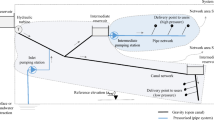
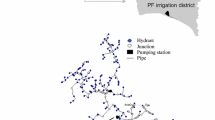
Abstract
In this paper, the focus was on the study of the management of irrigation networks, and a tool was implemented in the MATLAB® environment and developed using the EPANET® toolkit to minimize the energy costs at the pumping station. The tool was validated in an on-demand irrigation network located in Tarazona de La – Mancha (Albacete, Spain). Several scenarios were developed to determine the starting time for each irrigation event and hydrant. The results from the proposed methodology, based on a dynamic pressure regulation, were compared to the current irrigation management practice that used the pressure head as a constant value. On a daily basis, the energy savings achieved ranged from 4 to 8 %, whereas 13–36 % was saved in energy costs. On a festival day, without a high energy rate period, obtaining energy and cost savings close to 7–8 %, and 8–11 %, respectively was possible. Additionally, the savings obtained using the proposed methodology were increased with the use of two variable speed pumps activated sequentially, with the rest of the pumps as fixed, which improved the energy efficiency at the pumping station.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burt CM, Plusquellec HL (1992) Water delivery control. In: Hoffman G, Howell T, Solomon K (eds) Management of farm irrigation systems, Am Soc Agric Eng, Michigan, pp 373–423
Carrillo-Cobo MT (2009) Uso racional del agua y la energía en la Comunidad de Regantes de Fuente Palmera. Dissertation, University of Córdoba, Spain
Carrillo-Cobo MT, Rodríguez-Díaz JA, Montesinos P, López R, Camacho E (2010) Low energy consumption seasonal calendar for sectoring operation in pressurized irrigation networks. Irrig Sci 29:157–169
Daccache A, Lamaddalena N, Fratino U (2010) On-demand pressurized water distribution system impacts on sprinkler network design and performance. Irrig Sci 28:331–339
Fernández-García I, Rodríguez-Díaz JA, Camacho E, Montesinos P (2013) Optimal operation of pressurized irrigation networks with several supply sources. Water Resour Manag 27:2855–2869
Fernández-García I, Moreno MA, Rodríguez-Díaz JA (2014a) Optimum pumping station management for irrigation networks sectoring: case of Bembezar MI (Spain). Agric Water Manag 144:150–158
Fernández-García I, Montesinos P, Camacho E, Rodríguez-Díaz JA (2014b) Methodology for detecting critical points in pressurized irrigation networks with multiple water supply points. Water Resour Manag 28:1095–1109
Jiménez-Bello MA, Martínez-Alzamora F, Castel JR, Intrigliolo D (2011) Validation of a methodology for grouping intakes of pressurized irrigation networks into sectors to minimize energy consumption. Agric Water Manag 102:46–53
Jiménez-Bello MA, Royuela A, Manzano J, García Prats A, Martínez-Alzamora F (2015) Methodology to improve water and energy use by proper irrigation scheduling in pressurized networks. Agric Water Manag 149:91–101
Khadra R, Lamaddalena N (2006) A simulation model to generate the demand hydrograph in large scale irrigation systems. Biosyst Eng 93:335–346
Lamaddalena N, Khila S (2012) Energy saving with variable speed pumps in on-demand irrigation systems. Irrig Sci 30:157–166
Moradi-Jalal M, Rodin SI, Mariño MA (2004) Use of genetic algorithm in optimization of irrigation pumping stations. J Irrig Drain Eng 130:357–365
Moreno MA, Planells P, Ortega JF, Tarjuelo JM (2007a) New methodology to evaluate flow rates in on-demand irrigation networks. J Irrig Drain Eng 133:298–306
Moreno MA, Carrión PA, Planells P, Ortega JF, Tarjuelo JM (2007b) Measurement and improvement of the energy efficiency at pumping stations. Biosyst Eng 98:479–486
Moreno MA, Planells P, Ortega JF, Tarjuelo JM (2008) Calibration of on-demand irrigation network models. J Irrig Drain Eng 134:36–42
Moreno MA, Córcoles JI, Tarjuelo JM, Ortega JF (2010) Energy efficiency of pressurized irrigation networks managed on-demand and under a rotation schedule. Biosyst Eng 107:349–363
Nassim A, Emad S, Jumah A (2003) Modeling a rotation supply system in a pilot pressurized irrigation network in the Jordan Valley. Jordan Irrig Drain Syst 17:163–177
Navarro Navajas JM, Montesinos P, Camacho E, Rodríguez-Díaz JA (2012) Impacts of irrigation network sectoring as an energy saving measure on olive grove production. J Environ Manag 111:1–9
Planells P, Tarjuelo JM, Ortega JF, Casanova MI (2001) Design of water distribution networks for on-demand irrigation. Irrig Sci 20:189–201
Planells P, Carrión PA, Ortega JF, Moreno MA, Tarjuelo JM (2005) Pumping selection and regulation for water distribution networks. J Irrig Drain Eng 131:273–281
Rodríguez-Díaz JA, Camacho E, López R (2007) Model to forecast maximum flows in on-demand irrigation distribution networks. J Irrig Drain Eng 133:222–231
Rodríguez-Díaz JA, López R, Carrillo-Cobo MT, Montesinos P, Camacho Poyato E (2009) Exploring energy saving scenarios for on-demand pressurised irrigation networks. Biosyst Eng 104:552–561
Rodríguez-Díaz JA, Montesinos P, Camacho E (2012) Detecting critical points in on-demand irrigation pressurized networks – A new methodology. Water Resour Manag 26:1693–1713
Rossman LA (2001) EPANET 2. Users Manual. Water supply and Water Resources Division National Risk Management Research Laboratory. Cincinati, USA
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their gratitude to the Ministry of Education and Science (MEC) of Spain for funding the project, “Sprinkler irrigation: water application, agronomy and return flows (AGL2010-21681-C03-02)”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Córcoles, J.I., Tarjuelo, J.M., Carrión, P.A. et al. Methodology to Minimize Energy Costs in an On-Demand Irrigation Network Based on Arranged Opening of Hydrants. Water Resour Manage 29, 3697–3710 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-1024-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-1024-9