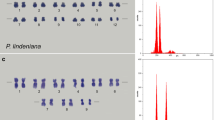
Abstract
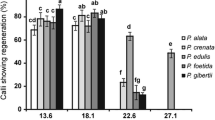
In vitro strategies for Passiflora have been developed owing to its economic and ecological importance. However, plantlet regeneration through somatic embryogenesis has presented some problems, such as the reproducibility of the protocol and formation of abnormal embryos and plantlets. Thus, this study aimed to establish a protocol exploring the embryogenic potential of immature zygotic embryos (IZE) of the wild species Passiflora miniata Vanderpl. and Passiflora speciosa Gardn. Friable calli, which formed on the abaxial surface of the cotyledons, yielded globular, heart-shaped, torpedo and cotyledonary somatic embryos, characterising the embryogenic response as asynchronous. A high percentage of normal regenerants (90 %) was obtained from IZE in media lacking 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) in comparison to the value of normal plantlets (60 %) regenerated from mature zygotic embryos inoculated in media with 2,4-D. This result demonstrates that IZE of P. miniata and P. speciosa possess sufficient levels of endogenous phytohormones to trigger a high rate of indirect somatic embryogenesis. All regenerated plantlets had the same genome size and chromosome number as the explant donor plants. Therefore, the indirect embryogenic pathway, employing IZE inoculated into media free of growth regulators, did not cause changes in the karyotype and morphology. Based on these results, IZE should be considered as explant for the establishment of somatic embryogenesis in other species. Besides, a new, reliable and relatively rapid protocol to recover plantlets of P. miniata and P. speciosa yielded several plants, which were acclimatised and used for ornamental purposes and breeding programs, and for reintroduction into biological reserves.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amorim JS, Souza MM, Viana AJC, Corrêa RX, Araújo IS, Ahnert D (2014) Cytogenetic, molecular and morphological characterization of Passiflora capsularis L. and Passiflora rubra L. Plant Syst Evol 300:1147–1162. doi:10.1007/s00606-013-0952-1
Amugune NO, Gopalan HNB, Bytebier B (1993) Leaf disc regeneration of passion fruit. Afr Crop Sci J 1:99–104. doi:10.4314/acsj.v1i2.69896
Anand SP, Jayakumar E, Jeyachandran R, Nandagobalan V, Doss A (2012) Direct organogenesis of Passiflora foetida L. through nodal explants. Plant Tissue Cult Biotech 22:87–91. doi:10.3329/ptcb.v22i1.11266
Bairu MW, Aremu AO, van Staden J (2011) Somaclonal variation in plants: causes and detection methods. Plant Growth Regul 63:147–173. doi:10.1007/s10725-010-9554-x
Benmahioul B, Kaïd-Harche M, Daguin F (2012) Influence of activated charcoal on in vitro embryo germination and growth of plantlets of pistachio (Pistacia vera L.). I J S N 3:613–616
Bernacci LC, Cervi AC, Milward-de-Azevedo MA, Nunes TS, Imig DC, Mezzonato AC (2014) Passifloraceae. In: Lista de espécies da flora do Brasil. In: Jardim Botânico do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro. http://www.floradobrasil.jbrj.gov.br/jabot/floradobrasil/FB12506. Accessed 27 Jan 2015
Berros B, Hasbún R, Radojevic L, Salajova T, Cañal MJ, Rodríguez R (2005) Protocol for hazelnut somatic embryogenesis. In: Jain SM, Gupta PK (eds) Protocol for somatic embryogenesis in woody plants. Springer, Netherlands, pp 413–426. doi:10.1007/1-4020-2985-3_33
Choi YE, Yang DC, Park JC, Soh WY, Choi KT (1998) Regenerative ability of somatic single and multiple embryos from cotyledons of Korean ginseng on hormone-free medium. Plant Cell Rep 17:544–551. doi:10.1007/s002990050439
Clarindo WR, Carvalho CR, Mendonça MAC (2012) Ploidy instability in long-term in vitro cultures of Coffea arabica L. monitored by flow cytometry. Plant Growth Regul 68:533–538. doi:10.1007/s10725-012-9740-0
