Abstract
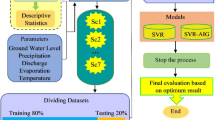
Combined simulation-optimization models have been widely used to address the management of water resources issues. This paper presents a simulation-optimization model for conjunctive use of surface water and groundwater at a basin-wide scale, the Zayandehrood river basin in west central Iran. In the Zayandehrood basin, in the past 10 years, a historical low rainfall in the head of the basin, combined with growing demand for water, has triggered great changes in water management at basin and irrigation system level. The conjunctive use model that coupled numerical simulation with nonlinear optimization is used to minimize shortages of water in meeting irrigation demands for four irrigation systems. Constraints guarantee the maximum/minimum cumulative groundwater drawdown and maximum capacity of irrigation systems. A support vector machines (SVMs) model is developed as a simulator of surface water and groundwater interaction model while a genetic algorithm (GA) is used as the optimization model. Conjunctive use model runs for three scenarios. Results show that the accuracy of SVMs as a simulator for surface water and groundwater interaction model is good and that it is possible to decrease the water shortage for irrigation systems with application of proposed SVMs-GA model.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asefa T, Kemblowski MW, Urroz G, McKee M, Khalil A (2004) Support vector-based groundwater head observation networks design. Water Resour Res 40:W11509
Barlow PM, Ahlfeld DP, Dickerman DC (2003) Conjunctive-management models for sustained yield of stream-aquifer systems. J Water Resour Plan Manage 129(1):35–48
Basagaoglu H, Mariño MA (1999) Joint management of surface and ground water supplies. Ground Water 37(2):214–222
Bazargan-Lari MR, Kerachian R, Mansoori A (2009) A conflict-resolution model for the conjunctive use of surface and groundwater resources that considers water-quality issues: a case study. Environ Manag 43(3):470–482
Behzad M, Asghari K, Coppola EA (2010) Comparative study of SVMs and ANNs in aquifer water level prediction. J Comput Civ Eng 24(5):408–413
Bhattacharjya RK, Datta B (2005) Optimal management of coastal aquifers using linked simulation optimization approach. Water Resour Manage 19:295–320
Chang CC and Lin CJ (2001) LIBSNM: a library for support vector machines. http:www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm, Ver 2.8
Chang LC, Ho CC, Yeh MS, Yang CC (2011) An integrated approach for conjunctive use planning of surface and subsurface water system. Water Resour Manage 25:59–78
Chavez-Morales J, Mariño MA, Holzapfel EA (1985) Planning model of irrigation district. J Irrig and Drain Engrg 113(4):549–564
Cristiniani N, Shawe-Taylor J (2000) An introduction to support vector machines. Cambridge University Press, New York
Doherty JL (2000) PEST: model independent parameter estimation. User manual, 4th edn. Watermark Numerical Computing, Brisbane
FAO (1992) CROPWAT- a computer program for irrigation planning and management. FAO irrigation and drainage paper no. 46. Food and Agriculture Organization, Rome
Hantush MSM, Mariño MA (1989) Chance-constrained model for management of stream-aquifer system. J Water Resour Plan Manage 115(3):259–277
Harbaugh AW, Banta ER, Hill MC, McDonald MG (2000) MODFLOW-2000, the U.S. Geological Survey modular groundwater model. Report No. 00–92, U.S. Geological Survey, Denver
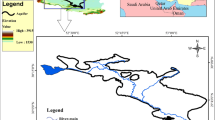
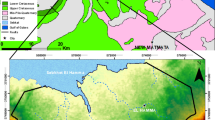
Isfahan Regional Water Authority (2010) Zayandehrood River Basin report. IRWA Publication, Isfahan, Iran (in Persian)
Karamouz M, Mohammad Rezapour Tabari M, Kerachian R (2007) Application of genetic algorithms and artificial neural networks in conjunctive use of surface and groundwater resources. Water Int 32(1):163–176
Maddock T III (1972) Algebraic technological function from a simulation model. Water Resour Res 8(1):129–134
