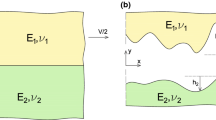
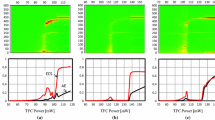
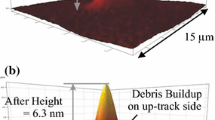
Abstract
A novel region of tribological interaction is explored by inducing near contact between the magnetic recording slider and disk. In this study, we performed frictional measurements over a wide range of subambient air pressure and disk rotation rate. Since the slider is supported over the disk by an air bearing, it has been found that cycling from ambient to subambient and then back up to ambient pressure over several minutes of time forms a frictional hysteresis loop. The high-friction branch of the loop, referred to as the bridged state, is characterized by an average frictional displacement and resonant vibration of the suspension mount assembly. The bridged state is currently employed for accelerated wear testing of magnetic slider/disk/lubricant systems. Future magnetic recording systems designed to operate at increasingly lower physical spacing will need to take into account these frictional forces which accompany the incipient contact between the lubricated disk and slider with finite surface roughness. A single degree of freedom model is solved to determine the equivalent dynamic friction force on the slider as an impulse series with random impulse frequency and amplitude from the measured frictional displacement in the bridged state. The mean slider-disk spacing in the bridged state is derived from the experimental friction force, the spacing probability density function, and the adhesion stress from the Lifshitz model for dispersion interaction energy.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yuan, Z-M., Liu, B., Wang, J.: Flash temperature induced magnetic degradation in high density magnetic recording. J. Appl. Phys. 87, 6158–6160 (2000)
Tao, Q., Lee, H.P., Lim, S.P.: Contact analysis of impact in magnetic head disk interfaces. Tribol. Int. 36, 49–56 (2003)
Thornton, B.H., Bogy, D.B.: Head-disk interface dynamic instability due to intermolecular forces. IEEE Trans. Magn. 39, 2420–2422 (2003)
Ambekar, R., Gupta, V., Bogy, D.B.: Experimental and numerical investigation of dynamic instability in the head disk interface at proximity. J. Tribol. 127, 530–536 (2005)
Kato, T., Watanabe, S., Matsuoka, H.: Dynamic characteristics of an in-contact head slider considering meniscus force: part 1—formulation and application to the disk with sinusoidal undulation. J. Tribol. 122, 633–638 (2000)
Kato, T., Watanabe, S., Matsuoka, H.: Dynamic characteristics of an in-contact head slider considering meniscus force: part 2—application to the disk with random undulation and design conditions. J. Tribol. 123, 168–174 (2001)
Tanaka, H., Yonemura, S., Tokisue, H.: Slider dynamics during continuous contact with textured and smooth disks in ultra low flying height. IEEE Trans. Magn. 37, 906–911 (2001)
Mate, C.M., Arnett, P.C., Baumgart, P., Dai, Q., Guruz, U.M., Knigge, B.E., Payne, R.N., Ruiz, O.J., Wang, G.J., Yen, B.K.: Dynamics of contacting head-disk interfaces. IEEE Trans. Magn. 40, 3156–3158 (2004)
Xu, J.G., Kohira, H., Tanaka, H., Saegusa, S.: Partial-contact head-disk interface approach for high-density recording. IEEE Trans. Magn. 41, 3031–3033 (2005)
Ono, K., Ohara, S.: Experimental identification of elastic, damping and adhesion forces in collision of spherical sliders with stationary magnetic disks. J. Tribol. 127, 365–375 (2005)
Ono, K., Yamane, M., Yamaura, H.: Experimental and analytical study of bouncing vibrations of a flying head slider in a near-contact regime. J. Tribol. 127, 376–386 (2005)
