Abstract
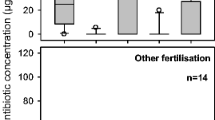
Sulfonamide antibiotics can enter agricultural soils by fertilisation with contaminated manure. While only rough estimations on the extent of such applications exist, this pathway results in trace level contamination of groundwater. Therefore, we studied the transport of three sulfonamides in leachates from field lysimeters after application of a sulfonamide-contaminated liquid manure. In a 3-year period, the sulfonamides were determined in 64% to 70% of all leachate samples at concentrations between 0.08 to 56.7 µg L−1. Furthermore, sulfonamides were determined in leachates up to 23 months after application, which indicated a medium- to long-term leaching risk. Extreme dry weather conditions resulted in highest dislocated amounts of sulfonamides in two of the three treatments. Furthermore, soil management such as tillage and cropping affected the time between application and breakthrough of sulfonamides and the intra-annual distribution of sulfonamide loads in leachates. Although the total sulfonamide leaching loads were low, the concentrations exceeded the limit value of the European Commission of 0.1 µg biocide L−1 in drinking water in more than 50% of all samples. Furthermore, the medium-term mean concentration of the sulfonamides ranged from 0.08 and 4.00 µg L−1, which was above the limit value of the European Commission in 91 out of 158 samples. Therefore, sulfonamides applied to soils in liquid manure under common agricultural practice may cause environmental and health risks which call for a setting up of more long-term studies on the fate of antibiotics.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accinelli, C., Koskinen, W. C., Becker, J. M., & Sadowsky, M. J. (2007). Environmental fate of two sulfonamide antimicrobial agents in soil. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55, 2677–2682.
ATV-DVWK (2002). Verdunstung in Bezug zur Landnutzung, Bezug und Boden - Merkblatt ATV-DVWK-M 504. Deutsche Vereinigung für Wasserwirtschaft, Abwasser und Abfall e.C., Hennef.
Aust, M.-O., Godlinski, F., Travis, G. R., Hao, X., McAllister, T. A., Leinweber, P., et al. (2008). Distribution of sulfamethazine, chlortetracycline and tylosin in manure and soil of Canadian feedlots after subtherapeutic use in cattle. Environmental Pollution, 156, 1243–1251.
Aust, M.-O., Thiele-Bruhn, S., Jandl, G., & Leinweber, P. (2008). Determination of six membered ring sulfonamides used in veterinary medicine in manure, soil and soil leachates using LC-ESI mass spectrometry. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 17, 331–340.
Blackwell, P. A., Kay, P., Ashauer, R., & Boxall, A. B. A. (2009). Effects of agricultural conditions on the leaching behaviour of veterinary antibiotics in soils. Chemosphere, 75, 13–19.
Boxall, A. B. A., Fogg, L. A., Blackwell, P. A., Kay, P., Pemberton, E. J., & Croxford, A. (2004). Veterinary medicines and the environment. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 180, 1–91.
Burkhardt, M., & Stamm, C. (2007). Depth distribution of sulfonamide antibiotics in pore water of an undisturbed loamy grassland soil. Journal of Environmental Quality, 36, 588–596.
Chemzoo Inc. (2009). Chemspider. Retrieved June 8, 2009, from: http://www.chemspider.com.
Commission of the European Communities. (1998). Council Directive 98/83/EU on the quality of water induced for human consumption. Official Journal of the European Communities Legislation, L330, 32–54.
Förster, M., Laabs, V., Lamshöft, M., Groeneweg, J., Zühlke, S., Spiteller, M., et al. (2009). Sequestration of manure-applied sulfadiazine residues in soils. Environmental Science & Technology, 43, 1824–1830.
Godlinski, F., Leinweber, P., Meissner, R., & Seeger, J. (2004). Phosphorus status of soil and leaching losses: results from operating and dismantled lysimeters after 15 experimental years. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 68, 47–57.
Groeneweg, J., Rützel, H., Pütz, T., & Vereecken, H. (2007). Translocation of the veterinary antibiotic sulfadiazine in lysimeters (in German). Conference proceeding of the 12th Gumpensteiner Lysimeter Conference, 71–74.
Grote, M., Vockel, A., Schwarze, D., Mehlich, A., & Freitag, M. (2004). Fate of antibiotics in food chain and environment originating from pigfattening (Part 1). Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 13, 1216–1224.
