Abstract
Objective
This study summarizes the evidence from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to assess the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on renal function and albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Materials/methods
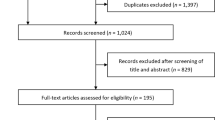
We searched PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library and EMBASE for reports published up to March 2018 and included RCTs reporting estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and/or urine albumin/creatinine ratio (UACR) changes. Data extraction and assessment of research quality based on Cochrane risk biasing tools. Data were calculated to represent the standardized mean difference (SMD) for each study, and the SMDs with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were pooled using a random effects model.
Results
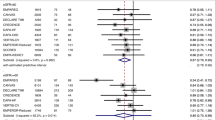
Fifty-one studies were included that evaluated eGFR levels, and 17 studies were included that evaluated UACR levels. A meta-analysis showed that SGLT2 inhibitors had no significant effect on eGFR levels (SMD − 0.02, 95% CI − 0.06, 0.03, p = 0.45), and eGFR reduction was observed in the subsets of the duration of the trial 12 < duration ≤ 26 weeks (SMD − 0.08, 95% CI − 0.13, − 0.02, p = 0.005) and mean baseline eGFR < 60 ml/min per 1.73 square meters (SMD − 0.22, 95% CI − 0.37, − 0.07, p = 0.004). We found that SGLT2 inhibitors reduced UACR levels in patients with type 2 diabetes (SMD − 0.11, 95% CI − 0.17, − 0.05, p = 0.0001). Compared with monotherapy, the combination with other hypoglycemic agents can reduce albuminuria levels (SMD − 0.13, 95% CI − 0.19, − 0.06, p < 0.0001).
Conclusions
The effect of SGLT2 inhibitor on eGFR in patients with T2DM was not statistically significant, but it was effective in reducing albuminuria levels.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Diabetes Federation (IDF) (2017) IDF Diabetes Atlas 8th edn. IDF. http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas
Parving HH, Lewis JB, Ravid M, Remuzzi G, Hunsicker LG (2006) Prevalence and risk factors for microalbuminuria in a referred cohort of type II diabetic patients: a global perspective. Kidney Int 69(11):2057–2063
Retnakaran R, Cull CA, Thorne KI, Adler AI, Holman RR (2006) Risk factors for renal dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: U.K. prospective diabetes study 74. Diabetes 55(6):1832–1839
Burrows NR, Hora I, Geiss LS, Gregg EW, Albright A (2017) Incidence of end-stage renal disease attributed to diabetes among persons with Diagnosed diabetes—United States and Puerto Rico, 2000–2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 66(43):1165–1170
Tuttle KR, Bakris GL, Bilous RW, Chiang JL, de Boer IH, Goldstein-Fuchs J et al (2014) Diabetic kidney disease: a report from an ADA consensus conference. Diabetes Care 37(10):2864–2883
DeFronzo RA, Hompesch M, Kasichayanula S, Liu X, Hong Y, Pfister M et al (2013) Characterization of renal glucose reabsorption in response to dapagliflozin in healthy subjects and subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 36(10):3169–3176
Tikkanen I, Narko K, Zeller C, Green A, Salsali A, Broedl UC et al (2015) Empagliflozin reduces blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Diabetes Care 38(3):420–428
Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S et al (2015) Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 373(22):2117–2128
Gembardt F, Bartaun C, Jarzebska N, Mayoux E, Todorov VT, Hohenstein B et al (2014) The SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin ameliorates early features of diabetic nephropathy in BTBR ob/ob type 2 diabetic mice with and without hypertension. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 307(3):F317–F325
Heerspink HJ, Desai M, Jardine M, Balis D, Meininger G, Perkovic V (2017) Canagliflozin slows progression of renal function decline independently of glycemic effects. J Am Soc Nephrol 28(1):368–375
Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, von Eynatten M, Mattheus M et al (2016) Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 375(4):323–334
Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, de Zeeuw D, Fulcher G, Erondu N et al (2017) Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 377(7):644–657
Liu XY, Zhang N, Chen R, Zhao JG, Yu P (2015) Efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials for 1 to 2 years. J Diabetes Complicat 29(8):1295–1303
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP et al (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ 339:b2700
Ji L, Ma J, Li H, Mansfield TA, T’Joen CL, Iqbal N et al (2014) Dapagliflozin as monotherapy in drug-naive Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, blinded, prospective phase III study. Clin Ther 36(1):84.e109–100.e109