Mayeed, M.S., Kato, T., Jhon, M.S., Mitsuya, Y.: Surface perturbations on the perfluoropolyether molecules in the melt and the gas-like conditions. IEEE Trans. Magn. 40, 3180–3182 (2004)
Matsuoka, H., Ohkubo, S., Fukui, S.: Corrected expression of the van der Waals pressure for multilayered system with application to analyses of static characteristics of flying head sliders with an ultrasmall spacing: Microsyst Techn. Micro Nanosyst—Inf. Stor. Proc. Syst. 11, 824–829 (2005)
Tanaka, K., Kato, T., Matsumoto, Y.: Molecular dynamics simulation of vibrational friction force due to molecular deformation in confined lubricant film. J. Tribol. 125, 587–591 (2003)
Kamei, D., Zhou, H., Suzuki, K., Konno, K., Takami, S., Kubo, M., Miyamoto, A.: Computational chemistry study on the dynamics of lubricant molecules under shear conditions. Tribol. Int. 36, 297–303 (2003)
Khurshudov, A., Baumgart, P., Waltman, R.J.: In-situ quantitative analysis of nano-scale lubricant migration at the slider-disk interface. Wear 229, 690–699 (1999)
Khurshudov, A., Waltman, R.J.: The contribution of thin PFPE lubricants to slider-disk spacing. Tribol. Lett. 11, 143–149 (2001)
Waltman, R.J., Khurshudov, A.G.: The contribution of thin PFPE lubricants to slider-disk spacing. 2. effect of film thickness and lubricant end groups. Tribol. Lett. 13, 197–202 (2002)
Novotny, V.J.: Mechanical integration of high recording density drives. IEEE Trans. Magn. 32, 1826–1831 (1996)
Karis, T.E., Tawakkul, M.A.: Water adsorption and friction on thin film magnetic recording disks. Tribol. Trans. 46, 469–478 (2003)
Karis, T.E., Nayak, U.V.: Liquid nanodroplets on thin film magnetic recording disks. Tribol. Trans. 47, 103–110 (2004)
Karis, T.E., Kim, W.T., Jhon, M.S.: Spreading and dewetting in nanoscale lubrication. Tribol. Lett. 18, 27–41 (2005)
Tagawa, N., Mori, A.: Effects of functional end-groups on nano-tribology characteristics of ultra-thin liquid lubricant films in hard disk drives. IEEE Trans. Magn. 41, 825–830 (2005)
Bai, M., Kato, K.: Analysis of contact deformation and stiction between textured disk and textured slider. J. Tribol. 123, 350–357 (2001)
Suh, A.Y., Polycarpou A.: Adhesive contact modeling for sub-5-nm ultralow flying magnetic storage head-disk interfaces including roughness effects. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 104328-1–104328-11 (2005)
Karis, T.E.: Lubricants for the disk drive industry. In: Rudnick, L. (ed.), Synthetic, Mineral Oil, and Bio-Based Lubricants Chemistry and Technology, CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, LLC, Boca Raton, FL, pp. 623–654 (2006)
Ambekar, R.P., Bogy D.B., Dai Q., Marchon B.: Critical clearance and lubricant instability at the head-disk interface of a disk drive. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 033104-1–033104-3 (2008)
Crone, R.M., Peck, P.R., Jhon, M.S., Karis, T.E.: Scaling criteria for slider miniaturization using the generalized reynolds equation. J. Tribol. 115, 566–572 (1993)
Karis, T.E., Guo, X.-C., Marinero, E., Marchon, B.: Surface chemistry of NiP plated substrates. IEEE Trans. Magn. 41, 3247–3249 (2005)
Karis, T.E.: Tribochemistry in contact recording. Tribol. Lett. 10, 149–162 (2001)
Karis, T.E.: Water adsorption on thin film magnetic recording media. J. Coll. Int. Sci. 225, 196–203 (2000)
Man, Y.J., Yu S.K., Liu B.: Characterization and formation mechanism understanding of asperities to be burnished. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 303, e101–e105 (2006)
Fred Li, Z., Chen, C-Y., Liu, J.J.: Study of head-disk interference at low-flying height. IEEE Trans. Magn. 39, 2462–2464 (2003)