Ćosić T, Vinterhalter B, Vinterhalter D, Mitić N, Cingel A, Savić J, Bohanec B, Ninković S (2013) In vitro plant regeneration from immature zygotic embryos and repetitive somatic embryogenesis in kohlrabi (Brassica oleracea var. gongylodes). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 49:294–303. doi:10.1007/s11627-013-9517-9
Dornelas MC, Vieira MLC (1994) Tissue culture studies on species of Passiflora. Plant Cell Tissue Org 36:211–217. doi:10.1007/BF00037722
Elhiti M, Stasolla C (2011) The use of zygotic embryos as explants for in vitro propagation: an overview. In: Thorpe TA, Yeung EC (eds) Plant embryo culture. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 229–255. doi:10.1007/978-1-61737-988-8_17
Fehér A, Pasternak TP, Dudits D (2003) Transition of somatic plant cells to an embryogenic state. Plant Cell Tissue Org 74:201–228. doi:10.1023/A:1024033216561
Fielding HB, Gardner G (1844) Sertum Plantarum; or drawings and descriptions of rare and undescribed plants from the author’s herbarium. Hippolyte Bailliere, London
Fischer IH, Rezende JAM (2008) Diseases of passion flower (Passiflora spp.). Global Science Book, Hong Kong
Gaj MD (2004) Factors influencing somatic embryogenesis induction and plant regeneration with particular reference to Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Plant Growth Regul 43:27–47. doi:10.1023/B:GROW.0000038275.29262.fb
Galbraith DW, Harkins KR, Maddox JM, Ayres JM, Sharma DP, Firoozabady E (1983) Rapid flow cytometric analysis of the cell cycle in intact plant tissue. Science 220:1049–1051
Gingas VM, Lineberger RD (1989) Asexual embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Quercus. Plant Cell Tissue Org 17:191–203. doi:10.1007/BF00046867
Hansen AK, Gilbert LE, Simpson BB, Downie SR, Cervi AC, Jansen RK (2006) Phylogenetic relationships and chromosome number evolution in Passiflora. Syst Bot 31:138–150. doi:10.1600/036364406775971769
Jain SM (2001) Tissue culture-derived variation in crop improvement. Euphytica 118:153–166. doi:10.1023/A:1004124519479
Jiménez VM, Thomas C (2005) Participation of plant hormones in determination and progression of somatic embryogenesis. In: Mujib A, Šamaj J (eds) somatic embryogenesis. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 103–118. doi:10.1007/7089_034
Johansson L, Andersson B, Eriksson T (1982) Improvement of anther culture technique: activated charcoal bound in agar medium in combination with liquid medium and elevated CO2 concentration. Physiol Plantarum 54:24–30. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1982.tb00571.x
Kamada H, Kobayashi K, Kiyosue T, Harada H (1989) Stress induced somatic embryogenesis in carrot and its application to synthetic seed production. In vitro Cell Dev Biol 25:1163–1166. doi:10.1007/BF02621268
Kamada H, Ishikawa K, Saga H, Harada H (1993) Induction of somatic embryogenesis in carrot by osmotic stress. Plant Tissue Cult Lett 10:38–44
Kong L, Attree SM, Fowke LC (1997) Changes of endogenous hormone levels in developing seeds, zygotic embryos and megagametophytes in Picea glauca. Physiol Plantarum 101:23–30. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1997.tb01815.x
Konieczny R, Pilarska M, Tuleja M, Salaj T, Ilnicki T (2010) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in zygotic embryos of Trifolium nigrescens (Viv.). Plant Cell Tissue Org 100:123–130. doi:10.1007/s11240-009-9625-8
Krosnick SE, Porter-Utley KE, MacDougal JM, Jørgensen PM, McDade LA (2013) New insights into the evolution of Passiflora subgenus Decaloba (Passifloraceae): phylogenetic relationships and morphological synapomorphies. Syst Bot 38:692–713. doi:10.1600/036364413X670359