Bailey CJ, Morales Villegas EC, Woo V, Tang W, Ptaszynska A, List JF (2015) Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin monotherapy in people with Type 2 diabetes: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled 102-week trial. Diabet Med 32(4):531–541
Kohan DE, Fioretto P, Tang W, List JF (2014) Long-term study of patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment shows that dapagliflozin reduces weight and blood pressure but does not improve glycemic control. Kidney Int 85(4):962–971
Wilding JP, Norwood P, T’Joen C, Bastien A, List JF, Fiedorek FT (2009) A study of dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving high doses of insulin plus insulin sensitizers: applicability of a novel insulin-independent treatment. Diabetes Care 32(9):1656–1662
Strojek K, Yoon KH, Hruba V, Sugg J, Langkilde AM, Parikh S (2014) Dapagliflozin added to glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus sustains glycemic control and weight loss over 48 weeks: a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Ther 5(1):267–283
Yang W, Ma J, Li Y, Li Y, Zhou Z, Kim JH et al (2018) Dapagliflozin as add-on therapy in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on insulin with or without oral antihyperglycemic drugs: a randomized controlled trial. J Diabetes 10(7):589–599
Bolinder J, Ljunggren O, Kullberg J, Johansson L, Wilding J, Langkilde AM et al (2012) Effects of dapagliflozin on body weight, total fat mass, and regional adipose tissue distribution in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with inadequate glycemic control on metformin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97(3):1020–1031
Araki E, Onishi Y, Asano M, Kim H, Yajima T (2017) Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin over 1 year as add-on to insulin therapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: the DAISY (Dapagliflozin Added to patients under InSulin therapY) trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 19(4):562–570
Schumm-Draeger PM, Burgess L, Koranyi L, Hruba V, Hamer-Maansson JE, de Bruin TW (2015) Twice-daily dapagliflozin co-administered with metformin in type 2 diabetes: a 16-week randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 17(1):42–51
Nauck MA, Del Prato S, Meier JJ, Duran-Garcia S, Rohwedder K, Elze M et al (2011) Dapagliflozin versus glipizide as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes who have inadequate glycemic control with metformin: a randomized, 52-week, double-blind, active-controlled noninferiority trial. Diabetes Care 34(9):2015–2022
Wilding JP, Woo V, Rohwedder K, Sugg J, Parikh S (2014) Dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving high doses of insulin: efficacy and safety over 2 years. Diabetes Obes Metab 16(2):124–136
Lambers Heerspink HJ, de Zeeuw D, Wie L, Leslie B, List J (2013) Dapagliflozin a glucose-regulating drug with diuretic properties in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 15(9):853–862
Rosenstock J, Chuck L, Gonzalez-Ortiz M, Merton K, Craig J, Capuano G et al (2016) Initial combination therapy with canagliflozin plus metformin versus each component as monotherapy for drug-naive type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 39(3):353–362
Inagaki N, Kondo K, Yoshinari T, Takahashi N, Susuta Y, Kuki H (2014) Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin rnonotherapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with diet and exercise: a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III study. Expert Opin Pharmacother 15(11):1501–1515
Stenlof K, Cefalu WT, Kim KA, Jodar E, Alba M, Edwards R et al (2014) Long-term efficacy and safety of canagliflozin monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with diet and exercise: findings from the 52-week CANTATA-M study. Curr Med Res Opin 30(2):163–175
Bode B, Stenlof K, Harris S, Sullivan D, Fung A, Usiskin K et al (2015) Long-term efficacy and safety of canagliflozin over 104 weeks in patients aged 55–80 years with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 17(3):294–303
Schernthaner G, Gross JL, Rosenstock J, Guarisco M, Fu M, Yee J et al (2013) Canagliflozin compared with sitagliptin for patients with type 2 diabetes who do not have adequate glycemic control with metformin plus sulfonylurea: a 52-week randomized trial. Diabetes Care 36(9):2508–2515
Sha S, Polidori D, Heise T, Natarajan J, Farrell K, Wang SS et al (2014) Effect of the sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor canagliflozin on plasma volume in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab 16(11):1087–1095
