Abstract
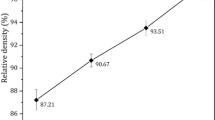
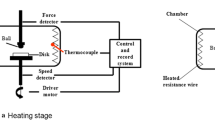
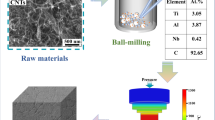
The TiAl matrix composites were manufactured using spark plasma sintering under the conditions of 1100 °C/10 min/30 MPa. The effect of Ti3SiC2 amount on microstructures and properties of TiAl matrix composites was investigated. Ti3SiC2 was homogeneously distributed in the TiAl matrix, and it partly decomposed to form Ti5Si3 and TiC. The TiAl matrix with 30 wt% of Ti3SiC2 exhibited the lowest friction coefficient and wear rate of 0.507 and 1.35 × 10–4 mm3 N−1 m−1 at room temperature and 0.423 and 0.21 × 10–4 mm3 N−1 m−1 at 550 °C, while the compression strength reached the maximum value of 1080 GPa at room temperature and 640 GPa at 550 °C, respectively. The hardness reached the value of 5.1 GPa. The TiAl matrix composites had a lower friction coefficient and wear rate at 550 °C than at room temperature. A Ti3SiC2 lubricating film was formed on the friction surface of the TiAl matrix composites after friction test at room temperature, while a Fe–Ti–Al–Si-oxide lubricating film was formed after friction test at 550 °C. The wear mechanisms of the TiAl matrix composites with the Ti3SiC2 addition were mainly abrasive wear and adhesive wear at room temperature and 550 °C, respectively.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bewlay, B.P., Nag, S., Suzuki, A., Weimer, M.J.: TiAl alloys in commercial aircraft engines. Mater. High Temp. 33, 549–559 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/09603409.2016.1183068
Cui, S., Cui, C.X., Xie, J.Q., Liu, S.J., Shi, J.J.: Carbon fibers coated with graphene reinforced TiAl alloy composite with high strength and toughness. Sci. Rep. 8, 2364 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20799-y
Pan, Y., Lu, X., Hayat, M., Yang, F., Liu, C.C., Li, Y., Li, X.Y., Xu, W., Qu, X.H., Cao, P.: Effect of Sn addition on the high-temperature oxidation behavior of high Nb-containing TiAl alloys. Corros. Sci. 116, 108449 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2020.108449
Tian, S.G., Lv, X.X., Yu, H.C., Wang, Q., Jiao, Z.H., Sun, H.F.: Creep behavior and deformation feature of TiAl-Nb alloy with various states at high temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 651, 490–498 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.10.096
Klocke, F., Herrig, T., Zeis, M., Klink, A.: Experimental research on the electrochemical machinability of selected γ-TiAl alloys for the manufacture of future aero engine components. Procedia CIRP 35, 50–54 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2015.08.050
Jung, J.Y., Park, C., Bae, C.: Effects of high-response TiAl turbine wheel on engine performance under transient conditions. JSAE 2015, 01 (1881). https://doi.org/10.4271/2015-01-1881
Cheng, J., Li, F., Zhu, S.Y., Yu, Y., Qiao, Z.H., Yang, J.: Electrochemical corrosion and tribological evaluation of TiAl alloy for marine application. Tribol. Int. 115, 483–492 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2017.06.027
Korotitskiy, A.V., Asnis, E.A., Piskun, N.V., Statkevich, I.I., Gorshenkov, M.V., Korotitski, A.V.: A promising microstructure/deformability adjustment of β-stabilized γ-TiAl intermetallics. Mater. Lett. 162, 180–184 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.09.139
Yeh, C.L., Sun, W.E.: Use of TiH2 as a reactant in combustion synthesis of porous Ti5Si3 and Ti5Si3/TiAl intermetallics. J. Alloy. Compd. 669, 66–71 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.01.236
Tian, S.W., Jiang, H.T., Guo, W.Q., Zhang, G.H., Zeng, S.W.: Hot deformation and dynamic recrystallization behavior of TiAl-based alloy. Intermetallics 112, 106521 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2019.106521
