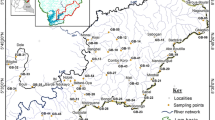
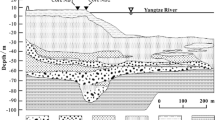
Abstract
Anthropogenic contamination by heavy metals in fluvial systems is mostly bound to fine-grained clay minerals and organic substances, which accumulate by vertical accretion in sediment traps along river courses (oxbow lakes, dams and floodplains). These environmental settings are considered as good archives of historical changes in contamination. Much less attention, however, is paid to deposits of river channels, which act as sourcing transport paths for these archives and/or build archives of their own. In order to provide a better insight into the spatio-temporal distribution of pollutants in channel deposits, we investigated contamination levels of Cu, Pb and Zn in a series of sediment cores along the River Morava, a left-hand tributary of the Danube River, Czech Republic. In particular, the relationships between metal concentrations, sediment lithology (facies), grain size, magnetic susceptibility and mineralogy and chemistry of fly-ash particles were investigated. Element chemistry and lithology of channel deposits were compared with those of the nearby floodplain deposits in the same catchment. Four river-channel facies were defined, ranging from sandy gravels to clayey silts, and confronted with the floodplain sediments. Al/Si ratios were found to be useful proxies of grain size, and Al was utilized as an excellent normalizing element for heavy metals, which filters out much of the grain size effects on contamination. The floodplain deposits are significantly less contaminated than their river-channel counterparts. Heavy-metal contamination of river bed sediments (expressed as enrichment factors, EFs) is not simply bound to fine-grained particles, and much of the contamination was found in coarse-grained, sandy facies. Elevated EFs of Zn, Cu and Pb in several sediment layers, which show high magnetic susceptibility (MS), high values of MS normalized to Fe and a high proportion of magnetic fly-ash spherules and their chemistry suggest that significant part of the heavy-metal contamination can be carried by magnetic fly-ash spherules. A part of this contamination is bound to coarse-grained fluvial facies, indicating that the magnetic spherules can be transported as bed load sediments. Magnetic pollution and heavy-metal pollution can therefore coincide in river bed deposits. It is suggested that most of this contamination can be related to local point sources of pollutants (fly-ash deposit spills).










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashley, G. M. (1990). Classification of large-scale subaqueous bedforms: a new look at an old problem. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 60(1), 160–172.
Bábek, O., Hilscherová, K., Nehyba, S., Zeman, J., Faměra, M., Franců, J., et al. (2008). Contamination history of river sediments accumulated in an oxbow lake over the last 25 years; Morava River (Danube Catchment Area), Czech Republic. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 8, 165–176.
Bábek, O., Faměra, M., Hilscherová, K., Kalvoda, J., Dobrovolný, P., Sedláček, J., et al. (2011). Geochemical traces of flood layers in the fluvial sedimentary archive; implications for contamination history analyses. Catena, 87, 281–290.
Birch, G., Siaka, M., & Owens, C. (2001). The source of anthropogenic heavy metals in fluvial sediments of a rural catchments: Coxs river, Australia. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 126, 13–35.
Bridge, J. S. (1993). Description and interpretation of fluvial deposits: a critical perspective. Sedimentology, 40, 801–810.
Bridge, J. S. (2003). Rivers and floodplains. Forms, processes, and sedimentary record (p 504). Oxford, UK: Blackwell Science Ltd.
Chamley, H. (1990). Sedimentology. Heidelberg: Springer.
Comans, R. N. J., Middelburg, J. J., Zonderhuis, J., Woittiez, J. R. W., De Lange, G. J., Das, H. A., et al. (1989). Mobilization of radiocaesium in pore water of lake sediments. Nature, 339, 367–369.
Davidson, W., Hilton, J., Hamilton-Taylor, J., Kelly, M., Livens, F., Rigg, E., et al. (1993). The transport of Chernobyl-derived radiocaesium through two freshwater lakes in Cumbria, UK. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 19(2), 125–153.
Ďurža, O. (1999). Heavy metals contamination and magnetic susceptibility in soils around metallurgical plant. Physics Chemistry Earth (A), 24(6), 541–543.
Faměra, M., Bábek, O., & Hernández, P. R. (2008). Mapping river bed morphology of River Morava at the locality Kvasice and Bělov (in Czech). Geol. Výzk. Mor. Slez. v R., 2007(15), 16–18.
Farmer, J. G., Mackenzie, A. B., Sugden, C. L., Edgar, P. J., & Eades, L. J. (1997). A comparison of the historical lead pollution records in peat and freshwater lake sediments from central Scotland. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 100, 253–270.
Fialová, H., Maier, G., Petrovský, E., Kapička, A., Boyko, T., & Scholger, R. (2006). Magnetic properties of soils from sites with different geological and environmental settings. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 59, 273–283.
