Abstract
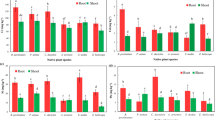
Contamination of metal ions in soil and water represents more pressing threats to resources as well as human health. The present research was carried out to screen the phytosequester plants growing in industrial waste- and wastewater-affected industrial areas of Okhla, New Delhi, India. Accumulation trend of metal Fe, Zn, Cu, Cr, Pb, Cd, Hg, and As from soil and wastewater by plants were collected for study. Among aquatic plants Hydrilla verticillata, Marsilea quadrifolia, and Ipomea aquatica were found to be highest metals accumulator, Eclipta alba and Sesbania cannabina among terrestrial plant were highest accumulator of metals. Among the algal spp. Spirulina platensis and Phormidium papyraceum were the most efficient in accumulating Cd and Hg. The maximum bioconcentration factor (BCF) was recorded in Hygroryza aristata for the metals (Hg, Cd) in M. quadrifolia (Cd, Cr), in E. alba (Cr, Cu), and in S. platensis (Hg, Pb). However, the translocation factor (TF) of metals was found more in M. quadrifolia followed by I. aquatica than other plants. Among all the plants, H. verticillata showed high TF and low BCF values for toxic metals (Pb, Cr) and was suitable for phytostabilization of these metals. Our study showed that native plant species growing on contaminated sites may have a potential of phytosequestration of these metals.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, A., & Alam, M. (2004). Sequestration and remediation of heavy metals by Brassica sp at Hindan river sites. Indian Journal of Chemical Technology, 11, 560–564.
Ajmal, M., Rao, R. A. K., Ahmad, R., Khan, M. A., et al. (2006). Adsorption studies on Parthenium hysterophorus weed: removal and recovery of Cd(II) from water. Journal of Hazardous Material B, 135, 242–248.
APHA. (1995). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 16th edn., APHA, AWWA and WPCF. 1995.
Audet, P., & Charest, C. (2007). Heavy metal phytoremediation from a meta-analytical perspective. Environmental Pollution, 147, 231–239.
Bhattacharya, A., Routh, J., Jacks, G., Bhattacharya, P., Morth, M., et al. (2006). Environmental assessment of abandoned mine tailings in Adak, Vasterbotten district (northern Sweden). Applied Geochemistry, 21, 1760–1780.
Degryse, F., & Smolders, E. (2006). Mobility of Cd and Zn in polluted and unpolluted Spodosols. European Journal of Soil Science, 57, 122–133.
Deng, H., Ye, Z. H., Wong, M. H., et al. (2004). Accumulation of lead, zinc, copper and cadmium by 12 wetland plant species thriving in metal-contaminated sites in China. Environmental Pollution, 132, 29–40.
Duthie, J. F. (1960). Flora of the upper gangetic plain and of adjacent Siwalik and Sub-Himalayan tracts, vol. I and II. Calcutta: Gouranya Press Private Ltd.
Dwivedi, S., Tripathi, R. D., Rai, U. N., Srivastava, S., Mishra, S., Shukla, M. K., et al. (2006). Dominance of algae in Ganga water polluted through fly-ash leaching: metal bioaccumulation potential of selected algal species. Bulletin of Environment Contamination and Toxicology, 77, 427–436.
Dwivedi, S., Srivastava, S., Mishra, S., Kumar, A., Tripathi, R. D., Rai, U. N., et al. (2010). Characterization of native microalgal strains for their chromium bioaccumulation potential: phytoplankton response in polluted habitats. Journal of Hazardous Material, 173, 95–101.
Eapen, S., & D’Souza, S. F. (2005). Prospects of genetic engineering of plants for phytoremediation of toxic metals. Biotechnology Advance, 23, 97–112.
Fischerova, Z., Tlustos, P., Szakova, J., Sichorova, K., et al. (2006). A comparison of phytoremediation capability of selected plant species for given trace elements. Environmental Pollution, 144, 93–100.
Ghassemzadeh, F., Yousefzadeh, H., & Arbab-Zavar, M. H. (2008). Arsenic phytoremediation by Phragmites australis: green technology. International Journal of Environmental Studies, 65, 587–594.
Ghosh, M., & Singh, S. P. (2005). A comparative study of cadmium phytoextraction by accumulator and weed species. Environmental Pollution, 133, 365–371.
Gokhale, S. V., Jyoti, K. K., & Lele, S. S. (2008). Kinetic and equilibrium modeling of chromium (VI) biosorption on fresh and spent Spirulina platensis/Chlorella vulgaris biomass. Bioresource Technology, 99, 3600–3608.
Gomez, K. A., & Gomez, A. A. (1984). Statistical procedures for agricultural research. New York: John Wiley.
Gratão, P. L., Prasad, M. N. V., Cardoso, P. F., Lea, P. J., Azevedo, R. A., et al. (2005). Phytoremediation: green technology for the clean up of toxic metals in the environment. Brazilian Journal Plant Physiology, 17, 53–64.