Haller, M. Y., Müller, S. R., McArdell, C. S., Alder, A. C., & Suter, M. J. F. (2002). Quantification of veterinary antibiotics (sulfonamides and trimethoprim) in animal manure by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 952, 111–120.
Halling-Sørensen, B., Jensen, J., Tjørnelund, J., & Montforts, M. H. M. M. (2001). Worst-case estimations of predicted environmental soil concentrations (PEC) of selected veterinary antibiotics and residues used in Danisch agriculture. In K. Kümmerer (Ed.), Pharmaceuticals in the environment (pp. 143–157). Berlin: Springer.
Hamscher, G., Pawelzick, H. T., Höper, H., & Nau, H. (2005). Different behaviour of tetracyclines and sulfonamides in sandy soils after repeated fertilization with liquid manure. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 24, 861–868.
Hirsch, R., Ternes, T. A., Haberer, K., & Kratz, K. L. (1999). Occurrence of antibiotics in the aquatic environment. Science of the Total Environment, 225, 109–118.
Höper, H., Schäfer, W., & Hamscher, G. (2007). On the compound displacement of veterinary medicinal agents with seepage water—Results from field-lysimeter experiments (in German). In R. Röder, K., Weiß & M. Sengl (Eds.), Veterinary medicines in the environment (58, pp. 83–104). Munich contributions on sewage, fishery and river biology, Munich.
Jablonowski, N. D., Modler, J., Schaeffer, A., & Burauel, P. (2008). Bioaccessibility of environmentally aged 14C-atrazine residues in an agriculturally used soil and its particle-size aggregates. Environmental Science & Technology, 42, 5904–5910.
Kahle, M., & Stamm, C. (2007). Time and pH-dependent sorption of the veterinary antimicrobial sulfathiazole to clay minerals and ferrihydrite. Chemosphere, 68, 1224–1231.
Kay, P., Blackwell, P. A., & Boxall, A. B. A. (2005a). A lysimeter experiment to investigate the leaching of veterinary antibiotics through a clay soil. Environmental Pollution, 134, 333–341.
Kay, P., Blackwell, P. A., & Boxall, A. B. A. (2005b). Column studies to investigate the fate of veterinary antibiotics in clay soils following slurry application to agricultural land. Chemosphere, 60, 497–507.
Kreuzig, R., & Höltge, S. (2005). Investigations on the fate of sulfadiazine in manured soil: Laboratory experiments and test plot studies. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 24, 771–776.
Kurwadkar, S. T., Adams, C. D., Meyer, M. T., & Kolpin, D. W. (2007). Effects of sorbate speciation on sorption of selected sulfonamides in three loamy soils. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55, 1370–1376.
Lamshöft, M., Sukul, P., Zühlke, S., & Spiteller, M. (2007). Metabolism of 14C-labelled and non-labelled sulfadiazine after administration to pigs. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 388, 1733–1745.
Langhammer, J. P., & Büning-Pfaue, H. (1989). Evaluation of manure-borne pharmaceutical residues in soil (in German). Lebensmittelchemie und Gerichtliche Chemie, 43, 108.
Langhammer, J. P., Richter, O., & Büning-Pfaue, H. (1990). Evaluation of residues using a simulation model (in German). Lebensmittelchemie, 44, 92.
Lennartz, B., & Louchart, X. (2007). Effect of drying on the desorption of diuron and terbuthylazine from natural soils. Environmental Pollution, 146, 180–187.
Meissner, R., Seeger, J., & Rupp, H. (2002). Effects of agricultural land use changes on diffuse pollution of water resources. Irrigation and Drainage, 51, 119–127.
Monteiro, S. C., & Boxall, A. B. A. (2009). Factors affecting the degradation of pharmaceuticals in agricultural soils. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 28, 2546–2554.
Peel, M. C., Finlayson, B. L., & McMahon, T. A. (2007). Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrology and Earth System Science, 11, 1633–1644.
Sakurai, H., & Ishimitsu, T. (1980). Microionization constants of sulphonamides. Talanta, 27, 293–298.
Sarmah, A. K., Meyer, M. T., & Boxall, A. B. A. (2006). A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere, 65, 725–759.
