Abstract
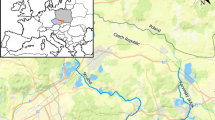
Pollution by heavy metals (Co, Cu, Ni, Pb, Sb and Zn), 226Ra and U was studied in eight profiles (1.0–1.8 m deep) in the floodplain sediments of the Ploučnice River, the Czech Republic. The element concentrations were processed by establishing local geochemical background functions from non-polluted overbank fines yet not affected by reductimorphic processes and a subsequent calculation of enrichment factors in the polluted strata. In the case of Cu and Ni, the geogenic variability of the watershed (Cretaceous marine sediments and Cenozoic volcanics and their weathering products) was successfully handled using different background functions in two parts of the studied area, which allowed us to decipher the anthropogenic and natural portions of the heavy metals and hence evaluate the history of pollution. The upper course of the river drains an extensive area of so-called chemical mining (underground acid leaching of low-grade U-bearing sediments) and hydrometallurgical processing in Stráž pod Ralskem that started in the late 1960s and operated without waste-processing plants up to 1989. The river system has consequently been impacted by U and gamma-emitting 226Ra and obviously also by divalent heavy metals (Co, Ni, Zn). In the entire study area, that pollution was preceded by increasing levels of Cu, Pb and Sb and by the 206Pb/207Pb ratio decreasing from 1.20 towards 1.17, which had started earlier in the twentieth century before the U mining. That pre-mining pollution can be attributed to diffuse anthropogenic activities of regional or continental importance. The most recent 206Pb/207Pb ratio in the Ploučnice alluvium coincides with that of peatbog profiles on the borders of the Czech Republic, showing the usefulness of floodplains as pollution archives of widespread regional to continental pollution signals.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bølviken, B., Bogen, J., Jartun, M., Langedal, M., Ottesen, R. T., & Volden, T. (2004). Overbank sediments: a natural bed blending sampling medium for large-scale geochemical mapping. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 74(1), 183–199.
Ciszewski, D. (2003). Heavy metals in vertical profiles of the middle Odra River overbank sediments: Evidence for pollution changes. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 143(1–4), 81–98.
Ciszewski, D., Czajka, A., & Blazej, S. (2008). Rapid migration of heavy metals and 137Cs in alluvial sediments, Upper Odra River valley, Poland. Environmental Geology, 55(7), 1577–1586.
Ciszewski, D., & Turner, J. (2009). Storage of sediment-associated heavy metals along the channelized Odra River, Poland. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 34(4), 558–572.
Covelli, S., & Fontolan, G. (1997). Application of a normalization procedure in determining regional geochemical baselines. Environmental Geology, 30(1–2), 34–45.
Datel, J.V., & Ekert, V. (2008). Environmental impact of mine water from chemical extraction and underground uranium mining—Straz pod Ralskem, Czech Republic. In: Rapantova, N., Hrkal, Z. (Editors), Mine Water and the Environment, Proceedings, pp. 197–200.
Ettler, V., Mihaljevič, M., Šebek, O., Molek, M., Grygar, T., & Zeman, J. (2006). Geochemical and Pb isotopic evidence for sources and dispersal of metal contamination in stream sediments from the mining and smelting district of Příbram, Czech Republic. Environmental Pollution, 142(3), 409–417.
Faměra, M., Bábek, O., Matys Grygar, T., & Nováková, T. (2013). Distribution of heavy-metal contamination in regulated river-channel deposits: A magnetic susceptibility and grain-size approach; River Morava, Czech Republic. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 224(5), 1525.
Frostick, A., Bollhofer, A., & Parry, D. (2011). A study of radionuclides, metals and stable lead isotope ratios in sediments and soils in the vicinity of natural U-mineralisation areas in the Northern Territory. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 102(10), 911–918.
Grosbois, C., Meybeck, M., Lestel, L., Lefevre, I., & Moatar, F. (2012). Severe and contrasted polymetallic contamination patterns (1900–2009) in the Loire River sediments (France). Science of the Total Environment, 435, 290–305.
