Abstract
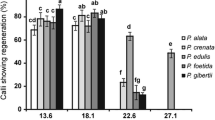
Tissue culture in Passiflora has emerged as a strategy to propagate species with agronomic relevance, which is the main focus of most in vitro studies. Different morphogenic responses have been obtained under the same environmental in vitro conditions, mainly for species of the subgenus Passiflora with distinct 2n chromosome numbers. The aims of this study were to verify and compare the in vitro responses in Passiflora species with distinct 2n chromosome numbers, ploidy levels and nuclear 2C values. Under the same in vitro conditions, only friable calli occurred from mature zygotic embryo explants of Passiflora coriacea (2n = 2x = 12 chromosomes, 2C = 1.00 pg), Passiflora lindeniana (2n = 4x = 24, 2C = 2.42 pg) and Passiflora contracta (2n = 8x = 48, 2C = 4.78 pg). In contrast, plantlets were regenerated from Passiflora foetida (2n = 20, 2C = 1.04 pg) and Passiflora miniata (2n = 18, 2C = 3.40 pg) via indirect organogenesis and indirect somatic embryogenesis, respectively. By now, from mature zygotic embryo explants, de novo shoot organogenesis and somatic embryos have been recovered for Passiflora species with 2n = 18 chromosomes and relative high nuclear 2C value (more than 2C = 2.93 pg—Passiflora cincinata), and only de novo shoot organogenesis for P. foetida with 2n = 20 chromosomes and relative low 2C value (2C = 1.04 pg). Therefore, in a taxonomic and evolutive context, this study showed that the in vitro morphogenic pathways pretty varied between the Passiflora species with distinct karyotype features.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IZE:
-
Immature zygotic embryos
- IO:
-
Indirect organogenesis
- ISE:
-
Indirect somatic embryogenesis
- MZE:
-
Mature zygotic embryos
References
Carvalho CR, Clarindo WR, Almeida PM (2007) Plant cytogenetics: still looking for the perfect mitotic chromosomes. Nucleus 50:453–462
Fehér A (2015) Somatic embryogenesis stress-induced remodeling of plant cell fate. Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul Mech 1849:385–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.07.005
Fehér A, Pasternak TP, Dudits D (2003) Transition of somatic plant cells to an embryogenic state. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 74:201–228. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024033216561
Ferreira DAT, Sattler MC, Carvalho CR, Clarindo WR (2015) Embryogenic potential of immature zygotic embryos of Passiflora: a new advance for in vitro propagation without plant growth regulators. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 122:629–638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0796-1
Feuillet C, Macdougal JM (2003) A new infrageneric classification of Passiflora L. (Passifloraceae). Passiflora 13:34–38
Galbraith DW, Harkins KR, Maddox JM, Ayres JM, Sharma DP, Firoozabady E (1983) Rapid flow cytometric analysis of the cell cycle in intact plant tissue. Sci 220:1049–1051. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.220.4601.1049
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-4827(68)90403-5
Garcia R, Pacheco G, Falcão E, Borges G, Mansur E (2011) Influence of type of explant, plant growth regeneration, salt composition of basal medium, and light on callogenesis and regeneration in Passiflora suberosa (Passifloraceae). Plant Cell Tissue Org 106:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9892-4
Guerra MS (1986) Reviewing the chromosome nomenclature of Levan et al. Rev Bras de Genét 9:741–743
Haberlandt G (1902) Culturversuche mit isolierten Pflanzenzellen. Sitzungsber. Akad. Wiss. Wien. Math.-Naturwiss
Hansen AK, Gilbert LE, Simpson BB, Downie SR, Cervi AC, Jansen RK (2006) Phylogenetic relationships and chromosome number evolution in Passiflora. Syst Bot 31:138–150. https://doi.org/10.1600/036364406775971769
Heringer AS, Barroso T, Macedo AF, Santa-Catarina C, Souza GHMF, Floh EIS, Silveira V (2015) Label-free quantitative proteomics of embryogenic and non-embryogenic callus during sugarcane somatic embryogenesis. PloS ONE 10:0127803. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0127803