Förstner, U. (2004). Sediment dynamics and pollutant mobility in rivers—an interdisciplinary approach. Lakes and Reservoirs, Research and Management, 9, 25–40.
Forstner, U., & Wittmann, G. T. W. (1981). Metal pollution in the aquatic environment. New York: Springer.
Gautam, P., Blaha, U., & Appel, E. (2005). Magnetic susceptibility of dust-loaded leaves as a proxy of traffic-related heavy metal pollution in Kathmandu city, Nepal. Atmospheric Environment, 39(12), 2201–2211.
Goddu, S. R., Appel, E., Jordanova, D., & Wehland, F. (2004). Magnetic properties of road dust from Visakhapatnam India)—relationship to industrial pollution and road traffic. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 29(13–14), 985–995.
Grygar, T., Kadlec, J., Žigová, A., Mihaljevič, M., Nekutová, T., Lojka, R., et al. (2009). Chemostratigraphic correlation of sediments containing expandable clay minerals based on ion exchange with Cu(II) triethylenetetramine. Clays and Clay Minerals, 57, 168–182.
Grygar, T., Světlík, I., Lisá, L., Koptíková, L., Bajer, A., Wray, D. S., et al. (2010). Geochemical tools for the stratigraphic correlation of floodplain deposits of the Morava River in Strážnické Pomoraví, Czech Republic from the last millennium. Catena, 80, 106–121.
Haque, M. M., Ghose, S., & Islam, S. M. A. (2011). A laboratory based study on the movement of radiocaesium in some soil columns by gamma spectrometer. Journal of Bangladesh Academy of Sciences, 35(2), 141–151.
Havlícek, P. (1994). The Morava River basin—its development during the last 15,000 years. Aardkundige Mededelingen, 6, 129–135.
Halfar, J., Walter, R., & Walther, H. (1998). Facies architecture and sedimentology of a meandering fluvial system: a Palaeogene example from the Weisselster Basin, Germany. Sedimentology, 45, 1–17.
Heller, P. L., & Paola, C. (1996). Downstream changes in alluvial architecture: an exploration of controls on channel-stacking patterns. Journal of Sedimentary Research, B66(2), 297–306.
Herr, C., & Gray, N. F. (1996). Seasonal variation of metal contamination of riverine sediments below a copper and sulphur mine in south-east Ireland. Water Science and Technology, 33, 255–261.
Hesselink, A. W., Weerts, H. J. T., & Berendsen, H. J. A. (2003). Alluvial architecture of the human-influenced river Rhine, The Netherlands. Sedimentary Geology, 161, 229–248.
Hilscherová, K., Dusek, L., Kubik, V., Cupr, P., Hofman, J., Klanova, J., et al. (2007). Redistribution of organic pollutants in river sediments and alluvial soils related to major floods. Journal Soils Sediments, 7, 167–177.
Hoffmann, T., Erkens, G., Gerlach, R., Klostermann, J., & Lang, A. (2009). Trends and controls of Holocene floodplain sedimentation in the Rhine catchment. Catena, 77, 96–106.
Horowitz, A. J., Elrick, K. A., Demas, C. R., & Demcheck, D. K. (1991). The use of sediment-trace element geochemical models for the identification of local fluvial baseline concentrations. Sediment-Trace Element Geochemical Models. In N. E. Peters & D. E. Walling (Eds.), Sediment and stream water quality in a changing environment: trends and explanation (p. 307). Vienna: IAHS.
Houben, P. (2007). Geomorphological facies reconstruction of Late Quaternary alluvia by the application of fluvial architecture concepts. Geomorphology, 86, 94–114.
Jordanova, D., Jordanova, N., & Hoffmann, V. (2006). Magnetic mineralogy and grain-size dependence of hysteresis parameters of single spherules from industrial waste products. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 154, 255–265.
Kapička, A., Jordanova, N., Petrovský, E., & Ustjak, S. (2000). Magnetic stability of power-plant ash in different soil solutions. Physics Chemistry Earth (A), 25(5), 431–436.
Knab, M., Hoffmann, V., Petrovský, E., Kapička, A., Jordanova, N., & Appel, E. (2006). Surveying the anthropogenic impact of the Moldau river sediments and nearby soils using magnetic susceptibility. Environmental Geology. doi:10.1007/s00254-005-0080-5.
Lecoanet, H., Le’veque, F., & Ambrosi, J. P. (2003). Combination of magnetic parameters: an efficient way to discriminate soil-contamination sources (south France). Environmental Pollution, 122, 229–234.
Liu, W. X., Li, X. D., Shen, Z. G., Wang, D. C., Wai, O. W. H., & Li, Y. S. (2003). Multivariate statistical study of heavy metal enrichment in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary. Environmental Pollution, 121, 377–388.