Greger, M., Malm, T., & Kautsky, L. (2007). Heavy metal transfer from composted macroalgae to crops. European Journal of Agronomy, 26, 257–265.
Gupta, A. K., & Sinha, S. (2006). Role of Brassica juncea L. Czern. (var. vaibhav) in the phytoextraction of Ni from soil amended with fly-ash: selection of extractant for metal bioavailability. Journal of Hazardous Material, 136, 371–378.
Gupta, A. K., Dwivedi, S., Sinha, S., Tripathi, R. D., Rai, U. N., Singh, S. N., et al. (2007). Metal accumulation and growth performance of Phaseolus vulgaris grown in fly ash amended soil. Bioresource Technology, 98, 3404–3407.
Hoang Ha, N. T., Sakakibara, M., Sano, S., et al. (2009). Phytoremediation of Sb, As, Cu, and Zn from contaminated water by the aquatic macrophyte. Eleocharis acicularis. CLEAN-Soil, Air, Water. doi:10.1002/clen.200900061.
Huang, R. Q., Gao, S. F., Wang, W. L., Staunton, S., Wang, G., et al. (2006). Soil arsenic availability and the transfer of soil arsenic to crops in suburban areas in Fujian province, southeast China. The Science of the Total Environment, 368, 531–541.
Jackson, M. L. (1967). Soil chemical analysis (p. 498). New Delhi: Prentice Hall of India Private Ltd.
Jackson, M. L. (1973). Soil chemical analysis. New Delhi: Prentice Hall of India Private Ltd.
Japenga, J., Koopmans, G. F., Song, J., Römkens, P. F. A. M., et al. (2007). A feasibility test to estimate the duration of phytoextraction of heavy metals from polluted soils. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 9, 115–132.
Kamal, M., Ghaly, A. E., Mahmoud, N., & Cote, R. (2004). Phytoaccumulation of heavy metals by aquatic plants. Environment International, 29, 1029–1039.
Khan, S., Cao, Q., Chen, B. D., Zhu, Y. G., et al. (2006). Humic acids increase the phytoavailability of Cd and Pb to wheat plants cultivated in freshly spiked contaminated soil. Journal Soil Sediment, 6, 236–242.
Kim, I. S., Kang, H. K., Johnson-Green, P., Lee, E. J., et al. (2003). Investigation of heavy metal accumulation in Polygonum thunbergii for phytoextraction. Environmental Pollution, 126, 235–243.
Koopmans, G. F., Römkens, P. F. A. M., Fokkema, M. J., Song, J., Luo, Y. M., Japenga, J., et al. (2008). Feasibility of phytoextration to remediate cadmium and zink contaminated soils. Environmental Pollution, 156, 905–914.
Kramer, U. (2005). Phytoremediation: novel approaches to cleaning up polluted soils. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 16, 133–141.
Kruatrachue, M., Pokethitiyook, P., Tanhan, P., Samranwanich, T., et al. (2008). Potential of Sonchus arvensis for the phytoremediation of lead-contaminated soil Wunrada Surat. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 10, 325–342.
Lee, S. B., Lee, Y. B., Lee, C. H., Hong, C. O., Kim, P. J., Yu, C., et al. (2008). Characteristics of boron accumulation by fly ash application in paddy soil. Bioresource Technology, 99, 5928–5932.
Li, T., & Xiong, Z. T. (2004). A novel response of wild-type duckweed (Lemna paucicostata Hegelm.) to heavy metals. Environmental Toxicology, 19, 95–102.
Lindsay, W. L., & Norvell, W. A. (1978). Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Soil Science Society of American Journal, 42, 421–428.
Liu, X., Gao, Y., Khan, S., Duan, G., Chen, A., Ling, L., et al. (2008). Accumulation of Pb, Cu, Zn in native plants growing on contaminated sites and their potential accumulation capacity in Heqing, Yunnan. Journal of Environmental Science, 20, 1469–1474.
Mahmud, R., Inoue, N., Kasajima, S., Shaheen, R., et al. (2008). Assessment of potential indigenous plant species for the phytoremediation of Arsenic-contaminated areas of Bangladesh. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 10, 119–132.
Malik, A. (2007). Environmental challenges vis a vis opportunity: the case of water hyacinth. Environment International, 33, 122–138.
Marques, A. P. G. C., Oliveira, R. S., Rangel, A. O. S. S., Castro, P. M. L., et al. (2008). Application of manure and compost to contaminated soils and its effect on zinc accumulation by Solanum nigrum inoculated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Environmental Pollution, 151, 608–620.
McGrath, S. P., & Zhao, F. J. (2003). Phytoextraction of metals and metalloids. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 14, 277–282.