Johansson L, Andersson B, Eriksson T (1982) Improvement of another culture technique: activated charcoal bound in agar medium in combination with liquid medium and elevated CO2 concentration. Physiol Plant 54:24–30. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1982tb00571.x
Killip EP (1938) The American species of Passifloraceae. Museum Natural History, Chicago
Levan A, Fredga A, Sanderberg AA (1964) Nomenclature for centromeric position in chromosome. Hereditas 52:201–220. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-5223.1964.tb01953.x
Melo NF, Guerra M (2003) Variability of the 5S and 45S rDNA sites in Passiflora L. species with distinct base chromosome numbers. Ann Bot 92:309–316. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcg138
Melo NF, Cervi AC, Guerra M (2001) Karyology and cytotaxonomy of the genus Passiflora L. (Passifloraceae). Plant Syst Evol 226:69–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s006060170074
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Muschner VC, Lorenz AP, Cervi AC, Bonato SL, Souza-Chies TT, Salzano FM, Freitas LB (2003) A first molecular phylogenetic analysis of Passiflora (Passifloraceae). Am J Bot 98:1229–1238. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.90.8.1229
Muschner VC, Zamberlan PM, Bonatto SL, Freitas LB (2012) Phylogeny, biogeography and divergence times in Passiflora (Passifloraceae). Genet Mol Biol 35:1036–1043. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-47572012000600019
Otto FJ (1990) DAPI staining of fixed cells for high-resolution flow cytometry of nuclear DNA. In: Darzynkiewicks Z, Crissman HA (eds) Methods in cell biology, 33:105–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0091-679X(08)60516-6
Ozarowski M, Thiem B (2013) Progress in micropropagation of Passiflora spp. to produce medicinal plants: a mini-review. Rev Bras Farmacogn 23:937–947. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-695X2013000600011
Pacheco G, Simão MJ, Vianna MG, Garcia RO, Vieira MLC, Mansur E (2016) in vitro conservation of Passiflora—a review. Sci Horticult 211:305–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2016.09.004
Pan MJ, Van Staden J (1998) The use of charcoal in in vitro culture—a review. Plant Grow Reg 26:155–163. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006119015972
Pinto DLP, Almeida AMR, Rêgo MM, Silva ML, Oliveira EJ, Otoni WC (2011) Somatic embryogenesis from mature zygotic embryos of commercial passionfruit (Passiflora edulis Sims) genotypes. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 107:521–530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-0003-y
Praça MM, Carvalho CR, Marcelino FC, Mendonça MAC (2008) Morphological aspects of Passiflora edulis f. flavicarpa chromosome using acridine orange banding and rDNA-FISH tools. Caryologia 61:154–159. https://doi.org/10.1080/00087114.2008.10589623
Praça-Fontes MM, Carvalho CR, Clarindo WR (2011) C-value reassessment of plant standards: an image cytometry approach. Plant Cell Rep 30:2303–2312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1135-6
Rocha DI, Monte-Bello CC, Dornelas MC (2015a) Alternative induction of de novo shoot organogenesis or somatic embryogenesis from in vitro cultures of mature zygotic embryos of passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims) is modulated by the ratio between auxin and cytokinin in the medium. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 120:1087–1098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0663-5
Rocha DI, Pinto DLP, Vieira LM, Tanaka FAO, Dornelas MC, Otoni WC (2015b) Cellular and molecular changes associated with competence acquisition during passion fruit somatic embryogenesis: ultrastructural characterization and analysis of SERK gene expression. Protoplasma 253:595–609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0837-y
Rosa YBCJ, Dornelas MC (2012) in vitro plant regeneration and de novo differentiation of secretory trichomes in Passiflora foetida L. (Passifloraceae). Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 108:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-0016-6
Rosa YBCJ, Bello CCM, Dornelas MC (2015) Species-dependent divergent responses to in vitro somatic embryo induction in Passiflora spp. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 120:69–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0580-7
