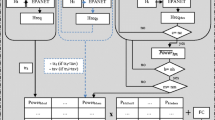
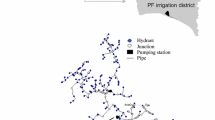
Abstract
In recent decades, on-demand irrigation systems have been promoted to increase water use efficiency. This study focused on the assessment of two traditional rotational pressurized irrigation systems with a central pumping station in the Foggia Province (Italy). Irrigation system A has an area of 564 ha with 319 pipelines and 251 hydrants, and irrigation system B has an area of 445 ha with 280 pipelines and 214 hydrants. The nominal discharge of each hydrant is 10 l/s. In each of the two irrigation systems, 1000 different operation scenarios were investigated using the COPAM model. To evaluate the performance of the systems, the indices of Relative Pressure Deficit (RPD) and Reliability (RI) were used. Results showed that the systems are quite flexible and allow the required flow rate to be increased by 1.6 times the peak period flow rate, if necessary. With such increased discharges, it is impossible to guarantee the RPD (\(RPD\ge 0\)) and RI (RI = 1) indices in 47% of the hydrants in the irrigation system A and in 36.9% of the hydrants in the irrigation system B. An updated methodology for optimizing the pipe diameters starting from the current situation was also implemented. Around 23% of pipelines in each system were changed with such methodology. After the new optimization, the number of unsatisfied hydrants in both systems decreased by 94.1% (from 118 to 7 hydrants) and 82.3% (from 79 to 14 hydrants), respectively. Thus, with this methodology, the irrigation system performance can be improved.
Graphical Abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Anwar AA, Haq ZU (2013) Genetic algorithms for the sequential irrigation scheduling problem. Irrig Sci 31(4):815–829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-012-0364-y
Bajany DM, Zhang L, Xu Y, Xia X (2021) Optimisation approach toward water management and energy security in Arid/Semiarid regions. Environ Process 8(4):1455–1480. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40710-021-00537-9
Béthery J, Meunier M, Puech C (1981) Analyse des défaillances et étude du renforcement des réseaux d’irrigation par aspersion. Onzième Congrés de la CIID, question 36:297–324
Béthery J (1990) Collective irrigation networks ramified under pressure, calculation and operation (p. 139). Cemagref Editions
Calejo M, Lamaddalena N, Teixeira J, Pereira LS (2008) Performance analysis of pressurized irrigation systems operating on-demand using flow-driven simulation models. Agric Water Manag 95(2):154–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2007.09.011
Clément R, Galand A (1979) Irrigation par aspersion et réseaux collectifs de distribution sous pression
Clément R (1966) Calculation of flows in demand-operated irrigation networks. The White Coal 5:553–576
Córcoles JI, Tarjuelo JM, Carrión PA, Moreno MÁ (2015) Methodology to minimize energy costs in an on-demand irrigation network based on arranged opening of hydrants. Water Resour Manag 29(10):3697–3710 (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11269-015-1024-9)
CTGREF Division Irrigation (1979) Programme ICARE - Calcul des caractéristiques indicées. Note Technique 6
Daccache A, Lamaddalena N, Fratino U (2010a) On-demand pressurized water distribution system impacts on sprinkler network design and performance. Irrig Sci 28(4):331–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-009-0195-7
Daccache A, Weatherhead K, Lamaddalena N (2010b) Climate change and the performance of pressurized irrigation water distribution networks under Mediterranean conditions: impacts and adaptations. Outlook Agric 39(4):277–283
Díaz JR, Urrestarazu LP, Poyato EC, Montesinos P (2012) Modernizing water distribution networks: Lessons from the Bembézar MD irrigation district, Spain. Outlook Agric 41(4):229–236
FernándezGarcía I, Montesinos P, Camacho Poyato E, Rodríguez Díaz J (2017) Optimal design of pressurized irrigation networks to minimize the operational cost under different management scenarios. Water Resour Manage 31(6):1995–2010. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11269-017-1629-2
Ferrarese G, Pagano A, Fratino U, Malavasi S (2021) Improving operation of pressurized irrigation systems by an off-grid control devices network. Water Resour Manag 1–15. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11269-021-02869-5