Loizeau, J. L., Jüstrich, S., & Wildi, W. (2010). Swiss examples of the impacts of dams on natural environments and management strategies for sediment control. NEAR Curriculum in Natural Environmental Science. Terre et Environnement, 88, 199–204.
MacKenzie, A. B., Cook, G. T., & McDonald, P. (1999). Radionuclide distributions and particle size associations in Irish Sea surface sediments: implications for actinide dispersion. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 44, 275–296.
Madej, M. A., Sutherland, D. G., Lisle, T. E., & Pryor, B. (2009). Channel responses to varying sediment input: a flume experiment modeled after Redwood Creek, California. Geomorphology, 103, 507–519.
Magiera, T., Strzyszcz, Z., Kapicka, A., & Petrovsky, E. (2006). Discrimination of lithogenic and anthropogenic influences on topsoil magnetic susceptibility in Central Europe. Geoderma, 130, 299–311.
Magiera, T., Kapicka, A., Petrovsky, E., Strzyszcz, Z., Fialová, H., & Rachwał, M. (2008). Magnetic anomalies of forest soils in the Upper Silesia-Northern Moravia region. Environmental Pollution, 156, 618–627.
Morton-Bermea, O., Hernandez, E., Martinez-Pichardo, E., Soler-Arechalde, A. M., Lozano Santa-Cruz, R., Gonzales-Hernandez, G., et al. (2009). Mexico City topsoils: heavy metals vs magnetic susceptibility. Geoderma, 151, 121–125.
Matys Grygar, T., Sedláček, J., Bábek, O., Nováková, T., Strnad, T., & Mihaljevič, M. (2012). Regional contamination of Moravia (South-Eastern Czech Republic): Temporal shift of Pb and Zn loading in fluvial sediments. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution. doi:10.1007/s11270-011-0898-2.
Miall, A. D. (2006). The geology of fluvial deposits. Sedimentary facies, basin analysis, and petroleum geology. Berlin: Springer.
Middelkoop, H. (2000). Heavy-metal pollution of the river Rhine and Meuse floodplains in The Netherlands. Geologie en Mijnbouw-Netherlands Journal of Geosciences, 79, 411–427.
Monna, F., van Oort, F., Hubert, P., Dominik, J., Bolte, J., Loizeau, J. L., et al. (2009). Modeling of 137Cs migration in soils using an 80-year soil archive: role of fertilizers and agricultural amendments. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 100, 9–16.
Nguyen, H. L., Braun, M., Szaloki, I., Baeyens, W., Van Grieken, R., & Leermakers, M. (2009). Tracing the metal pollution history of the Tisza River through the analysis of a sediment depth profile. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 200, 119–132.
Nováková, T., Matys Grygar, T., Bábek, O., Faměra, M., Mihaljevič, M., Strnad, L. (2012). Fluvial sediments of the Morava River, Czech Republic: distinguishing regional and local sources of pollution by heavy metals and magnetic particles. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 13, 460–473.
Orescanin, V., Lulic, S., Pavlovic, G., & Mikelic, L. (2004). Granulometric and chemical composition of the Sava river sediments upstream and downstream of the Krsko nuclear power plant. Environmental Geology, 46, 605–613.
Petrovský, E., Kapička, A., Zapletal, K., Šebestová, E., Spanilá, T., Dekkers, M. J., et al. (1998). Correlation between magnetic parameters and chemical composition of lake sediments from northern Bohemia—preliminary study. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 23(9–10), 1123–1126.
Putyrskaya, V., & Klemt, E. (2007). Modeling 137Cs migration processes in lake sediments. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 96, 54–62.
Putyrskaya, V., Klemt, E., & Röllin, S. (2009). Migration of 137Cs in tributaries, lake water and sediment of lago Maggiore (Italy, Switzerland)—analysis and comparison with Lago di Lugano and other lakes. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 100, 35–48.
Reneau, S. L., Drakos, P. G., Katzman, D., Malmon, D. V., McDonald, E. V., & Ryti, R. T. (2004). Geomorphic controls on contaminant distribution along an ephemeral stream. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 29, 1209–1223.
Ridgway, J., Flight, D. M. A., Martiny, B., Gomezcaballero, A., Maciasromo, C., & Greally, K. (1995). Overbank sediments from central Mexico—an evaluation of their use in regional geochemical mapping and in studies of contamination from modern and historical mining. Applied Geochemistry, 10, 97–109.
Ritchie, J. C., & McHenry, J. R. (1990). Application of radioactive fallout cesium-137 for measuring soil erosion and sediment accumulation rates and patterns: a review. Journal Environmental Quality, 19, 215–233.