Grygar, T., Kadlec, J., Žigová, A., Mihaljevič, M., Nekutová, T., Lojka, R., & Světlík, I. (2009). Chemostratigraphic correlation of sediments containing expandable clay minerals based on ion exchange with Cu(II) triethylenetetramine. Clays and Clay Minerals, 57(2), 168–182.
Grygar, T., Světlík, I., Lisá, L., Koptíková, L., Bajer, A., Wray, D. S., et al. (2010). Geochemical tools for the stratigraphic correlation of floodplain deposits of the Morava River in Straznicke Pomoravi, Czech Republic from the last millennium. Catena, 80(2), 106–121.
Hanslík, E. J., Mansfeld, A. M., & Šimonek, P. J. (1995). Impact of the Straz uranium mine (northern Bohemia) on the river Ploucnice (pp. 604–605). Vienna: In International Atomic Energy Agency (group author), Environmental Impact of Radioactive Releases IAEA.
Hanslík, E., Mansfeld, A., Justýn, J., Moucha, V., & Šimonek, P. (2002). Vliv těžby uranových rud na vývoj kontaminace hydrosféry Ploučnice v období 1966–2000 (Influence of mining uranium ores on the development of contamination of the Ploučnice hydrosphere in period 1966–2000) (Internal report, in Czech). Praha: Výzkumný ústav vodohospodářský T.G. Masaryka.
Hanslík, E., Kalinová, E., Brtvová, M., Ivanovova, D., Sedlářová, B., Svobodová, J., et al. (2005). Radium isotopes in river sediments of Czech Republic. Limnologica, 35(3), 177–184.
Hanslík E. (2010) Contamination of the Ploučnice watershed by radioactive materials from uranium mining and its change in 1992–2009 (pp. 91–104). In Hanslík, E. (Ed), Proceedings of the XXI. Conference Radionuclides and Ionizing Radiation in Water Management. Česká vědeckotechnická vodohospodářská společnost: České Budějovice.
Hrdoušek, F. (2005). Heavy metals in sediments of Panenský Creek and middle reach of Ploučnice. Diploma Thesis (in Czech). Prague: Faculty of Science, Charles University.
Kolář, J. (2004). Distribution of selected heavy metals in sediments of upper reach of Ploučnice. Diploma Thesis (in Czech). Prague: Faculty of Science, Charles University.
Komárek, M., Ettler, V., Chrastný, V., & Mihaljevič, M. (2008). Lead isotopes in environmental sciences: A review. Environment International, 34, 562–577.
Krüger, F., Schwartz, R., Kunert, M., & Friese, K. (2006). Methods to calculate sedimentation rates of floodplain soils in the middle region of the Elbe River. Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica, 34(3), 175–187.
Kühn, P. (1995). Measurements of the distribution of radioactive contamination in sediments of the Ploucnice River Valley (northern Bohemia): Basis for its rehabilitation (pp. 666–669). Vienna: In International Atomic Energy Agency (group author), Environmental Impact of Radioactive Releases IAEA.
Kühn, J. (1996). Distribution of uranium and selected heavy metals in the floodplain sediments of Ploučnice. PhD Thesis (in Czech). Prague: Faculty of Science, Charles University.
Kühn, P., Smetana, R., Šimák, J., Kratochvíl, L., & Proskočilová, Š. (1997). Solution of the problem of contamination of litoral zone of the Ploučnice. Final report. DIAMO, Stráž pod Ralskem, Czech Republic.
Macklin, M. G., Ridgway, J., Passmore, D. G., & Rumsby, B. T. (1994). The use of overbank sediment for geochemical mapping and contamination assessment—Results from selected English and Welsh floodplains. Applied Geochemistry, 9(6), 689–700.
Macklin, M. G., Brewer, P. A., Hudson-Edwards, K. A., Bird, G., Coulthard, T. J., Dennis, I. A., et al. (2006). A geomorphological approach to the management of rivers contaminated by metal mining. Geomorphology, 79(3–4), 423–447.
Matys Grygar, T., Nováková, T., Mihaljevič, M., Strnad, L., Světlík, I., Koptíková, L., et al. (2011). Surprisingly small increase of the sedimentation rate in the floodplain of Morava River in the Strážnice area, Czech Republic, in the last 1300 years. Catena, 86(3), 192–207.