Qiu R, Capuano G, Meininger G (2014) Efficacy and safety of twice-daily treatment with canagliflozin, a sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor, added on to metformin monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Transl Endocrinol 1(2):54–60
Ji L, Han P, Liu Y, Yang G, Dieu Van NK, Vijapurkar U et al (2015) Canagliflozin in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes on metformin alone or metformin in combination with sulphonylurea. Diabetes Obes Metab 17(1):23–31
Lavalle-Gonzalez FJ, Januszewicz A, Davidson J, Tong C, Qiu R, Canovatchel W et al (2013) Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin compared with placebo and sitagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes on background metformin monotherapy: a randomised trial. Diabetologia 56(12):2582–2592
Wilding JP, Charpentier G, Hollander P, Gonzalez-Galvez G, Mathieu C, Vercruysse F et al (2013) Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with metformin and sulphonylurea: a randomised trial. Int J Clin Pract 67(12):1267–1282
Cefalu WT, Leiter LA, Yoon KH, Arias P, Niskanen L, Xie J et al (2013) Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin versus glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin (CANTATA-SU): 52 week results from a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 382(9896):941–950
Forst T, Guthrie R, Goldenberg R, Yee J, Vijapurkar U, Meininger G et al (2014) Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin over 52 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes on background metformin and pioglitazone. Diabetes Obes Metab 16(5):467–477
Yale JF, Bakris G, Cariou B, Yue D, David-Neto E, Xi L et al (2013) Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in subjects with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Diabetes Obes Metab 15(5):463–473
Rodbard HW, Seufert J, Aggarwal N, Cao A, Fung A, Pfeifer M et al (2016) Efficacy and safety of titrated canagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on metformin and sitagliptin. Diabetes Obes Metab 18(8):812–819
Kadowaki T, Haneda M, Inagaki N, Terauchi Y, Taniguchi A, Koiwai K et al (2014) Empagliflozin monotherapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II trial. Adv Ther 31(6):621–638
Lewin A, DeFronzo RA, Patel S, Liu D, Kaste R, Woerle HJ et al (2015) Initial combination of empagliflozin and linagliptin in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 38(3):394–402
Roden M, Merker L, Christiansen AV, Roux F, Salsali A, Kim G et al (2015) Safety, tolerability and effects on cardiometabolic risk factors of empagliflozin monotherapy in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind extension of a Phase III randomized controlled trial. Cardiovasc Diabetol 14:154
Hadjadj S, Rosenstock J, Meinicke T, Woerle HJ. Initial combination of empagliflozin and metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes. 2016,39(10):1718–1728
Nishimura R, Tanaka Y, Koiwai K, Inoue K, Hach T, Salsali A et al (2015) Effect of empagliflozin monotherapy on postprandial glucose and 24-hour glucose variability in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 4-week study. Cardiovasc Diabetol 14:11
DeFronzo RA, Lewin A, Patel S, Liu D, Kaste R, Woerle HJ et al (2015) Combination of empagliflozin and linagliptin as second-line therapy in subjects with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin. Diabetes Care 38(3):384–393
Ross S, Thamer C, Cescutti J, Meinicke T, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC (2015) Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin twice daily versus once daily in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin: a 16-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 17(7):699–702
Softeland E, Meier JJ, Vangen B, Toorawa R, Maldonado-Lutomirsky M, Broedl UC (2017) Empagliflozin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with linagliptin and metformin: a 24-week randomized, double-blind, parallel-group trial. Diabetes Care 40(2):201–209
Haring HU, Merker L, Seewaldt-Becker E, Weimer M, Meinicke T, Broedl UC et al (2014) Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Care 37(6):1650–1659
Rosenstock J, Jelaska A, Zeller C, Kim G, Broedl UC, Woerle HJ (2015) Impact of empagliflozin added on to basal insulin in type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on basal insulin: a 78-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 17(10):936–948
Rosenstock J, Jelaska A, Frappin G, Salsali A, Kim G, Woerle HJ et al (2014) Improved glucose control with weight loss, lower insulin doses, and no increased hypoglycemia with empagliflozin added to titrated multiple daily injections of insulin in obese inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 37(7):1815–1823