Silva ML, Pinto DLP, Guerra MP, Floh EIS, Bruckner CH, Otoni WC (2009) A novel regeneration system for a wild passion fruit species (Passiflora cincinnata Mast.) based on somatic embryogenesis from mature zygotic embryos. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 99:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-009-9574-2
Silva GM, Cruz AC, Otoni WC, Pereira TN, Rocha DI, Silva ML (2015) Histochemical evaluation of induction of somatic embryogenesis in Passiflora edulis Sims (Passifloraceae). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol-Plant 51:539–545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-015-9699-4
Sugimoto K, Jiao Y, Meyerowitz EM (2010) Arabidopsis regeneration from multiple tissues occurs via a root development pathway. Dev Cell 18:463–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2010.02.004
Thomas TD (2008) The role of activated charcoal in plant tissue culture. Biotechnol Adv 26:618–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.08.003
Yockteng R, Nadot S (2004) Phylogenetic relationships among Passiflora species based on the glutamine synthetase nuclear gene expressed in chloroplast (ncpGS). Mol Phylogenet Evol 31:379–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1055-7903(03)00277-X
Yotoko KS, Dornelas MC, Togni PD, Fonseca TC, Salzano FM, Bonatto SL, Freitas LB (2011) Does variation in genome sizes reflect adaptive or neutral processes? New clues from Passiflora. PLoS ONE 6:e18212. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0018212
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq, Brasília—DF, Brazil, grants 443801/2014-2 and 448671/2014-0), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Espírito Santo (FAPES, Vitória—ES, Brazil, grants 65942604/2014 and 0438/2015) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES, Brasília—DF, Brazil) for financial support. We also thank M. S. Joaquim Gasparini dos Santos for images of in vitro tissue culture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors CTL, DATF, MMP-F and WRC conceived, designed and conducted the tissue culture experiments. The authors ATV, CRC and WRC conducted the flow cytometry analysis. The authors ATV and WRC contributed with chromosome number determination and karyotype characterization. CTL, WRC and AF conceived, designed and conducted the statistical analyses. All authors equally contributed to the manuscript editing and revision and approved the final manuscript version for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Sergei Krasnyanski.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11240_2018_1536_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Response surface showing the influence of time (in days) (x – time) and 2,4-D concentration (in μM) (y) on the explant responsive rate (z – rate) of the P. coriacea (a), P. lindeniana (b) and P. contracta (c). As in the Fig. 2, the graphics show that, for three species, the explant responsive rate (friable calli formation rate) increased in relation to exposure time and increasing 2,4-D concentration. The highest explant responsive rates were observed in 2,4-D concentrations up to 72.48 μM: 97% in M8 (72.48 μM 2,4-D, arrow) for P. coriacea, 73% in M7 (36.24 μM 2,4-D, arrow) for P. lindeniana, and 46% in M6 (27.18 μM 2,4-D, arrow) for P. contracta. Note that the lowest friable calli formation rate was observed for P. contracta, which possesses 2n = 48. Fitted quadratic models were significant (P < 0.05) by regression analysis for: a) P. coriacea, z = 0.5619 + 21.0x + 38.7544y + 3271.8428y2; b) P. lindeniana, z = 0.2209 + 21.0x + 47.8857y + 4191.9973y2; and c) P. contracta, z = 0.1342 + 21.0x + 38.7544y + 3271.8428y2. Supplementary material 1 (TIF 69938 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leite, C.T., Ferreira, D.A.T., Vieira, A.T. et al. In vitro responses in Passiflora species with different chromosome numbers, ploidy levels and nuclear 2C values: revisiting and providing new insights. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 136, 549–560 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-018-01536-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-018-01536-9