Matys Grygar, T., Sedláček, J., Bábek, O., Nováková, T., Strnad, L., & Mihaljevič, M. (2012). Regional contamination of Moravia (South-Eastern Czech Republic): Temporal shift of Pb and Zn loading in fluvial sediments. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 223(2), 739–753.
Matys Grygar, T., Nováková, T., Bábek, O., Elznicová, J., & Vadinová, N. (2013). Robust assessment of moderate heavy metal contamination levels in floodplain sediments: A case study on the Jizera River, Czech Republic. Science of the Total Environment, 452–453, 233–245.
Matys Grygar, T., & Mach, K. (2013). Regional chemostratigraphic key horizons in the macrofossil-barren siliciclastic lower Miocene lacustrine sediments (Most Basin, Eger Graben, Czech Republic). Bulletin of Geosciences. doi:10.3140/bull.geosci.1372.
Meier, L. P., & Kahr, G. (1999). Determination of the cation exchange capacity (CEC) of clay minerals using the complexes of copper(II) ion with triethylenetetramine and tetraethylenepentamine. Clays and Clay Minerals, 47(3), 386–388.
Meybeck, M., Lestel, L., Bonte, P., Moilleron, R., Colin, J. L., Rousselot, O., et al. (2007). Historical perspective of heavy metals contamination (Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Pb, Zn) in the Seine River basin (France) following a DPSIR approach (1950–2005). Science of the Total Environment, 375(1–3), 204–231.
Middelkoop, H. (2000). Heavy-metal pollution of the river Rhine and Meuse floodplains in The Netherlands. Geologie en Mijnbouw-Netherlands Journal of Geosciences, 79(4), 411–427.
Mihaljevič, M., Ettler, V., Strnad, L., Šebek, O., Vonásek, F., Drahota, P., & Rohovec, J. (2009). Isotopic composition of lead in Czech coals. International Journal of Coal Geology, 78(1), 38–46.
Notebaert, B., Houbrechts, G., Verstraeten, G., Broothaerts, N., Haeckx, J., Reynders, M., et al. (2011). Fluvial architecture of Belgian river systems in contrasting environments: Implications for reconstructing the sedimentation history. Netherlands Journal of Geosciences-Geologie en Mijnbouw, 90(1), 31–50.
Novák, M., Emmanuel, S., Ville, M. A., Erel, Y., Veron, A., Pačes, T., et al. (2003). Origin of lead in eight Central European peat bogs determined from isotope ratios, strengths, and operation times of regional pollution sources. Environmental Science and Technology, 37(3), 437–445.
Nováková, T., Matys Grygar, T., Bábek, O., Faměra, M., Mihaljevič, M., & Strnad, L. (2013). Distinguishing regional and local sources of pollution by trace metals and magnetic particles in fluvial sediments of the Morava River, Czech Republic. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 13(2), 460–473.
Ottesen, R. T., Bogen, J., Bølviken, B., & Volden, T. (1989). Overbank sediment—A representative sample medium for regional geochemical mapping. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 32(1–3), 257–277.
Papastergios, G., Filippidis, A., Fernandez-Turiel, J. L., Gimeno, D., & Sikalidis, C. (2011). Surface soil geochemistry for environmental assessment in Kavala Area, Northern Greece. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 216(1–4), 141–152.
Reimann, C., & Garret, R. G. (2005). Geochemical background—Concept and reality. Science of the Total Environment, 350, 12–27.
Reimann, C., & de Caritat, P. (2005). Distinguishing between natural and anthropogenic sources for elements in the environment: Regional geochemical surveys versus enrichment factors. Science of the Total Environment, 337(1–3), 91–107.
Reimann, C., Flem, B., Arnoldussen, A., Englmaier, P., Finne, T. E., Koller, F., & Nordgulen, Ø. (2008). The biosphere: A homogeniser of Pb isotope signals. Applied Geochemistry, 23(4), 705–722.
Reimann, C., Flem, B., Fabian, K., Birke, M., Ladenberger, A., Negrel, P., et al. (2012). Lead and lead isotopes in agricultural soils of Europe—The continental perspective. Applied Geochemistry, 27(3), 532–542.