Marchon, B., Karis, T., Dai, Q., Pit, R.: A model for lubricant flow from disk to slider. IEEE Trans. Magn. 39, 2447–2449 (2003)
Ma, X., Chen, J., Richter, H.J., Tang, H., Gui, J.: Contribution of lubricant thickness to head—media spacing. IEEE Trans. Magn. 37, 1824–1826 (2001)
Papoulis, A.: Probability, Random Variables, and Stochastic Processes, McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, NY (1965)
Yoshizawa, H., Chen, Y-L., Israelachvili, J.: Fundamental mechanisms of interfacial friction. 1. relation between adhesion and friction. J. Phys. Chem. 97, 4128–4140 (1993)
Persson, B.N.J.: Theory of friction: friction dynamic for boundary lubricated surfaces. Phys. Rev. B 55, 8004–8012 (1997)
Yatsue, T., Ishihara, H., Matsumoto, H., Tani, H.: Design of carbon surface functional groups on the viewpoint of lubricant layer structure. Trib. Trans. 43, 802–808 (2000)
French, R.H.: Origins and applications of london dispersion forces and hamaker constants in ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 83, 2117–2146 (2000)
Ninham, B.W., Parsegian, V.A.: Van der walls forces across triple-layer films. J. Chem. Phys. 52, 4578–4587 (1970)
White, L.R., Dagastine, R.R., Jones, P.M., Hsia Y-T.: Van der waals force calculation between laminated media, pertinent to the magnetic storage head-disk interface. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 104503 (2005)
Hough, D.B., White, L.R.: The calculation of hamaker constants from lifshitz theory with applications to wetting phenomena. Adv. Coll. Int. Sci. 14, 3–41 (1980)
Dagastine, R.R., White, L.R., Jones, P.M., Hsia Y-T.: Effect of media overcoat on van der waals interaction at the head-disk interface. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 126106 (2005)
Karis, T.E., Guo X-C.: Molecular adhesion model for the bridged state of a magnetic recording slider. IEEE Trans. Magn. 43, 2232–2234 (2007)
Marchon, B., Karis, T., Dai, Q., Pit, R.: A model for lubricant flow from disk to slider. IEEE Trans. Magn. 39, 2447–2449 (2003)
Ma, Y.S., Liu, G.: Lubricant transfer from disk to slider in hard disk drives. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 143516 (2007)
Waltman, R.J., Tyndall, G.W., Pacansky, J., Berry, R.J.: Impact of polymer structure and confinement on the kinetics of zdol 4000 bonding to amorphous-hydrogenated carbon. Tribol. Lett. 7, 91–102 (1999)
Aranson, I.S., Tsimring, L.S., Vinokur, V.M.: Stick-slip friction and nucleation dynamics of ultrathin liquid films. Phys. Rev. B 65, 125402 (2002)
Narumanchi, S.V.J., Murthy, J.Y., Amon, C.H.: Boltzmann transport equation-based thermal modeling approaches for hotspots in microelectronics. Heat Mass Transfer 42, 478–491 (2006)
Cannara, R.J., Brukman, M.J., Cimatu, K., Sumant, A.V., Baldelli, S., Carpick, R.W.: Nanoscale friction varied by isotopic shifting of surface vibrational frequencies. Science 318, 780–783 (2007)
Mriziq, K.S., Dai, H.J., Dadmun, M.D., Jellison, G.E., Cochran, H.D.: High-shear-rate optical rheometer. Rev. Sci. Instr. 75, 2171–2176 (2004)
Acknowledgments
We thank B. Marchon, P. Baumgart, M. Mate, V. Nayak, R. Payne, B. Knigge, F. Hendriks, and Q. Dai for technical discussions. The authors are also grateful to J. He, R. White, J. Hopkins, and R-H. Wang for their assistance with the investigations of surface indentations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karis, T.E., Guo, XC. & Juang, JY. Dynamics in the Bridged State of a Magnetic Recording Slider. Tribol Lett 30, 123–140 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-008-9319-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-008-9319-0