Abstract
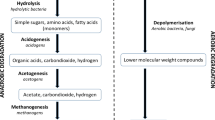
Data on the influence of substrate composition on the anaerobic degradation of peptone in a bench-scale packed-bed reactor are presented and discussed. The experiments were conducted in a horizontal-flow anaerobic immobilised biomass reactor operated with a hydraulic detention time of 4 h. Peptone was the sole carbon source in the first experiment (E1). In the second experiment (E2), the reactor was fed with peptone and carbohydrates, and in the third experiment (E3), lipids were also added. At end of each experiment, the samples were collected to obtain spatial profiles of the substrates and intermediary metabolites. A modified first-order kinetic expression fits well with the chemical oxygen demand data, allowing kinetic parameter inference in both E1 and E2. The presence of lipids in the E3 influent clearly disturbed the equilibrium of the process, which could be better represented by two first-order kinetic expressions in series. A kinetic model of irreversible first-order reactions (in series and in parallel) with two intermediate products was proposed for representing the entire process. Several modifications of the metabolic routes were clearly represented by the values of the model parameters. It was also possible to conclude that the adsorption of lipids in the fixed bed caused a decrease in the consumption rate of proteins and acetate. Microscopy examinations and fluorescence in situ hybridisation analyses corroborated the conclusions from the kinetic study. The frequencies of the microorganisms changed as the substrate composition was modified, indicating the capability of the microorganisms to adapt.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amann, R. I., Binder, B. G., Olson, R. J., Chrisholm, S. W., Devereux, R., & Stahl, D. A. (1990). Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analysing mixed microbial populations. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 56(6), 1919–1925.
APHA. (1988). Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington: American Public Health Association.
Batstone, D. J., Keller, J., Angelidaki, R. I., Kalyuzhnyi, S. V., Pavlostathis, S. G., Rozzi, A., et al. (2002). Anaerobic digestion model no. 1. STR no. 13. London: IWA.
Borja, R., Martín, A., Sánchez, E., Rincón, B., & Raposo, F. (2005). Kinetic modelling of the hydrolysis, acidogenic and methanogenic steps in the anaerobic digestion of two-phase olive pomace (TPOP). Process Biochemistry, 40(5), 1841–1847.
Breure, A. M., Mooijman, K. A., & van Andel, J. G. (1986). Protein degradation in anaerobic digestion: influence of volatile fatty acids and carbohydrates on hydrolysis and acidogenic fermentation of gelatin. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 24(5), 426–431.
Cattony, E. B. M., Chinalia, F. A., Riberio, R., Zaiat, M., Foresti, E., & Varesche, M. B. A. (2005). Ethanol and toluene removal in a horizontal-flow anaerobic immobilized biomass reactor in the presence of sulfate. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 92(2), 44–53.
Cubas, S. A., Foresti, E., Rodrigues, J. A. D., Ratusznei, S. M., & Zaiat, M. (2004). Influence of liquid-phase mass transfer on the performance of a stirred anaerobic sequencing batch reactor containing immobilized biomass. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 17(2), 99–105.
Damianovic, M. H. R. Z., Moraes, E. M., Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (2009). Pentachlorophenol (PCP) dechlorination in horizontal-flow anaerobic immobilized biomass (HAIB) reactors. Bioresource Technology, 100(19), 4361–4367.
de Nardi, I. R., Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (1999). Influence of the tracer characteristics on hydrodynamic models of packed-bed bioreactors. Bioprocess Engineering, 21(5), 469–476.
de Nardi, I. R., Varesche, M. B. A., Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (2002). Anaerobic degradation of BTEX in a packed-bed reactor. Water Science and Technology, 45(10), 175–180.
de Nardi, I. R., Ribeiro, R., Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (2005). Anaerobic packed-bed reactor for bioremediation of gasoline-contaminated aquifers. Process Biochemistry, 40(2), 587–592.
Domingues, M. R., Moraes, E. M., Vazoller, R. F., & Varesche, M. B. A. (2006). Analysis of microbial community in biofilms and planktonic cells of anaerobic thermophilic reactors. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology, 49(SI), 1–9.
Dubois, M., Guilles, K. A., Hamilton, J. K., Rebers, P. A., & Smith, F. (1956). Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Analytical Chemistry, 28(3), 350–356.
Foresti, E., Zaiat, M., Cabral, A. K. A., & Del Nery, V. (1995). Horizontal-flow anaerobic immobilized sludge (HAIS) reactor for paper industry wastewater treatment. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 12, 235–239.
Lalman, J. A., & Bagley, M. (2000). Anaerobic degradation and inhibitory effects on linoleic acid. Water Research, 34(17), 4220–4228.
Leite, J. A. C., Fernandes, B. S., Pozzi, E., Barboza, M., & Zaiat, M. (2008). Application of an anaerobic packed-bed bioreactor for the production of hydrogen and organic acids. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 33(2), 579–586.
Lens, P. N., Dijkema, C., & Stams, A. J. (1998). 13C-NMR study of propionate metabolism by sludges from bioreactors treating sulfate and sulfide rich wastewater. Biodegradation, 9(3/4), 179–186.
Lima, C. A. A., Ribeiro, R., Foresti, E., & Zaiat, M. (2005). Morphological study of biomass during the start-up period of a fixed-bed anaerobic reactor treating domestic sewage. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology, 48(5), 841–849.
Lokshina, L. Y., Vavilin, V. A., Kettunen, R. H., Rintala, J. A., Holliger, C., & Nozhevnikova, A. N. (2001). Evaluation of kinetic coefficients using integrated Monod and Haldane models of low-temperature acetoclastic methanogenesis. Water Research, 35(12), 2913–2922.