McGrath, S. P., Lombi, E., Gray, C. W., Caille, N., Dunham, S. J., Zhao, F. J., et al. (2006). Field evaluation of Cd and Zn phytoextraction potential by the hyperaccumulators Thlaspi caerulescens and Arabidopsis halleri. Environmental Pollution, 141, 115–125.
Mishra, V. K., & Tripathi, B. D. (2008). Concurrent removal and accumulation of heavy metals by the three aquatic macrophytes. Bioresource Technology, 99, 7091–7097.
Mishra, S., Srivastava, S., Tripathi, R. D., Kumar, R., Seth, C. S., Gupta, D. K., et al. (2006). Lead detoxification by coontail (Ceratophyllum dermersum L.) involves induction of phytochelatins and antioxidant system in response to its accumulation. Chemosphere, 65, 1027–1039.
Moreno, F. N., Anderson, C. W. N., Steward, R. B., & Robinson, B. H. (2008). Phytofiltration of mercury contaminated water: volatization and plant accumulation aspects. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 62, 78–85.
Padmavathiamma, P. K., & Li, L. Y. (2007). Phytoremediation technology: hyper-accumulation metals in plants. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 184, 105–126.
Pandey, V. C., Abhilash, P. C., & Singh, N. (2009). The Indian perspective of utilizing fly ash in phytoremediation, phytomanagement and biomass production. Journal of Environmental Management, 90, 2943–2958.
Prescott, G. W. (1951). Monograph algae of the Western great lakes area. Michigan: Cambrook Institute of Sciences.
Pulford, I. D., & Watson, C. (2003). Phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated land by trees-a review. Environment International, 29, 529–540.
Pulford, I. D., Riddell-Black, D., Stewart, C., et al. (2002). Heavy metal uptake by willow clones from sewage sludge-treated soil: the potential for phytoremediation. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 4, 59–72.
Quartacci, M. F., Argilla, A., Baker, A. J. M., Navari-Izzo, F., et al. (2006). Phytoextraction of metals from a multiply contaminated soil by Indian mustard. Chemosphere, 63, 918–925.
Rangsayatorn, N., Pokethitiyook, P., Upatham, E. S., Lanza, G. R., et al. (2005). Cadmium biosorption by cells of Spirulina platensis TISTR 8217 immobilized in alginate and silica gel. Environment International, 30, 57–62.
Robinson, N., Kim, M., Marchetti, C., Moni, L., Schroeter, C., van den Dijssel, G., et al. (2006). Arsenic hyperaccumulation by aquatic macrophytes in the Taupo volcanic zone, New Zealand. Environment Experimental Botany, 58, 206–215.
Satoha, A., Vudikariab, L. Q., Kuranoa, N., Miyachia, S., et al. (2005). Evaluation of the sensitivity of marine microalgal strains to the heavy metals, Cu, As, Sb, Pb and Cd. Environment International, 31, 713–722.
Segura-Muñoz, S. I., Oliveira, A. D. S., Nikaido, M., Trevilato, T. M. B., Bocio, A., Takayanagui, A. M. M., et al. (2006). Metal levels in sugar cane (Saccharum spp.) samples from an area under the influence of a municipal landfill and a medical waste treatment system in Brazil. Environment International, 32, 52–57.
Sikka, R., & Kansal, B. D. (1995). Effect of fly-ash application on yield and nutrient composition of rice, wheat and on pH and available nutrient status of soils. Bioresources Technology, 51, 199–203.
Smedley, P. L., & Kinniburgh, D. G. (2002). A review of the source, behavior and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 517–568.
Solisio, C., Lodi, A., Torre, P., Converti, A., Del Borghi, M., et al. (2006). Copper removal by pre-treated non-living biomass of Spirulina platensis. Bioresource Technology, 97, 1756–1760.
Srivastava, S., Mishra, S., Tripathi, R. D., Dwivedi, S., Trivedi, P. K., Tandon, P. K., et al. (2007). Phytochelatins and antioxidant systems respond differentially during arsenite and arsenate stress in Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle. Environmental Science Technology, 41, 2930–2936.
Van-Engelen, D. L., Sharpe-Pedler, R. C., Moorhead, K. K., et al. (2007). Effect of chelating agents and solubility of cadmium complexes on uptake from soil by Brassica juncea. Chemosphere, 68, 401–408.
Wang, S., Nan, Z., Liu, X., Li, Y., Qin, S., Ding, H., et al. (2009). Accumulation and bioavailability of copper and nickel in wheat plants grown in contaminated soils from the oasis, northwest China. Geodermal, 152, 290–295.
Acknowledgement
The author would like to thank R & D Cluster unit for technical assistance during the course of this research. Moreover, the financial support from the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS-2007, Ministry Higher Ecducation, Malaysia) is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, A., Ghufran, R. & Zularisam, A.W. Phytosequestration of Metals in Selected Plants Growing on a Contaminated Okhla Industrial Areas, Okhla, New Delhi, India. Water Air Soil Pollut 217, 255–266 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0584-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0584-9