Fouial A, García IF, Bragalli C, Brath A, Lamaddalena N, Diaz JAR (2017) Optimal operation of pressurised irrigation distribution systems operating by gravity. Agric Water Manag 184:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2017.01.010
Kanakis P, Papamichail D, Georgiou P (2014) Performance analysis of on-demand pressurized irrigation network designed with linear and fuzzy linear programming. Irrig Drain 63(4):451–462
Khadra R, Lamaddalena N (2006) A simulation model to generate the demand hydrographs in large-scale irrigation systems. Biosys Eng 93(3):335–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2005.12.006
Khadra R, Lamaddalena N, Inoubli N (2013) Optimization of on demand pressurized irrigation networks and on-farm constraints. Procedia Environ Sci 19:942–954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2013.06.104
Lamaddalena N, Sagardoy JA (2000) Performance Analysis of on-demand pressurized irrigation systems. FAO Irrigation and drainage. Water Resources, Paper, p 59
Lamaddalena N, Pereira LS (2007) Pressure-driven modeling for performance analysis of irrigation systems operating on demand. Agric Water Manag 90(1–2):36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2007.02.004
Maqbool A, Ashraf MA, Khaliq A, Hui W, Saeed M (2021) Efficient water allocation strategy to overcoming water inequity crisis for sustainability of agricultural land: a case of Southern Punjab, Pakistan. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 35(2):245–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01903-z
Monserrat J, Alduan A (2020) Cost reduction in pressurized irrigation networks under a rotation schedule. Water Resour Manag 34(10):3279–3290 (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11269-020-02612-6)
Moreno MA, Planells P, Ortega JF, Tarjuelo J (2007) New methodology to evaluate flow rates in on-demand irrigation networks. J Irrig Drain Eng 133(4):298–306. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(2007)133:4(298)
Moreno M, Córcoles J, Tarjuelo J, Ortega J (2010) Energy efficiency of pressurised irrigation networks managed on-demand and under a rotation schedule. Biosys Eng 107(4):349–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2010.09.009
Pereira L, Calejo M, Lamaddalena N, Douieb A, Bounoua R (2003) Design and performance analysis of low pressure irrigation distribution systems. Irrig Drain Syst 17(4):305–324. https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1023/B:IRRI.0000004558.56077.d4.pdf
Replogle JA, Kruse EG (2007) Delivery and distribution systems. In Design and Operation of Farm Irrigation Systems, American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, 2nd Edition, pp 347–391
Salvador R, Latorre B, Paniagua P, Playán E (2011) Farmers’ scheduling patterns in on-demand pressurized irrigation. Agric Water Manag 102(1):86–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2011.10.009
Sheibani H, Alizadeh H, Shourian M (2019) Optimum design and operation of a reservoir and irrigation network considering uncertainty of hydrologic, agronomic and economic factors. Water Resour Manag 33(2):863–879 (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11269-018-2148-5)
Stefopoulou A, Dercas N (2017) NIREUS: A new software for the analysis of on-demand pressurized collective irrigation networks. Comput Electron Agric 140:58–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2017.05.024
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: [Younes Aminpour, Nicola Lamaddalena], Methodology: [Younes Aminpour], Formal analysis and investigation: [Younes Aminpour, Eisa Maroufpoor, Nicola Lamaddalena], Writing—original draft preparation: [Younes Aminpour]; Writing—review and editing: [Eisa Maroufpoor], Resources: [Nicola Lamaddalena], Supervision: [Eisa Maroufpoor, Nicola Lamaddalena].
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aminpour, Y., Lamaddalena, N. & Maroufpoor, E. Investigation of Infrastructural and Management Actions to Increase the Resilience of Existing Pressurized Irrigation Networks. Water Resour Manage 36, 6073–6092 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03342-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03342-7