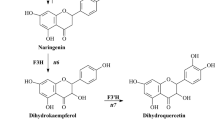
Abstract
Flavonoids are widely distributed secondary metabolic products with many biological functions in plants. Further elucidation of the accumulation and localization patterns of its biosynthesis enzymes will broaden our understanding of flavonoids biosynthesis and regulation. Chalcone isomerase (CHI, EC 5.5.1.6) is an early-step enzyme in the flavonoids biosynthesis pathway. In this study, using an antibody specifically developed against grapevine CHI enzyme, we found that the accumulation of CHI protein exhibited temporal and spatial specificity. In grape berries, CHI was investigated mainly in the outer hypodermis cells of exocarp tissues, in the vascular bundles of mesocarp; and in the integument and the cells around the raphe of seeds. At the subcellular level, CHI was visualized in the cytoplasm, nucleus, and plastids (chloroplasts) of the exocarp cells, while only in the cytoplasm of mesocarp vascular bundle cells. In grapevine vegetable organs, the leaf mesophyll and phloem of leaf veins, the pith ray and primary phloem of stems, the primary phloem and endoderm of roots, and the young leaves, leaf primordium, and the growth point of leaf buds were CHI signal-positive. In these tissue cells, CHI was primarily observed in the cytoplasm, cell wall, and nucleus. The distinct localization patterns of CHI suggested the complexity of flavonoids biosynthesis in grapevine.
Key Message
The distribution of CHI protein exhibited temporal and spatial specificity. Different subcellular localization patterns were observed in grape berries and grapevine vegetable tissues.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PAL:
-
Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase
- C4H:
-
Cinnamate 4-hydroxylase
- CHI:
-
Chalcone isomerase
- CHS:
-
Chalcone synthase
- ANS:
-
Anthocyanidin synthase
- IgG:
-
Immunoglobulin fractions
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- BS:
-
Blocking solution
- RSR:
-
Regular salt rinse solution
- DFAB:
-
Days after full bloom
References
Agati G, Brunetti C, Ferdinando MD, Ferrini F, Pollastri S, Tattini M (2013) Functional roles of flavonoids in photoprotection: New evidence, lessons from the past. Plant Physiol Biochem 72:35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.03.014
Ayre BG, Keller F, Turgeon R (2003) Symplastic continuity between companion cells and the translocation stream: long-distance transport is controlled by retention and retrieval mechanisms in the phloem. Plant Physiol 131:1518–1528. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.012054
Azuma A, Yakushiji H, Koshita Y, Kobayashi S (2012) Flavonoid biosynthesis-related genes in grape skin are differentially regulated by temperature and light conditions. Planta 236:1067–1080. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1650-x
Bardford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Biała W, Jasiński M (2018) The phenylpropanoid case—it is transport that matters. Front Plant Sci 9:1610. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01610
Bogs J, Jaffe FW, Takos AM, Walker AR, Robinson SP (2007) The grapevine transcription factor VvMYBPA1 regulates proanthocyanidin synthesis during fruit development. Plant Physiol 143:1347–1361. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.093203
Bondada BR, Matthews MA, Shackel KA (2005) Functional xylem in the post-veraison grape berry. J Exp Bot 56:2949–2957. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eri291
Braidot E, Zancani M, Petrussa E, Peresson C, Bertolini A, Patui S, Macrì F, Vianello A (2008) Transport and accumulation of flavonoids in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Plant Signal Behav 3(9):626–632. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.3.9.6686
Buer CS (2010) Flavonoids: New roles for old molecules. J Integr Plant Biol 52(1):98–111. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2010.00905.x
Buer CS, Muday GK, Djordjevic MA (2008) Implications of long-distance flavonoid movement in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Signal Behav 3(6):415–417. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.3.6.5440
Cadot Y, Minana-castelloa MT, Chevalier M (2006) Anatomical, histological, and histochemical changes in grape seeds from Vitis vinifera L. cv Cabernet Franc during fruit development. J Agric Food Chem 54:9206–9215. DOI: 10.1021/jf061326f
Chen JY, Wen PF, Kong WF, Pan QH, Wan SB, Huang WD (2006) Changes and subcellular localizations of the enzymes that involved in phenylpropanoid metabolism during grape berry development. J Plant Physiol 163:115–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2005.07.006
Cheng H, Li L, Cheng S, Cao F, Wang Y, Yuan H (2011) Molecular cloning and function assay of a chalcone isomerase gene (GbCHI) from Ginkgo biloba. Plant Cell Rep 30(1):49–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-010-0943-4
Dastmalchi M, Dhaubhadel S (2015) Soybean chalcone isomerase: evolution of the fold, and the differential expression and localization of the gene family. Planta 241(2):507–523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-014-2200-5