Larkin PJ, Scowcroft WR (1981) Somaclonal variation: a novel source of variability from cell cultures for plant improvement. Theor Appl Genet 60:197–214. doi:10.1007/BF02342540
Linnaeus C (1753) Species Plantarum. Stockholm, Sweden
López-Pérez AJ, Carreño J, Martínez-Cutillas A, Dabauza M (2005) High embryogenic ability and plant regeneration of table grapevine cultivars (Vitis vinifera L.) induced by activated charcoal. Vitis 44:79–85
Luo Y, Koop HU (1997) Somatic embryogenesis in cultured immature zygotic embryos and leaf protoplasts of Arabidopsis thaliana ecotypes. Planta 202:387–396. doi:10.1007/s004250050141
Mosquin D (2007) Passiflora miniata. In: UBC Botanical Garden, Vancouver, BC. http://www.botanicalgarden.ubc.ca/potd/2007/06/passiflora_miniata.php. Accessed 24 Jan 2015
Mujib A, Banerjee S, Ghosh PD (2007) Callus induction, somatic embryogenesis and chromosomal instability in tissue culture-raised hipperastrum (Hippeastrum hybridum cv. United Nations). Propag Ornam Plants 7:169–174
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plantarum 15:473–497
Nakayama F (1966) Cultivo in vitro de tejidos de Passiflora caerulea. Revista de la Facultad de Agronomía de la Universidad Nacional de La Plata 42:63–74
Nissen P, Minocha SC (1993) Inhibition by 2,4-D of somatic embryogenesis in carrot as explored by its reversal by difluoromethylornithine. Physiol Plantarum 89:673–680. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1993.tb05272.x
Nomura K, Komamine A (1985) Identification and isolation of single cells that produce somatic embryos at a high frequency in a carrot suspension culture. Plant Physiol 79:988–991
Otto FJ (1990) DAPI staining of fixed cells for high-resolution flow cytometry of nuclear DNA. In: Darzynkiewicks Z, Crissman HA (eds) Methods in cell biology, vol 33. Academic, San Diego, pp 105–110
Pan MJ, van Staden J (1998) The use of charcoal in in vitro culture: a review. Plant Growth Regul 26:155–163. doi:10.1023/A:1006119015972
Pasternak TP, Prinsen E, Ayaydin F, Miskolczi P, Potters G, Asard H, van Onckelen HA, Dudits D, Fehér A (2002) The role of auxin, pH, and stress in the activation of embryogenic cell division in leaf protoplast-derived cells of alfalfa. Plant Physiol 129:1807–1819. doi:10.1104/pp.000810
Pavlović S, Vinterhalter B, Zdravković-Korać S, Vinterhalter D, Zdravković J, Cvikić D, Mitić N (2013) Recurrent somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature zygotic embryos of cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) and cauliflower (Brassica oleracea var. botrytis). Plant Cell Tissue Org 113:397–406. doi:10.1007/s11240-012-0279-6
Pescador R, Kerbauy GB, Viviani D, Kraus JE (2008) Anomalous somatic embryos in Acca sellowiana (O. Berg) Burret (Myrtaceae). Revista Brasil Bot 31:155–164. doi:10.1590/S0100-84042008000100014
Pinto DLP, Barros BA, Viccini LF, Campos JMS, Silva ML, Otoni WC (2010) Ploidy stability of somatic embryogenesis-derived Passiflora cincinnata Mast. plants as assessed by flow cytometry. Plant Cell Tissue Org 103:71–79. doi:10.1007/s11240-010-9756-y
Pinto DLP, Almeida AMR, Rêgo MM, Silva ML, Oliveira EJ, Otoni WC (2011) Somatic embryogenesis from mature zygotic embryos of commercial passionfruit (Passiflora edulis Sims) genotypes. Plant Cell Tissue Org 107:521–530. doi:10.1007/s11240-011-0003-y
Praça-Fontes MM, Carvalho CR, Clarindo WR (2009) A practical and reliable procedure for in vitro induction of tetraploid tomato. Sci Hort 122:501–505. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2009.05.032
Praça-Fontes MM, Carvalho CR, Clarindo WR (2011a) C-value reassessment of plant standards: an image cytometry approach. Plant Cell Rep 30:2303–2312. doi:10.1007/s00299-011-1135-6