Sun, Y.J., Lin, Y.F., Zhang, N., Zhang, D.L.: Microstructures and mechanical properties of TiAl alloy fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 34, 2040036 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217979220400366
Xu, Z.S., Shi, X.L., Zhang, Q.X., Zhai, W.Z., Yao, J., Chen, L., Zhu, Q.S., Xiao, Y.C.: High-temperature tribological performance of Ti3SiC2/TiAl self-lubricating composite against Si3N4 in air. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 23, 2255–2264 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-0969-9
Xu, Z.S., Xue, B., Shi, X.L., Zhang, Q.X., Zhai, W.Z., Yao, J., Wang, Y.F.: sliding speed and load dependence of tribological properties of Ti3SiC2/TiAl composite. Tribol. Trans. 58, 87–96 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/10402004.2014.951748
Shen, Q., Shi, X.L., Zou, J.L., Yang, K., Huang, C., Zhang, A., Ibrahim, M.M., Wang, Y.F.: Tribological performance and self-lubricating film formation mechanism of TiAl-based composites at elevated temperatures. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 26, 268–276 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2433-5
Xu, Z.S., Shi, X.L., Wang, M., Zhai, W.Z., Yao, J., Song, S.Y., Zhang, Q.X.: Effect of Ag and Ti3SiC2 on tribological properties of TiAl matrix self-lubricating composites at room and increased temperatures. Tribol. Lett. 53, 617–629 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-014-0299-y
Xu, Z.S., Zhang, Q.X., Shi, X.L., Zhai, W.Z., Yang, K.: Tribological properties of TiAl matrix self-lubricating composites containing multilayer graphene and Ti3SiC2 at high temperatures. Tribol. Trans. 58(6), 1131–1141 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/10402004.2015.1046007
Xu, Z.S., Shi, X.L., Zhang, Q.X., Zhai, W.Z., Li, X.X., Yao, J., Chen, L., Zhu, Q.S., Xiao, Y.C.: Effect of sliding speed and applied load on dry sliding tribological performance of TiAl matrix self-lubricating composites. Tribol. Lett. 55(3), 393–404 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-014-0367-3
Ghosh, N., Harimkar, S.: Microstructure and wear behavior of spark plasma sintered Ti3SiC2 and Ti3SiC2–TiC composites. Ceram. Int. 39, 4597–4607 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.105-106.31
Rahmani, K., Majzoobi, G.: The effect of particle size on microstructure, relative density and indentation load of Mg-B4C composites fabricated at different loading rates. J. Compos. Mater. 54(17), 1–15 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1177/0021998319896009
Gürbüz, M., Mutuk, T., Uyan, P.: Mechanical, wear and thermal behaviors of graphene reinforced titanium composites. Met. Mater. Int. 27, 744–752 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00673-1
Zhang, Z.F., Sun, Z.M., Hashimoto, H.: Rapid synthesis of ternary carbide Ti3SiC2 through pulse-discharge sintering technique from Ti/Si/TiC powders. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 33, 3321–3328 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-002-0320-1
Talero, R., Trusilewicz, L., Delgado, A., Pedrajas, C., Lannegrand, R., Rahhal, V., Mejía, R., Delvastoe, S., Ramírezf, F.A.: Comparative and semi-quantitative XRD analysis of Friedel’s salt originating from pozzolan and Portland cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 25, 2370–2380 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2010.11.037
El-Raghy, T., Barsoum, M.W., Sika, M.: Reaction of Al with Ti3SiC2 in the 800–1000 °C temperature range. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 298, 174–178 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(00)01281-8
Gu, W.L., Yan, C.K., Zhou, Y.C.: Reactions between Al and Ti3SiC2 in temperature range of 600–650 °C. Scripta Mater. 49, 1075–1080 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2003.08.016