Falginella L, Gaspero GD, Castellarin SD (2012) Expression of flavonoid genes in the red grape berry of ‘Alicante Bouschet’ varies with the histological distribution of anthocyanins and their chemical composition. Planta 236:1037–1051. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1658-2
Famiani F, Walker RP, Tecsi L, Chen ZH, Proietti P, Leegood RC (2000) An immunohistochemical study of the compartmentation of metabolism during the development of grape (Vitis Vinifera L.) berries. J Exp Bot 51:675–683. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/51.345.675
Fang J, Jogaiah S, Guan L, Sun X, Abdelrahman M (2018) Coloring biology in grape skin: a prospective strategy for molecular farming. Physiola plantarum 164(4):429–441. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12822
Flamini R, Mattivi F, Rosso MD, Arapitsas P, Bavaresco L (2013) Advanced knowledge of three important classes of grape phenolics: anthocyanins, stilbenes and flavonols. Int J Mol Sci 14:19651–19669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141019651
Georgiev V, Ananga A, Tsolova V (2014) Recent advances and uses of grape flavonoids as nutraceuticals. Nutrients 6:391–415. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6010391
Gholami M (2004) Biosynthesis of anthocyanins in Shiraz grape berries. Acta Hortic (ISHS) 640:353–359. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2004.640.42
Gouot JC, Smith JP, Holzapfel BP, Walker AR, Barril C (2018) Grape berry flavonoids: a review of their biochemical responses to high and extreme high temperatures. J Exp Bot. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery392
Grotewold E (2004) The challenges of moving chemicals within and out of cells: insights into the transport of plant natural products. Planta 219:906–909. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1336-0
Hou ZX, Huang WD (2005) Immunohistochemical localization of IAA and ABP1 in strawberry shoot apexes during floral induction. Planta 222:678–687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-005-0014-1
Isla MI, Vattuone MA, Sampietro AR (1998) Essential group at the active site of Frapaeolum invertase. Phytochemistry 47:1189–1193. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(97)00757-7
Jeong ST, Goto-Yamamoto N, Hashizume K, Esaka M (2008) Expression of multi-copy flavonoid pathway genes coincides with anthocyanin, flavonol and flavan-3-ol accumulation of grapevine. Vitis 47(3):135–140
Kaltenbach M, Burke JR, Dindo M, Pabis A, Munsberg FS, Rabin A, Kamerlin SCL, Noel JP, Tawfik DS (2018) Evolution of chalcone isomerase from a noncatalytic ancestor. Nat Chem Biol 14(6):548. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-018-0042-3
Khan NM, Ahmad I, Ansari MY, Haqqi TM (2017) Wogonin, a natural flavonoid, intercalates with genomic DNA and exhibits protective effects in IL-1β stimulated osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Chem Biol Interact 274:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2017.06.025
Knogge W, Weissenböck G (1986) Tissue-distribution of secondary phenolic biosynthesis in developing primary leaves of Avena sativa L. Planta 167(2):196–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391415
Lepiniec L, Debeaujon I, Routaboul JM, Baudry A, Pourcel L, Nesi N, Caboche M (2006) Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonoids. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:405–430. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105252
Ma J, Fu X, Zhang T, Qian H, Zhao J (2019) Cloning and analyzing of chalcone isomerase gene (AaCHI) from Artemisia annua. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult (in press)
Park SH, Lee CW, Cho SM, Lee H, Park H, Lee J, Lee JH (2018) Crystal structure and enzymatic properties of chalcone isomerase from the Antarctic vascular plant Deschampsia antarctica Desv. PLoS ONE 13(2):e0192415. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0192415
Peer WA, Murphy AS (2007) Flavonoids and auxin transport: modulators or regulators ? Trends Plant Sci 12(12):556–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2007.10.003
Petroni K, Tonelli C (2011) Recent advances on the regulation of anthocyanin synthesis in reproductive organs. Plant Sci 181:219–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.05.009
Petrussa E, Braidot E, Zancani M, Peresson C, Bertolini A, Patui S, Vianello A (2013) Plant flavonoids—biosynthesis, transport and involvement in stress responses. Int J Mol Sci 14:14950–14973. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140714950
Saslowsky D, Winkel-Shirley B (2001) Localization of flavonoid enzymes in Arabidopsis roots. Plant J 27:37–48. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01073.x
Saslowsky DE, Warek U, Winkel-Shirley B (2005) Nuclear localization of flavonoid enzymes in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 280:23735–23740. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M413506200
Scott AC, Wyatt S, Tsou P, Robertson D, Allen NS (1999) Model system for plant cell biology: GFP imaging in living onion epidermal cells. Biotechniques 26:1125–1132. https://doi.org/10.2144/99266st04