Manz, W., Amann, R., Ludwig, W., Wagner, M., & Schleifer, K. H. (1992). Phylogenetic oligodeoxynucleotide probes for the major subclasses of Proteobacteria: problems and solutions. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 15(4), 593–600.
Maya-Altamira, L., Baun, A., Angelidaki, I., & Schmidt, J. E. (2008). Influence of wastewater characteristics on methane potential in food-processing industry wastewaters. Water Research, 42(8–9), 2195–2203.
McCarty, P. L., et al. (1982). One hundred years of anaerobic treatment. In Hughes (Ed.), Anaerobic digestion 1981 (pp. 3–22). London: Elsevier.
McInerney, M. J. (1988). Anaerobic hydrolysis and fermentation of fats and proteins. In A. J. B. Zendher (Ed.), Biology of anaerobic microorganisms (pp. 381–402). New Jersey: Wiley.
Moraes, E. M., Adorno, M. A. T., Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (2000). Determination of volatile acids by gas chromatography in effluents from anaerobic reactors treating liquid and solid waste. Anais da VI Oficina e Seminário Latino Americano de Digestão Anaeróbia, Recife, 2, 146–149 (in Portuguese).
Oliveira, S. V. W. B., Moraes, E. M., Adorno, M. A. T., Varesche, M. B. A., Foresti, E., & Zaiat, M. (2004). Formaldehyde degradation in an anaerobic packed-bed bioreactor. Water Research, 38(7), 1685–1694.
Peterson, G. L. (1979). Review of the Folin phenol protein quantification method of Lowry, Rosebrough, Farr and Randall. Analytical Biochemistry, 100(2), 201–219.
Pinho, S. C., Fernandes, B. S., Rodrigues, J. A. D., Ratusznei, S. M., Foresti, E., & Zaiat, M. (2005). Feasibility of treating swine manure in an anaerobic sequencing batch biofilm reactor with mechanical stirring. Appl Biochem Biotech, 120(2), 109–120.
Postma, T., & Stroes, J. A. P. (1968). Lipid screening in clinical chemistry. Clinica Chimica Acta, 22(4), 569–578.
Sanz, J. L., & Köchling, T. (2007). Molecular biology techniques used in wastewater treatment: an overview. Process Biochemistry, 42(2), 119–133.
Sayed, S., Vanderzanden, J., Wijffels, R., & Lettinga, G. (1988). Anaerobic degradation of the various fractions of slaughterhouse waste-water. Biological Wastes, 3(2), 117–142.
Seborg, D. E., Edgar, T. F., & Mellichamp, D. A. (1989). Process dynamics and control. New York: Wiley.
Shimada, T., Zilles, J., Raskin, L., & Morgenroth, E. (2007). Carbohydrate storage in anaerobic sequencing batch reactors. Water Research, 41(20), 4721–4729.
Speece, R. E. (1996). Anaerobic biotechnology for industrial wastewater. Nashville: Archae.
Stahl, D. A., & Amann, R. (1991). Development and application of nucleic acid probes in bacterial systematics. In E. Stackebrandt, & M. Goodfellow (Eds.), Sequencing and hybridization techniques in bacterial systematics (pp. 205–248). England: John Wiley and Sons.
Tommaso, G., Varesche, M. B. A., Zaiat, M., Vazoller, R. F., & Foresti, E. (2002). Morphological observation and microbial population dynamics in anaerobic polyurethane foam biofilm degradatin gelatin. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 19(3), 287–292.
Tommaso, G., Ribeiro, R., Varesche, M. B. A., Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (2003). Influence of multiple substrates on anaerobic protein degradation in a packed-bed bioreactor. Water Science and Technology, 48(6), 23–31.
Tommaso, G., Chinalia, F. A., Varesche, M. B. A., Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (2005). Evaluation of anaerobic degradation of wastewater from poultry slaughterhouse in relation to the kinetics of substrate consumption and active biomass. VIII Taller e Simposio Latinoamericano Sobre Digestión Anaerobia, 2, 35–39 (in Portuguese).
Vidal, G., Carvalho, A., Mendez, R., & Lema, J. M. (2000). Influence of the content in fats and proteins on the anaerobic biodegradability of dairy wastewaters. Bioresource Technology, 74(3), 231–239.
Voordouw, G. (1995). The genus Desulfovibrio: the centennial. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 61(8), 2813–2819.
Zaiat, M., & Foresti, E. (1997). Method for estimating the kinetics of substrate degradation in horizontal-flow anaerobic immobilized sludge (HAIS) reactor. Biotechnology Techniques, 11(5), 315–318.
Zaiat, M., Cabral, A. K. A., & Foresti, E. (1994). Horizontal-flow anaerobic immobilised-biomass for wastewater treatment: design and preliminary assessment of performance. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 11(2), 33–42 (in Portuguese).
Zaiat, M., Passig, F. H., & Foresti, E. (2000). Treatment of domestic sewage in horizontal-flow anaerobic immobilized biomass (HAIB) reactor. Environmental Technology, 21(10), 1139–1145.
Zhu, G.-F., Li, J.-Z., Wu, P., Jin, H.-Z., & Wang, Z. (2008). The performance and phase separated characteristics of an anaerobic baffled reactor treating soybean protein processing wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 99(17), 8027–8033.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to FAPESP (Sao Paulo Research Foundation) and CNPq (National Counsel of Technological and Scientific Development) for funding and to colleagues of the Laboratory of Biological Process, for all the enriching discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tommaso, G., Domingues, M.R., Ribeiro, R. et al. Anaerobic Degradation of Protein: Simplified Kinetic Modelling and Microbial Dynamics. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1554 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1554-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1554-9