Rubio, B., Nombela, M. A., & Vilas, F. (2000). Geochemistry of major and trace elements in sediments of the Ria de Vigo (NW Spain): an assessment of metal pollution. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40(11), 698–980.
Sageman, B. B., & Lyons, T. W. (2005). Geochemistry of fine-grained sediments and sedimentary rocks. In F. T. Mackenzie (Ed.), Sediments, diagenesis, and sedimentary rocks (pp. 115–158). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Strebl, F., Gerzabeka, M. H., Kargb, V., & Tataruch, F. (1996). 137Cs-migration in soils and its transfer to roe deer in an Austrian forest stand. The Science of the Total Environment, 181, 237–247.
Strzyszcz, Z. (1993). Magnetic susceptibility of soils in the areas influenced by industrial emissions. In R. Schulin, A. Desaules, R. Webster, B. von Steiger (Eds.), Soil monitoring: early detection and surveying of soil contamination and degradation (pp. 255–269). Birkhäuser: Basel.
Strzyszcz, Z., & Magiera, T. (1998). Magnetic susceptibility and heavy metals contamination in soils of Southern Poland. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 23(9–10), 1127–1131.
Tobin, G. A., Brinkmann, R., & Montz, B. E. (2000). Flooding and the distribution of selected metals in floodplain sediments in St. Maries, Idaho. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 22, 219–232.
Tornqvist, T. E., Vaan Ree, M. H. M., & Faessen, E. (1993). Longitudinal facies architectural changes of Middle Holocene anastomosing distributary systems (Rhine-Meuse delta, Central Netherlands). Sedimentary Geology, 85, 203–219.
Van der Perk, M., Jetten, V. G., Karssenberg, D., He, Q., Walling, D. E., Laptev, G. V., et al. (2000). Assessment of spatial redistribution of Chernobyl-derived radiocaesium within catchments using GIS-embedded models. In M. Stone (Ed.), The role of erosion and sediment transport in nutrient and contaminant transfer (pp. 277–284). Waterloo: IAHS.
Ver Straeten, C. A., Brett, C. E., & Sageman, B. B. (2011). Mudrock sequence stratigraphy: a multi-proxy (sedimentological, paleobiological and geochemical) approach, Devonian Appalachian Basin. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 304, 54–73.
Viers, J., Dupré, B., & Gaillardet, J. (2009). Chemical composition of suspended sediments in world rivers: new insights from a new database. The Science of the Total Environment, 407, 853–868.
Vijver, M. G., Spijker, J., Vink, J. P. M., & Posthuma, l. (2008). Determining metal origins and availability in fluvial deposits by analysis of geochemical baselines and solid–solution partitioning measurements and modelling. Environmental Pollution, 156(3), 832–839.
Walling, D. E. (1983). The sediment delivery problem. Journal of Hydrology, 65, 209–237.
Walling, D. E., & He, Q. (1997). Use of fallout 137Cs in investigation of overbank sediment deposition on river floodplains. Catena, 29, 263–282.
Wildi, W., Dominik, J., Loizeau, J. L., Thomas, R. L., Favarger, P. Y., Haller, L., et al. (2004). River, reservoir and lake sediment contamination by heavy metals downstream from urban areas of Switzerland. Lakes and Reservoirs, Research and Management, 9, 75–87.
Yang, T., Liu, Q. S., Zeng, Q. L., & Chan, L. S. (2009). Environmental magnetic responses of urbanization processes: evidence from lake sediments in East Lake, Wuhan, China. Geophysical Journal International, 179(2), 873–886.
Zhang, C. X., Huang, B. C., Li, Z. Y., & Liu, H. (2006). Magnetic properties of highroad-side pine tree leaves in Beijing and their environmental significance. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 51(24), 3041–3052.
Zhang, C. X., Qiao, Q., Appel, E., & Huang, B. (2012). Discriminating sources of anthropogenic heavy metals in urban street dusts using magnetic and chemical methods. Journal Geochemical Exploration, 119–120, 60–75.
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by the projects P210/12/0573 (GA ČR), GA UK 462 10, IAAX00130801 (Grant Agency of AS CR), and RVO 61388980. Our special thanks belongs to Jana Dörflová, Zuzana Hájková and Petr Vorm (Institute of Inorganic Chemistry AS CR, Řež) for their laboratory samples processing, and to Zdeněk Dolníček, Jan Hladík, Tomáš Urubek (Department of Geology, Palacký University of Olomouc) for their assistance in the field.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Famera, M., Babek, O., Matys Grygar, T. et al. Distribution of Heavy-Metal Contamination in Regulated River-Channel Deposits: a Magnetic Susceptibility and Grain-Size Approach; River Morava, Czech Republic. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1525 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1525-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1525-1