Scheib, A. (2004). Kinetics of sulfonamides` antibiotics' dissipation- and binding in selected soil samples (in German), Diploma-Thesis, Universität Rostock, Institute for Land Use, Chair for soil science.
Schimel, J., Balser, T. C., & Wallenstein, M. (2007). Microbial stress-response physiology and its implications for ecosystem function. Ecology, 88, 1386–1394.
Schmidt, B., Ebert, J., Lamshöft, M., Thiede, B., Schumacher-Buffel, R., Ji, R., et al. (2008). Fate in soil of C-14-sulfadiazine residues contained in the manure of young pigs treated with a veterinary antibiotic. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part B-Pesticides Food Contaminants and Agricultural Wastes, 43, 8–20.
Seeger, J., & Meissner, R. (2001). Estimation of the risk potential of agricultural management practices in the area of the Querfurt Plateau using nitrogen as an example (in German). In UFZ-Report. Effect of land use on natural environment and biodiversity in agriculture dominated areas (in German) (pp. 134–153).
Seeger, J., Meissner, R., Rupp, H., Müller, L., & Eulenstein, F. (1999). Experiences from using conservative tracers as tool to transfer results from lysimeter to open land experiments (in German). In D. Klotz & K.-P. Seiler (Eds.), Determination of the leachate velocity in lysimeters (in German) (pp. 37–42).
Stevenson, F. J. (1994). Humus chemistry, genesis, composition, reactions. New York: Wiley.
Stoob, K., Singer, H. P., Stettler, S., Hartmann, N., Mueller, S. R., & Stamm, C. H. (2006). Exhaustive extraction of sulfonamide antibiotics from aged agricultural soils using pressurized liquid extraction. Journal of Chromatography A, 1128, 1–9.
Stoob, K., Singer, H. P., Mueller, S. R., Schwarzenbach, R. P., & Stamm, C. H. (2007). Dissipation and transport of veterinary sulfonamide antibiotics after manure application to grassland in a small catchment. Environmental Science & Technology, 41, 7349–7355.
Sukul, P., Lamshöft, M., Zühlke, S., & Spiteller, M. (2008). Sorption and desorption of sulfadiazine in soil and soil-manure systems. Chemosphere, 73, 1344–1350.
Thiele-Bruhn, S., & Aust, M.-O. (2004). Effects of pig slurry on the sorption of sulfonamide antibiotics in soil. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 47, 31–39.
van Elsas, J. D., & Smalla, K. (1999). Methods for sampling soil microbes. In C. J. Hurst, G. R. Knudsen, M. J. McInerney, L. D. Stetzenbach & M. V. Walter (Eds.), Manuals of environmental microbiology (pp. 383–390). Washington: ASM.
Wang, Q. Q., Guo, M., & Yates, S. R. (2006). Degradation kinetics of manure-derived sulfadimethoxine in amended soil. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 54, 157–163.
Zsolnay, A. (1996). Dissolved humus in soil waters. In A. Piccolo (Ed.), Humic substances in terrestrial ecosystems (pp. 171–223). Amsterdam: Elsevier Science B.V.
Acknowledgements
The project was funded by the Scholarship programme of the German Federal Environmental Foundation (DBU, grant no. 20003/498). Parts of the LC-MS/MS system were funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG, grant no. Th 678/6-2) and the Mass Spectrometry Laboratory of the Rostock Soil Science Group was funded by the “Exzellenzförderprogramm” of the Ministerium für Bildung, Wissenschaft und Kultur Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, project UR 07 079. We gratefully acknowledge the technical support of Britta Balz, Jette Schwarz and Kai-Uwe Eckhardt, University of Rostock. We are grateful to an anonymous reviewer, whose valuable comments significantly improved the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
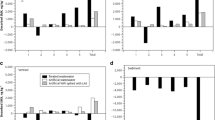
Water storage in three lysimeters from sandy loam under cultivation following agricultural practice resulting from the calculation of the water balance according to the capacitive Turc-Wendling approach (ATV-DVWK 2002; see Table 2 for details; the vertical broken line indicates the turn of the hydrological year)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aust, MO., Thiele-Bruhn, S., Seeger, J. et al. Sulfonamides Leach from Sandy Loam Soils Under Common Agricultural Practice. Water Air Soil Pollut 211, 143–156 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0288-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0288-1