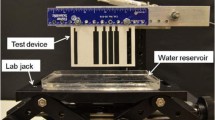
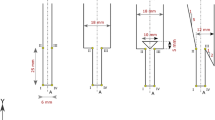
Abstract
Paper-based microfluidics has grown continuously over the last few years. One of the most important characteristics of paper-based microfluidic devices is the ability to pump fluids with the single action of capillary forces. However, fluid flow control in paper-based microfluidic devices has been studied primarily through empirical approaches; and as paper-based microfluidic devices have become more complex, more general and precise models of fluid flow are required. Particularly difficult to model are unsaturated flow conditions, which are critical to the overall performance of paper-based analytical devices, which may contain pre-adsorbed reagents such as indicator particles or antibodies. In this work we propose an objective test and a discussion on the suitability of different models (including a novel model derived here from LET-based models) that represent fluid imbibition dynamics in paper substrates. We reproduce experimental fluid fronts with the best parameter fits of the different models to show their actual capabilities to represent the moisture content function and present an analysis of propagation of uncertainties to obtain a final objective quantification of the quality of model fits. This objective analysis will endow the paper-based microfluidics community with objective information about modeling tools to improve the designs and performance of these devices.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Notes
The set of physicochemical hypotheses of this model is described in the supporting information.
References
Bear, J., Cheng, A.H.D.: Modeling Groundwater Flow and Contaminant Transport, vol. 23. Springer, Dordrecht (2010)
Berli, C.L.A., Kler, P.A.: A quantitative model for lateral flow assays. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 20(7), 104 (2016)
Boltzmann, L.: Zur integration der diffusionsgleichung bei variabeln diffusionscoefficienten (to integrate the diffusion equation with variable diffusion coefficients). Ann. Phys. 289(13), 959–964 (1894)
Brooks, S.: Markov chain Monte Carlo method and its application. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. D (the Statistician) 47(1), 69–100 (1998)
Brooks, R., Corey, T.: Hydraulic properties of porous media. Hydrol. Pap. Colo. State Univ. 24, 37 (1964)
Brooks, S., Gelman, A., Jones, G., Meng, X.: Handbook of Markov Chain Monte Carlo. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2011)
Bruce, R., Klute, A.: The measurement of soil moisture diffusivity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 20(4), 458–462 (1956)
Chakravarti, N.: Isotonic median regression: a linear programming approach. Math. Oper. Res. 14(2), 303–308 (1989)
Cummins, B.M., Chinthapatla, R., Ligler, F.S., Walker, G.M.: Time-dependent model for fluid flow in porous materials with multiple pore sizes. Anal. Chem. 89(8), 4377–4381 (2017)
Das, S., Mitra, S.K.: Different regimes in vertical capillary filling. Phys. Rev. E 87(6), 063005 (2013)
Das, S., Waghmare, P.R., Mitra, S.K.: Early regimes of capillary filling. Phys. Rev. E 86(6), 067301 (2012)
Elizalde, E., Urteaga, R., Berli, C.L.A.: Precise capillary flow for paper-based viscometry. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 20(10), 1–8 (2016)
Espejo, A., Giráldez, J.V., Vanderlinden, K., Taguas, E., Pedrera, A.: A method for estimating soil water diffusivity from moisture profiles and its application across an experimental catchment. J. Hydrol. 516, 161–168 (2014)
Evangelides, C., Tzimopoulos, C., Arampatzis, G.: Flux–saturation relationship for unsaturated horizontal flow. Soil Sci. 170(9), 671–679 (2005)
Evangelides, C., Arampatzis, G., Tzimopoulos, C.: Estimation of soil moisture profile and diffusivity using simple laboratory procedures. Soil Sci. 175(3), 118–127 (2010)
Feinberg, J., Langtangen, H.P.: Chaospy: an open source tool for designing methods of uncertainty quantification. J. Comput. Sci. 11, 46–57 (2015)
Feldt, R.: BlackBoxOptim.jl (2019). https://github.com/robertfeldt/BlackBoxOptim.jl