Shotyk W. (2008). Comment on “The biosphere: A homogeniser of Pb isotope signals” by C. Reimann, B. Flem, A. Arnoldusses, P. Englemeier, T.E. Fine, F. Koller and Ø. Nordgulen. Applied Geochemistry, 23(8), 2514–2518.
Škácha, P., Goliáš, V., Sejkora, J., Plášil, J., Strnad, L., Škoda, R., & Ježek, J. (2009). Hydrothermal uranium-polymetallic mineralization of the Jánská vein, Březové Hory, Příbram, Czech Republic: Lead isotopes and CHIME dating. Journal of Geosciences, 54(1), 1–13.
Steinnes, E. (2009). Comment on "Geochemical gradients in soil O-horizon samples from southern Norway: Natural or anthropogenic?" by C. Reimann, P. Englmaier, B. Flem, L. Gough, P. Lamothe, O. Nordgulen, and D. Smith. Applied Geochemistry, 24(10), 2019–2022.
Strnad, L., Mihaljevič, M., & Šebek, O. (2005). Laser ablation and solution ICP-MS determination of REE in USGS BIR-1G, BHVO-2G and BCR-2G glass reference materials. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 29(3), 303–314.
Swennen, R., & van der Sluys, J. (1998). Zn, Pb, Cu and As distribution patterns in overbank and medium order stream sediment samples: Their use in exploration and environmental geochemistry. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 65(1), 27–45.
Ulrych, J., Dostál, J., Hegner, E., Balogh, K., & Ackerman, L. (2008). Late Cretaceous to Paleocene melilitic rocks of the Ohře/Eger Rift in northern Bohemia, Czech Republic: Insights into the initial stages of continental rifting. Lithos, 101(1–2), 141–161.
Vijver, M. G., Spijker, J., Vink, J. P. M., & Posthuma, L. (2008). Determining metal origins and availability in fluvial deposits by analysis of geochemical baselines and solid-solution partitioning measurements and modelling. Environmental Pollution, 156(3), 832–839.
Xia, P., Meng, X.-W., Feng, A.-P., Yin, P., Wang, X.-Q., & Zhang, J. (2012). 210Pb chronology and trace metal geochemistry in the intertidal sediment of Qinjiang River estuary, China. Journal of Ocean University of China, 11(2), 165–173.
Yesilonis, I. D., Pouyat, R. V., & Neerchal, N. K. (2008). Spatial distribution of metals in soils in Baltimore, Maryland: Role of native parent material, proximity to major roads, housing age and screening guidelines. Environmental Pollution, 156(3), 723–731.
Varga, Z., Wallenius, M., Mayer, K., Keegan, E., & Millett, S. (2009). Application of lead and strontium isotope ratio measurements for the origin assessment of uranium ore concentrates. Analytical Chemistry, 81(20), 8327–8334.
Zachmann, D. W., van der Veen, A., & Friese, K. (2013). Floodplain lakes as an archive for the metal pollution in the River Elbe (Germany) during the 20th century Original Research Article. Applied Geochemistry, 35, 14–27.
Zuna, M., Mihaljevič, M., Šebek, O., Ettler, V., Handley, M., Navrátil, T., & Goliáš, V. (2011). Recent lead deposition trends in the Czech Republic as recorded by peat bogs and tree rings. Atmospheric Environment, 45(28), 4950–4958.
Acknowledgment
Laboratory sample processing and analyses were mostly performed by P. Vorm, R. Barochová and Z. Hájková (IIC Řež). T. Nováková (IIC Řež) helped with data processing and graphical presentation. Institutional funding in IIC (RVO 61388980) was essential for this work. The geoinformatic work, ICP and radiochemical analyses were funded by OPVK project ENVIMOD (CZ.1.07/2.2.00/28.0205).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Majerová, L., Matys Grygar, T., Elznicová, J. et al. The Differentiation between Point and Diffuse Industrial Pollution of the Floodplain of the Ploučnice River, Czech Republic. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1688 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1688-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1688-9