Maddock T III (1973) Management model as a tool for studying the worth of data. Water Resour Res 9(2):270–280
Mariño MA (2001) Conjunctive management of surface water and groundwater. In: Schumann AH et al (eds) Regional management of water resources. IAHS Publ 268. IAHS, Wallingford, 165–173
Matsukawa J, Finney BA, Willis R (1992) Conjunctive use planning in Mad river basin. J Water Resour Plan Manage 118(2):115–132
Mohammad Rezapur Tabari M, Soltani J (2013) Multi-objective optimal model for conjunctive use management using SGAs and NSGA-II models. Water Resour Manag 27(1):37–53
Morel-Seytoux HJ (1975) A simple case of conjunctive surface ground water management. Ground Water 10(6):506–515
Nayak PC, Satyajirao YR, Sudheer KP (2006) Groundwater level forecasting in a shallow aquifer using artificial neural network approach. Water Resour Manage 20:77–90
Pulido-Velazquez M, Andreu J, Sahuquillo A (2006) Economic optimization of conjunctive use of surface water and groundwater at the basin scale. J Water Resour Plan Manage 132(6):454–467
Ramakrishnan K, Suribabu CR, Neelakantan TR (2010) Crop calendar adjustment study for Sathanur irrigation system in India using genetic algorithm. Water Resour Manage 24(14):3835–3851
Safavi HR, Alijanian MA (2011) Optimal crop planning and conjunctive use of surface water and groundwater resources using fuzzy dynamic programming. J Irrig Drain Eng 137(6):383–397
Safavi HR, Bahreini GR (2009) Conjunctive simulation of surface water and groundwater resources under uncertainty. Iran J Sci Tech Trans B 33(B1):79–94
Safavi HR, Afshar A, Mariño MA (2002) Integrated water resources management: a complex challenge. Proc. 6th Internat Conf. on Civil Eng., 305–312, Isfahan, Iran
Safavi HR, Darzi F, Mariño MA (2010) Simulation-optimization modeling of conjunctive use of surface water and groundwater. Water Resour Manage 24(10):1965–1988
Sethi LN, Kumar DN, Panda SN, Chandramal B (2002) Optimal crop planning and conjunctive use of water resources in a costal river. Water Resour Manage 16:145–169
Shakhnarovich G, El-Yaniv R, Baram Y (2001) Smoothed bootstrap and statistical data cloning for classifier evaluation. Int. Conf. on Machine Learning, Williams Coll, Berkshires, Mass
Singh KK, Pal M, Ojha CSP, Singh VP (2008) Estimation of removal efficiency for settling basins using neural networks and support vector machines. J Hydrol Eng 13(3):146–155
Smola AJ (1996) Regression estimation with support vector learning machines, MSc Thesis, Technische Universitat Munchen, Germany
Ticlavilca AM, McKee M (2010) Multivariate Bayesian regression approach to forecast releases from a system of multi reservoirs. Water Resour Manage 25(2):523–543
Todd KD, Mays LW (2005) Groundwater hydrology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, NJ
Trichakis IC, Nikolos IK, Karatzas GP (2011) Artificial neural network (ANN) based modeling for karstic groundwater level simulation. Water Resour Manage 25:1143–1152
Vapnik VN (1995) The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, New York
Vedula S, Mujumdar PP, Chandra Sekhar G (2005) Conjunctive use modeling for multicrop irrigation. Agric Water Manag 73:193–221
Yang CC, Chang LC, Chen CS, Yeh MS (2009) Multi-objective planning for conjunctive use of surface and subsurface water using genetic algorithm and dynamics programming. Water Resour Manage 23:417–437
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Isfahan Regional Water Company for providing access to their database. The authors would also like to express their appreciation to two anonymous reviewers for their critical comments and helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Safavi, H.R., Esmikhani, M. Conjunctive Use of Surface Water and Groundwater: Application of Support Vector Machines (SVMs) and Genetic Algorithms. Water Resour Manage 27, 2623–2644 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-013-0307-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-013-0307-2