Franck, N., Schaumburg, F., Kler, P.A., Urteaga, R.: Precise electroosmotic flow measurements on paper substrates. Electrophoresis 42(7–8), 975–982 (2021)
Fritsch, F.N., Carlson, R.E.: Monotone piecewise cubic interpolation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 17(2), 238–246 (1980)
Gamazo, P., Slooten, L.J., Carrera, J., Saaltink, M.W., Bea, S., Soler, J.: Proost: object-oriented approach to multiphase reactive transport modeling in porous media. J. Hydroinform. 18(2), 310–328 (2016)
Gerlero, G.S., Kler, P.A., Berli, C.L.A.: Fronts.jl (2020). https://github.com/gerlero/Fronts.jl
Gerlero, G.S., Márquez Damián, S., Schaumburg, F., Franck, N., Kler, P.A.: Numerical simulations of paper-based electrophoretic separations with open-source tools. Electrophoresis 42, 1543–1551 (2021)
Gratiet, L.L., Marelli, S., Sudret, B.: Metamodel-Based Sensitivity Analysis: Polynomial Chaos Expansions and Gaussian Processes. In: Ghanem R., Higdon D., Owhadi H. (eds) Handbook of Uncertainty Quantification. Springer, Cham, pp. 1–37 (2016)
Hassan, Su., Tariq, A., Noreen, Z., Donia, A., Zaidi, S.Z., Bokhari, H., Zhang, X.: Capillary-driven flow microfluidics combined with smartphone detection: an emerging tool for point-of-care diagnostics. Diagnostics 10(8), 509 (2020)
Hertaeg, M.J., Tabor, R.F., Berry, J.D., Garnier, G.: Radial wicking of biological fluids in paper. Langmuir 36(28), 8209–8217 (2020)
Hong, S., Kim, W.: Dynamics of water imbibition through paper channels with wax boundaries. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 19(4), 845–853 (2015)
Horgue, P., Soulaine, C., Franc, J., Guibert, R., Debenest, G.: An open-source toolbox for multiphase flow in porous media. Comput. Phys. Commun. 187, 217–226 (2015)
Kim, T.H., Hahn, Y.K., Kim, M.S.: Recent advances of fluid manipulation technologies in microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (\(\mu\)pads) toward multi-step assays. Micromachines 11(3), 269 (2020)
Lim, H., Jafry, A.T., Lee, J.: Fabrication, flow control, and applications of microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Molecules 24(16), 2869 (2019)
Lomeland, F.: Overview of the LET family of versatile correlations for flow functions. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium of the Society of Core Analysts, pp. SCA2018–056 (2018)
Lomeland, F., Ebeltoft, E.: A new versatile capillary pressure correlation. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium of the Society of Core Analysts, vol 29, pp. SCA2008–08 (2008)
Lomeland, F., Ebeltoft, E., Thomas, W.H.: A new versatile relative permeability correlation. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium of the Society of Core Analysts, vol 112, pp. SCA2005–32 (2005)
Modha, S., Castro, C., Tsutsui, H.: Recent developments in flow modeling and fluid control for paper-based microfluidic biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron., 178, 113026 (2021)
Mora, M.F., Garcia, C.D., Schaumburg, F., Kler, P.A., Berli, C.L., Hashimoto, M., Carrilho, E.: Patterning and modeling three-dimensional microfluidic devices fabricated on a single sheet of paper. Anal. Chem. 91(13), 8298–8303 (2019)
Nagel, J., Sudret, B.: Spectral likelihood expansions for Bayesian inference. J. Comput. Phys. 309, 267–294 (2016)
Ozer, T., McMahon, C., Henry, C.S.: Advances in paper-based analytical devices. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 13, 85–109 (2020)
Pan, B., Clarkson, C.R., Atwa, M., Tong, X., Debuhr, C., Ghanizadeh, A., Birss, V.I.: Spontaneous imbibition dynamics of liquids in partially-wet nanoporous media: experiment and theory. Transp. Porous Media 137(3), 555–574 (2021)
Perez-Cruz, A., Stiharu, I., Dominguez-Gonzalez, A.: Two-dimensional model of imbibition into paper-based networks using Richards’ equation. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 21(5), 98 (2017)
Philip, J.: Numerical solution of equations of the diffusion type with diffusivity concentration-dependent. Trans. Faraday Soc. 51, 885–892 (1955)
Rath, D., Toley, B.J.: Modeling-guided design of paper microfluidic networks: a case study of sequential fluid delivery. ACS Sens. 6, 91–99 (2020)
