. (1898). About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens Handlingar, 24, 1–39.
Lakshmi, U. R., Srivastava, V. C., Mall, I. D., & Lataye, D. H. (2009). Rice husk ash as an effective adsorbent: evaluation of adsorptive characteristics for indigo carmine dye. Journal of Environmental Management, 90, 710–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.01.002.
Langmuir, I. (1918). The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Journal of American Chemical Society, 38, 2221–2295.
Manna, S., Roy, D., Saha, P., Gopakumar, D., & Thomas, S. (2017). Rapid methylene blue adsorption using modified lignocellulosic materials. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 107, 346–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.03.008.
Marrakchi, Z., Khiari, R., Oueslati, H., Mauret, E., & Mhenni, F. (2011). Pulping and papermaking properties of Tunisian alfa stems ( Stipa tenacissima )—effects of refining process. Industrial Crops and Products, 34, 1572–1582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2011.05.022.
Mendoza-Castillo, D. I., Villalobos-Ortega, N., Bonilla-Petriciolet, A., & Tapia-Picazo, J. C. (2015). Neural network modeling of heavy metal sorption on lignocellulosic biomasses: effect of metallic ion properties and sorbent characteristics. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 54(1), 443–453. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie503619j.
Miraboutalebi, S. M., Nikouzad, S. K., Peydayesh, M., Allahgholi, N., Vafajoo, L., & McKay, G. (2017). Methylene blue adsorption via maize silk powder: kinetic, equilibrium, thermodynamic studies and residual error analysis. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 106, 191–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.01.010.
Miretzky, P., & Cirelli, A. F. (2010). Cr ( VI ) and Cr ( III ) removal from aqueous solution by raw and modified lignocellulosic materials: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 180, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.04.060.
Mitrogiannis, D., Markou, G., Çelekli, A., & Bozkurt, H. (2015). Biosorption of methylene blue onto Arthrospira platensis biomass: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 3, 670–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.02.008.
Moyo, M., Chikazaza, L., Nyamunda, B. C., & Guyo, U. (2013). Adsorption batch studies on the removal of Pb (II) using maize tassel based activated carbon. Journal of Chemistry, 2013, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/508934.
Nayak, A. K., & Pal, A. (2017). Green and efficient biosorptive removal of methylene blue by Abelmoschus esculentus seed: process optimization and multi-variate modeling. Journal of Environmental Management, 200, 145–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.05.045.
Panday, K. K., Prasad, G., & Singh, V. N. (1985). Copper (ii) removal from aqueous solutions by fly ash. Water Research, 19(7), 869–873.
Petrović, M., Šoštarić, T., Stojanović, M., Milojković, J., Mihajlović, M., Stanojević, M., & Stanković, S. (2015). Removal of Pb2+ ions by raw corn silk (Zea mays L.) as a novel biosorbent. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 0, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.06.025.
Ramzi, K., Nizar, M., Farouk, M., Naceur, B. M., & Evelyne, M. (2011). Sodium carboxylmethylate cellulose from date palm rachis as a sizing agent for cotton yarn. Fibers and Polymers, 12(5), 587–593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-011-0587-1.
Rehman, R., Javaria, Z., & Nisar, H. (2014). Adsorption studies of removal of indigo caramine dye from water by formaldehyde and urea treated cellulosic waste of citrus reticulata peels. Asian Journal Chemistry, 26(1), 43–47.
Reza, R. A., & Ahmaruzzaman, M. (2015). Comparative study of waste derived adsorbents for sequestering methylene blue from aquatic environment. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 3, 395–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2014.06.006.
Rodrigues, A. C. D., do Amaral Sobrinho, N. M. B., dos Santos, F. S., dos Santos, A. M., Pereira, A. C. C., & Lima, E. S. A. (2017). Biosorption of toxic metals by water lettuce (Pistia stratiotes) biomass. Water Air, and Soil Pollution, 228, 156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3340-6.
Sakr, F., Sennaoui, A., Elouardi, M., Tamimi, M., & Assabbane, A. (2015). Étude de l ’ adsorption du Bleu de Méthylène sur un biomatériau à base de Cactus (adsorption study of Methylene Blue on biomaterial using cactus ). Journal of materials and Environmental Science, 6(2), 397–406.
Salazar-Rabago, J. J., Leyva-Ramos, R., Rivera-Utrilla, J., Ocampo-Perez, R., & Cerino-Cordova, F. J. (2017). Biosorption mechanism of methylene blue from aqueous solution onto white pine (Pinus durangensis) sawdust: effect of operating conditions. Sustainable Environment Research, 27, 32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.serj.2016.11.009.
Santoni, I., Callone, E., Sandak, A., Sandak, J., & Dirè, S. (2015). Solid state NMR and IR characterization of wood polymer structure in relation to tree provenance. Carbohydrate Polymers, 117, 710–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.10.057.
Temkin, M. (1941). Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics of process on non-homogeneous surfaces and in the interaction between adsorbed molecules. Journal of Physical Chemical, 15, 296–233.
Tichaona, N., & Olindah, H. (2013). Equilibrium isotherm analysis of the biosorption of Zn2+ ions by acid treated Zea mays leaf powder. International Journal of Advances in Engineering & Technology, 6(1), 128–139.
Tran, H. N., You, S. J., & Chao, H. P. (2017). Insight into adsorption mechanism of cationic dye onto agricultural wastes. Journal of Chemical Engineering communications, 204(9), 1020–1036. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-017-0056-7.
Vafakhah, S., Bahrololoom, M. E., & Saeedikhani, M. (2016). Adsorption kinetics of cupric ions on mixture of modified corn stalk and modified tomato waste. Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 8, 1238–1250. https://doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2016.813095.
Zhang, S., Wang, Z., Zhang, Y., Pan, H., & Tao, L. (2016). Adsorption of methylene blue on organosolv lignin from rice straw. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 31, 3–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2016.02.001.
Funding
The authors express their sincere gratitude to the Laboratory of Energy and Materials (High School of Sciences and Technology of Hammam Sousse) for the financial support of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. SI
(DOCX 27 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mbarki, F., Kesraoui, A., Seffen, M. et al. Kinetic, Thermodynamic, and Adsorption Behavior of Cationic and Anionic Dyes onto Corn Stigmata: Nonlinear and Stochastic Analyses. Water Air Soil Pollut 229, 95 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3749-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3749-6