Praça-Fontes MM, Carvalho CR, Clarindo WR, Cruz CD (2011b) Revisiting the DNA C-values of the genome size-standards used in plant flow cytometry to choose the “best primary standards”. Plant Cell Rep 30:1183–1191. doi:10.1007/s00299-011-1026-x
Riquelme PC, Leal DR, Carrillo KS, Moraga MU, Aguilar SV, Bolus SJ, Olate MS (2011) Endogenous quantification of abscisic acid and indole-3-acetic acid in somatic and zygotic embryos of Nothofagus alpine (Poepp. & Endl.) Oerst. Chil J Agric Res 71:542–548. doi:10.4067/S0718-58392011000400007
Rosa YBCJ, Dornelas MC (2012) In vitro plant regeneration and de novo differentiation of secretory trichomes in Passiflora foetida L. (Passifloraceae). Plant Cell Tissue Org 108:91–99. doi:10.1007/s11240-011-0016-6
Rosa YBCJ, Bello CCM, Dornelas MC (2015) Species-dependent divergent responses to in vitro somatic embryo induction in Passiflora spp. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 120:69–77. doi:10.1007/s11240-014-0580-7
Sharp WR, Sohndahl MR, Evans AE, Caldas LA, Maraffa SB (1980) The physiology of in vitro asexual embryogenesis. Hortic Rev 2:268–310. doi:10.1002/9781118060759.ch6
Silva TC, Carvalho CR (2013) Vertical heterogeneity of DNA ploidy level assessed by flow cytometry in calli of Passiflora cincinnata. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 50:158–165. doi:10.1007/s11627-013-9582-0
Silva ML, Pinto DLP, Guerra MP, Floh EIS, Bruckner CH, Otoni WC (2009) A novel regeneration system for a wild passion fruit species (Passiflora cincinnata Mast.) based on somatic embryogenesis from mature zygotic embryos. Plant Cell Tissue Org 99:47–54. doi:10.1007/s11240-009-9574-2
Smith DL, Krikorian AD (1990) Somatic proembryo production from excised, wounded zygotic carrot embryos on hormone-free medium: evaluation of the effects of pH, ethylene and activated charcoal. Plant Cell Rep 9:34–37. doi:10.1007/BF00232131
Tenning P, Weich EW, Kjärsgaard UB, Lelu MA, Nihjgård (1992) Somatic embryogenesis from zygotic embryos of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Plant Sci 81:103–109. doi:10.1016/0168-9452(92)90029-L
Vanderplank J (2006) Plate 562. Passiflora miniata (Passifloraceae). Curtis’s Bot Mag 23:223–230. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8748.2006.00533.x
Vieira LM, Rocha DI, Taquetti MF, Silva LC, Campos JMS, Viccini LF, Otoni WC (2014) In vitro plant regeneration of Passiflora setacea D.C. (Passifloraceae): the influence of explant type, growth regulators, and incubation conditions. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 50:738–745. doi:10.1007/s11627-014-9650-0
Von Arnold S (2008) Somatic embryogenesis. In: George EF, Hall MA, De Klerk G-J (eds) Plant propagation by tissue culture. Exegetics, Basingstoke, UK
Yockteng R, d’Eeckenbrugge GC, Souza-Chies TT (2011) Passiflora. In: Kole C (ed) Wild crop relatives: genomic and breeding resources. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 129–171
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq; Brasília, DF—Brazil), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Espírito Santo (FAPES; Vitória, ES—Brazil) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES; Brasília, DF—Brazil) for financial support, and to the researchers of the Parque Estadual Cachoeira da Fumaça Atlantic rainforest (Alegre, ES—Brazil) and Amazon rainforest (Carlinda, MT—Brazil) for support in collecting the biological material.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreira, D.A.T., Sattler, M.C., Carvalho, C.R. et al. Embryogenic potential of immature zygotic embryos of Passiflora: a new advance for in vitro propagation without plant growth regulators. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 122, 629–638 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0796-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0796-1