Rath, D., Sathishkumar, N., Toley, B.J.: Experimental measurement of parameters governing flow rates and partial saturation in paper-based microfluidic devices. Langmuir 34(30), 8758–8766 (2018)
Richards, L.A.: Capillary conduction of liquids through porous mediums. Physics 1(5), 318–333 (1931)
Ruoff, A.L., Prince, D.L., Giddings, J.C., Stewart, G.H.: The diffusion analogy for solvent flow in paper. Kolloid Z. 166(2), 144–151 (1959)
Ruoff, A.L., Stewart, G.H., Shin, H.K., Giddings, J.C.: Diffusion of liquids in unsaturated paper. Kolloid Z. 173(1), 14 (1960)
Salentijn, G.I., Grajewski, M., Verpoorte, E.: Reinventing (bio) chemical analysis with paper. Anal. Chem. 90(23), 13815–13825 (2018)
Saltelli, A., Ratto, M., Andres, T., Campolongo, F., Cariboni, J., Gatelli, D., Saisana, M., Tarantola, S.: Global Sensitivity Analysis. The Primer, vol. 304. Wiley, Hoboken (2008)
Salvatier, J., Wiecki, T., Fonnesbeck, C.: Probabilistic programming in python using pymc3. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2, e55 (2016)
Santagata, T., Solimene, R., Aprea, G., Salatino, P.: Modelling and experimental characterization of unsaturated flow in absorbent and swelling porous media: material characterization. Transp. Porous Media 134(3), 725–753 (2020)
Schaumburg, F., Berli, C.L.A.: Assessing the rapid flow in multilayer paper-based microfluidic devices. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 23(8), 98 (2019)
Schaumburg, F., Kler, P.A., Berli, C.L.A.: Numerical prototyping of lateral flow biosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 259, 1099–1107 (2018a)
Schaumburg, F., Urteaga, R., Kler, P.A., Berli, C.L.A.: Design keys for paper-based concentration gradient generators. J. Chromatogr. A 1561, 83–91 (2018b)
Sobol, I.: Global sensitivity indices for nonlinear mathematical models and their Monte Carlo estimates. Math. Comput. Simul. 55(1–3), 271–280 (2001)
Taylor, J.: Introduction to Error Analysis, the Study of Uncertainties in Physical Measurements. University Science Books, New York (1997)
Terzis, A., Yang, G., Zarikos, I., Elizalde, E., Weigand, B., Kalfas, A., Ding, X.: A temperature-based diagnostic approach for paper-based microfluidics. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 22(3), 1–6 (2018)
Tirapu-Azpiroz, J., Silva, A.F., Ferreira, M.E., Candela, W.F.L., Bryant, P.W., Ohta, R.L., Engel, M., Steiner, M.B.: Modeling fluid transport in two-dimensional paper networks. J. Micro/Nanolithogr. MEMS MOEMS 17(2), 025003 (2018)
Tumidajski, P.J., Chan, G.W.: Boltzmann–Matano analysis of chloride diffusion into blended cement concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 8(4), 195–200 (1996)
Urteaga, R., Elizalde, E., Berli, C.L.A.: Transverse solute dispersion in microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (\(\mu\)PADs). Analyst 143(10), 2259–2266 (2018)
Urteaga, R., Mercuri, M., Gimenez, R., Bellino, M.G., Berli, C.L.: Spontaneous water adsorption–desorption oscillations in mesoporous thin films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 537, 407–413 (2019)
Van Genuchten, M.T.: A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 44(5), 892–898 (1980)
Vincent, O., Marguet, B., Stroock, A.D.: Imbibition triggered by capillary condensation in nanopores. Langmuir 33(7), 1655–1661 (2017)
Yamada, K., Shibata, H., Suzuki, K., Citterio, D.: Toward practical application of paper-based microfluidics for medical diagnostics: state-of-the-art and challenges. Lab Chip 17(7), 1206–1249 (2017)
Yetisen, A.K., Akram, M.S., Lowe, C.R.: Paper-based microfluidic point-of-care diagnostic devices. Lab Chip 13(12), 2210–2251 (2013)
Funding
This research was supported by CONICET, ANPCyT (Grant PICT 2018-02920), UTN (Grant PID ASUTNFE0005525) UNL(Grant CAI+D 50620190100114LI), Argentina and by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare the complete absence of financial/commercial conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerlero, G.S., Valdez, A.R., Urteaga, R. et al. Validity of Capillary Imbibition Models in Paper-Based Microfluidic Applications. Transp Porous Med 141, 359–378 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-021-01724-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-021-01724-w