Kovacs CS, Seshiah V, Merker L, Christiansen AV, Roux F, Salsali A et al (2015) Empagliflozin as add-on therapy to pioglitazone with or without metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Ther 37(8):1773–1788.e1771
Merker L, Haring HU, Christiansen AV, Roux F, Salsali A, Kim G et al (2015) Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin in people with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 32(12):1555–1567
Haering HU, Merker L, Christiansen AV, Roux F, Salsali A, Kim G et al (2015) Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin plus sulphonylurea in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 110(1):82–90
Barnett AH, Mithal A, Manassie J, Jones R, Rattunde H, Woerle HJ et al (2014) Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin added to existing antidiabetes treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2(5):369–384
Fonseca VA, Ferrannini E, Wilding JP, Wilpshaar W, Dhanjal P, Ball G et al (2013) Active- and placebo-controlled dose-finding study to assess the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of multiple doses of ipragliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Complicat 27(3):268–273
Kashiwagi A, Kazuta K, Takinami Y, Yoshida S, Utsuno A, Nagase I (2015) Ipragliflozin improves glycemic control in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the BRIGHTEN study. Diabetol Int 6(1):8–18
Wilding JP, Ferrannini E, Fonseca VA, Wilpshaar W, Dhanjal P, Houzer A (2013) Efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin: a dose-finding study. Diabetes Obes Metab 15(5):403–409
Lu CH, Min KW, Chuang LM, Kokubo S, Yoshida S, Cha BS (2016) Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of ipragliflozin in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and inadequate glycemic control with metformin: results of a phase 3 randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicenter trial. J Diabetes Investig 7(3):366–373
Kashiwagi A, Akiyama N, Shiga T, Kazuta K, Utsuno A, Yoshida S et al (2015) Efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin as an add-on to a sulfonylurea in Japanese patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: results of the randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase III EMIT study. Diabetol Int 6(2):125–138
Kashiwagi A, Shiga T, Akiyama N, Kazuta K, Utsuno A, Yoshida S et al (2015) Efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin as an add-on to pioglitazone in Japanese patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (the SPOTLIGHT study). Diabetol Int 6(2):104–116
Kashiwagi A, Takahashi H, Ishikawa H, Yoshida S, Kazuta K, Utsuno A et al (2015) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study on long-term efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and renal impairment: results of the long-term ASP1941 safety evaluation in patients with type 2 diabetes with renal impairment (LANTERN) study. Diabetes Obes Metab 17(2):152–160
Kaku K, Watada H, Iwamoto Y, Utsunomiya K, Terauchi Y, Tobe K et al (2014) Efficacy and safety of monotherapy with the novel sodium/glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor tofogliflozin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a combined Phase 2 and 3 randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group comparative study. Cardiovasc Diabetol 13:65
Terra SG, Focht K, Davies M (2017) Phase III, efficacy and safety study of ertugliflozin monotherapy in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with diet and exercise alone. Diabetes Obes Metab 19(5):721–728
Xu L, Li Y, Lang J, Xia P, Zhao X, Wang L et al (2017) Effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibition on renal function and albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PeerJ 5:e3405
Rahmoune H, Thompson PW, Ward JM, Smith CD, Hong G, Brown J (2005) Glucose transporters in human renal proximal tubular cells isolated from the urine of patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes 54(12):3427–3434
Tabatabai NM, Sharma M, Blumenthal SS, Petering DH (2009) Enhanced expressions of sodium-glucose cotransporters in the kidneys of diabetic Zucker rats. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 83(1):e27–e30
Freitas HS, Anhe GF, Melo KF, Okamoto MM, Oliveira-Souza M, Bordin S et al (2008) Na(+)-glucose transporter-2 messenger ribonucleic acid expression in kidney of diabetic rats correlates with glycemic levels: involvement of hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha expression and activity. Endocrinology 149(2):717–724
Chichger H, Cleasby ME, Srai SK, Unwin RJ, Debnam ES, Marks J (2016) Experimental type II diabetes and related models of impaired glucose metabolism differentially regulate glucose transporters at the proximal tubule brush border membrane. Exp Physiol 101(6):731–742