Wang, Q., Chen, G.Q., Wang, K., Fu, X.S., Zhou, W.L.: Microstructural evolution and growth kinetics of interfacial compounds in TiAl/Ti3SiC2 diffusion bonding joints. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 756, 149–155 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.04.034
Dang, W.T., Ren, S.F., Zhou, J.S., Yu, Y.J., Wang, L.Q.: The tribological properties of Ti3SiC2/Cu/Al/SiC composite at elevated temperatures. Tribol. Int. 104, 294–302 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2016.09.008
Zuo, L.J., Ye, B., Feng, J., Zhang, H.X., Kong, X.Y., Jiang, H.Y.: Effect of ε-Al3Ni phase on mechanical properties of Al–Si–Cu–Mg–Ni alloys at elevated temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 772, 138794 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.138794
Shi, X.L., Yao, J., Xu, Z.S., Zhai, W.Z., Song, S.Y., Wang, M., Zhang, Q.X.: Tribological performance of TiAl matrix self-lubricating composites containing Ag, Ti3SiC2 and BaF2/CaF2 tested from room temperature to 600 °C. Mater. Des. 53, 620–633 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.07.053
Xu, Z.S., Shi, X.L., Zhang, Q.X., Zhai, W.Z., Li, X.X., Yao, J., Song, S.Y.: Wear and friction of TiAl matrix self-lubricating composites against Si3N4 in air at room and elevated temperatures. Tribol. Trans. 57(6), 1017–1027 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/10402004.2014.931497
Zhai, W.Z., Shi, X.L., Wang, M., Xu, Z.S., Yao, J., Song, S.Y., Zhang, Q.X.: Friction and wear properties of TiAl-Ti3SiC2-MoS2 composites prepared by spark plasma sintering. Tribol. Trans. 57(3), 416–424 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/10402004.2014.880539
Xu, Z.S., Yao, J., Shi, X.L., Zhai, W.Z., Ibrahim, A.M.M., Xiao, Y.C., Chen, L., Zhu, Q.S., Zhang, A.: A study of the frictional layer of TiAl-12Ag-5TiB2 composite during dry sliding wear. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 24(8), 2875–2884 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1569-z
Barsoum, M.W.: The MN+1AXN phases: a new class of solids: thermodynamically stable nanolaminates. Prog. Solid State Chem. 28, 201–281 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6786(00)00006-6
Gupta, S., Barsoum, M.W.: On the tribology of the MAX phases and their composites during dry sliding: a review. Wear 271, 1878–1894 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2011.01.043
Kalin, M.: Influence of flash temperatures on the tribological behaviour in low-speed sliding: a review. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 374, 390–397 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2004.03.031
Wang, L., Cheng, J., Zhu, S.Y., Yuan, Y., Qiaio, Z.H., Yang, J., Liu, W.M.: High temperature wear behaviors of TiAl-TiB2 composites. Tribol. Lett. 65, 144 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-017-0924-7
An, Q., Huang, L.J., Bao, T., Zhang, R., Jiang, S., Gen, L., Xiao, M.M.: Microstructure and tribological behavior of in situ synthesized (TiB+TiC)/Ti6Al4V (TiB/TiC=1/1) composites. Tribol. Int. 121, 252–259 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2020.106177
Yang, J., Gu, W., Pan, L.M., Song, K., Chen, X., Qiu, T.: Friction and wear properties of in situ (TiB2 + TiC)/Ti3SiC2 composites. Wear 271, 2940–2946 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2011.06.017
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Program of Scientific Research of Higher Education of Hebei Province (Grant No. ZD2021099).
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, Q., Lou, Z., Guan, Y. et al. Effect of Ti3SiC2 Amount on Microstructures and Properties of TiAl Matrix Composites. Tribol Lett 70, 37 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-022-01571-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-022-01571-w