Shi J, Yu J, Pohorly JE, Kakuda Y (2003) Polyphenolics in grape seeds—biochemistry and functionality. J Med Food 6:291–299. https://doi.org/10.1089/109662003772519831
Sun BS, Ribes AM, Leandro MC, Belchior AP, Spranger MI (2006) Stilbenes: quantitative extraction from grape skins, contribution of grape solids to wine and variation during wine maturation. Anal Chim Acta 563:382–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2005.12.002
Wang W, Tang K, Yang H-R, Wen P-F, Zhang P, Wang H-L, Huang W-D (2010a) Distribution of resveratrol and stilbene synthase in young grape plants (Vitis vinifera L. cv. Cabernet Sauvignon) and the effect of UV-C on its accumulation. Plant Physiol Biochem 48(2–3):142–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2009.12.002
Wang HL, Wang W, Zhang P, Pan QH, Zhan JC, Huang WD (2010b) Gene transcript accumulation, tissue and subcellular localization of anthocyanidin synthase (ANS) in developing grape berries. Plant Sci 179:103–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.04.002
Wang HL, Wang W, Li H, Zhan JC, Huang WD (2011) Expression, tissue and sub-cellular localization of anthocyanidin synthase (ANS) in grapevine. Protoplasma 248:267–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-010-0160-6
Wang W, Wang HL, Wan SB, Zhang JH, Zhang P, Zhan JC, Huang WD (2012) Chalcone isomerase in grapevine: gene expression and localization in the developing fruit. Biol Plantarum 56(3):545–550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-011-0216-2
Wang HL, Wang W, Zhan JC, Huang WD, Xu HY (2015) An efficient PEG-mediated transient gene expression system in grape protoplasts and its application in subcellular localization studies of flavonoids biosynthesis enzymes. Sci Horticult 191:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2015.04.039
Wang HL, Wang W, Zhan JC, Yan AL, Sun L, Zhang GJ, Wang XY, Ren JC, Xu HY (2016) The accumulation and localization of chalcone synthase in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 106:165–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.04.042
Wen PF, Chen JY, Kong WF, Pan QH, Wan SB, Huang WD (2005) Salicylic acid induced the expression of phenylalanine ammonialyase gene in grape berry. Plant Sci 169:928–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2005.06.011
Winkel BS (2017) When an enzyme isn’t just an enzyme anymore. J Exp Bot 68(7):1387–1389
Wolfe K, Wu X, Liu RH (2003) Antioxidant activity of apple peels. J Agric Food Chem 51:609–614. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf020782a
Wu YQ, Zhu MY, Jiang Y, Zhao DQ, Jun TAO (2018) Molecular characterization of chalcone isomerase (CHI) regulating flower color in herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.). J Integr Agric 17(1):122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(16)61628-3
Yin YC, Zhang XD, Gao ZQ, Hu T, Liu Y (2018) The research progress of chalcone isomerase (CHI) in plants. Mol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-018-0130-3
Yu XH, Chen MH, Liu CJ (2008) Nucleocytoplasmic-localized acyltransferases catalyze the malonylation of 7-O-glycosidic (iso) flavones in Medicago truncatula. Plant J 55:382–396. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0960-7412.2008.03509.x
Zamora P, Pardo A, Fierro A, Prieto H, Zúñiga GE (2013) Molecular characterization of the chalcone isomerase gene family in Deschampsia antarctica. Polar biol 36(9): 1269–1280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-013-1346-0
Zhao J, Dixon RA (2010) The ‘ins’ and ‘outs’ of flavonoid transport. Trends Plant Sci 15(2):72–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2009.11.006
Zhao FL, Li YJ, Hu Y, Gao YR, Zang XW, Ding Q, Wang YJ, Wen YQ (2016) A highly efficient grapevine mesophyll protoplast system for transient gene expression and the study of disease resistance proteins. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 125:43–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0928-7
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the special fund of China Agriculture Research System (CARS-29), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31601712), Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (No. 6182007), and the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Science (No. QNJJ201604).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Weidong Huang and Haiying Xu designed the experiments and revised the manuscript; Huiling Wang, Wei Wang, Jicheng Zhan performed the experiments; Huiling Wang and Wei Wang processed statistical analysis; Huiling Wang prepared the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Yu-Jin Hao.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Wang, W., Zhan, J. et al. Tissue-specific accumulation and subcellular localization of chalcone isomerase (CHI) in grapevine. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 137, 125–137 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-019-01557-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-019-01557-y