Hannedouche TP, Delgado AG, Gnionsahe DA, Boitard C, Lacour B, Grunfeld JP (1990) Renal hemodynamics and segmental tubular reabsorption in early type 1 diabetes. Kidney Int 37(4):1126–1133
Vallon V, Richter K, Blantz RC, Thomson S, Osswald H (1999) Glomerular hyperfiltration in experimental diabetes mellitus: potential role of tubular reabsorption. J Am Soc Nephrol 10(12):2569–2576
Brenner BM (1983) Hemodynamically mediated glomerular injury and the progressive nature of kidney disease. Kidney Int 23(4):647–655
Vallon V, Rose M, Gerasimova M, Satriano J, Platt KA, Koepsell H et al (2013) Knockout of Na-glucose transporter SGLT2 attenuates hyperglycemia and glomerular hyperfiltration but not kidney growth or injury in diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 304(2):F156–F167
Yale JF, Bakris G, Cariou B, Nieto J, David-Neto E, Yue D et al (2014) Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin over 52 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. Diabetes Obes Metab 16(10):1016–1027
Rajasekeran H, Reich HN, Hladunewich MA, Cattran D, Lovshin JA, Lytvyn Y et al (2018) Dapagliflozin in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: a combined human-rodent pilot study. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 314(3):F412–Ff422
Macha S, Mattheus M, Halabi A, Pinnetti S, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC (2014) Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of empagliflozin, a sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, in subjects with renal impairment. Diabetes Obes Metab 16(3):215–222
Vallon V, Gerasimova M, Rose MA, Masuda T, Satriano J, Mayoux E et al (2014) SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin reduces renal growth and albuminuria in proportion to hyperglycemia and prevents glomerular hyperfiltration in diabetic Akita mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 306(2):F194–F204
Cherney D, Lund SS, Perkins BA, Groop PH, Cooper ME, Kaspers S et al (2016) The effect of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition with empagliflozin on microalbuminuria and macroalbuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 59(9):1860–1870
Gangadharan Komala M, Gross S, Mudaliar H, Huang C, Pegg K, Mather A et al (2014) Inhibition of kidney proximal tubular glucose reabsorption does not prevent against diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetic eNOS knockout mice. PLoS ONE 9(11):e108994
Iemitsu K, Iizuka T, Takihata M, Takai M, Nakajima S, Minami N et al (2016) Factors influencing changes in hemoglobin A1c and body weight during treatment of type 2 diabetes with ipragliflozin: interim analysis of the ASSIGN-K study. J Clin Med Res 8(5):373–378
Perkovic V, Heerspink HL, Chalmers J, Woodward M, Jun M, Li Q et al (2013) Intensive glucose control improves kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Kidney Int 83(3):517–523
Kramer H, Reboussin D, Bertoni AG, Marcovina S, Lipkin E, Greenway FL III, et al (2009) Obesity and albuminuria among adults with type 2 diabetes: the Look AHEAD (action for health in diabetes) study. Diabetes Care 32(5):851–853
Huang M, Matsushita K, Sang Y, Ballew SH, Astor BC, Coresh J (2015) Association of kidney function and albuminuria with prevalent and incident hypertension: the atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. Am J Kidney Dis 65(1):58–66
Abdel-Wahab AF, Bamagous GA, Al-Harizy RM, ElSawy NA, Shahzad N, Ibrahim IA et al (2018) Renal protective effect of SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin alone and in combination with irbesartan in a rat model of diabetic nephropathy. Biomed Pharmacother 103:59–66
Petrykiv SI, Laverman GD, de Zeeuw D, Heerspink HJL (2017) The albuminuria-lowering response to dapagliflozin is variable and reproducible among individual patients. Diabetes Obes Metab 19(10):1363–1370
Petrykiv S, Laverman GD, de Zeeuw D, Heerspink HJL (2018) Does SGLT2 inhibition with dapagliflozin overcome individual therapy resistance to RAAS inhibition? Diabetes Obes Metab 20(1):224–227
Sakai S, Kaku K, Seino Y, Inagaki N, Haneda M, Sasaki T et al (2016) Efficacy and safety of the SGLT2 inhibitor luseogliflozin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus stratified according to baseline body mass index: pooled analysis of data from 52-week phase III trials. Clin Ther 38(4):843.e849–862.e849
Funding
The current study was founded by the Zhejiang Medical and Health Platform Project of China (2017ZD007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, C., Wu, M., Chen, Z. et al. Effect of SGLT2 inhibitor on renal function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int Urol Nephrol 51, 655–669 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-019-02112-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-019-02112-6