Abstract
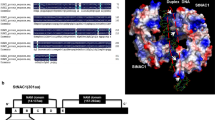
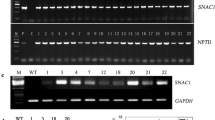
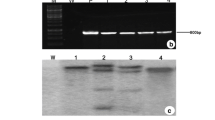
Transgenic sweetpotato (cv. Lizixiang) plants exhibiting enhanced salt tolerance were developed using LOW OSMOTIC STRESS 5 (LOS5) with Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. A. tumefaciens strain EHA105 harbors the pCAMBIA1300 binary vector with the LOS5 and hygromycin phosphotransferase II (hptII) genes. Selection culture was conducted using 25 mg l−1 hygromycin. A total of 26 plants were produced from the inoculated 200 cell aggregates of Lizixiang via somatic embryogenesis. PCR analysis showed that 23 of the 26 regenerated plants were transgenic plants. All of the transgenic plants exhibited higher salt tolerance compared to the untransformed control plants by in vitro assay for salt tolerance with 86 mM NaCl. When plants were exposed to 86 mM NaCl, 16 transgenic plants had significantly higher levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD), proline, and abscisic acid (ABA) and significantly lower malonaldehyde (MDA) contents than those in untransformed control plants. Salt tolerance of these 16 plants was further evaluated with Hoagland solution containing 86 mM NaCl in a greenhouse. Four of the sixteen had significantly better growth and rooting ability than the remaining 12 plants and control plants. Stable integration of the LOS5 gene into the genome of the 4 salt-tolerant transgenic plants was confirmed by Southern blot analysis, and the copy number of integrated LOS5 gene ranged from 1 to 3. High level of LOS5 gene expression in the 4 salt-tolerant transgenic plants was demonstrated by real-time quantitative PCR analysis. This study provides an important approach for improving salt tolerance of sweetpotato.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- AS:
-
Acetosyringone
- Carb:
-
Carbenicillin
- CTAB:
-
Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay
- hptII:
-
Hygromycin phosphotransferase II gene
- Hyg:
-
Hygromycin
- LB:
-
Luria-Bertani
- MDA:
-
Malonaldehyde
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
References
Apse MP, Aharon GS, Snedden WA, Blumwald E (1999) Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport in Arabidopsis. Science 285:1256–1258
Bao AK, Wang SM, Wu GQ, Xi JJ, Zhang JL, Wang CM (2009) Overexpression of the Arabidopsis H+-PPase enhanced resistance to salt and drought stress in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Sci 176:232–240
Chen LH, Zhang B, Xu ZQ (2008) Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of Arabidopsis vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene AtNHX1 in common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum). Transgenic Res 17:121–132
Chinnusamy V, Zhu JH, Zhu JK (2006) Salt stress signaling and mechanisms of plant salt tolerance. In: Setlow JK (ed) Genetic engineering, vol 27. Springer, New York, pp 141–177
Choi HJ, Chandrasekhar T, Lee HY, Kim KM (2007) Production of herbicide-resistant transgenic sweet potato plants through Agrobacterium tumefaciens method. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 91:235–242
Cipriani G, Michaud D, Brunelle F, Golmirzaie A, Zhang DP (1999) Expression of soybean proteinase inhibitor in sweetpotato. CIP Program Rep 1997–1998:271–277
Dhindsa RS, Plumb-Dhindsa P, Thorpe TA (1981) Leaf senescence: correlated with increased levels of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation, and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase. J Exp Bot 32:93–101
Dhir SK, Oglesby J, Bhagsari AS (1998) Plant regeneration via embryogenesis and transient gene expression in sweet potato protoplasts. Plant Cell Rep 17:665–669
Duncan DB (1955) Multiple range and multiple F tests. Biometrics 11:1–42
Gao XH, Ren ZH, Zhao YX, Zhang H (2003) Overexpression of SOD2 increases salt tolerance of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 133:1873–1881
Gao S, Yu B, Yuan L, Zhai H, He SZ, Liu QC (2011) Production of transgenic sweetpotato plants resistant to stem nematodes using oryzacystatin-I gene. Sci Hortic 128:408–414
Gupta S, Srivastava J (1990) Effect of salt stress on morphophysiological parameters in wheat. Indian J Plant Physiol 32:162–171
Hasthanasombut S, Supaibulwatana K, Mii M, Nakamura I (2011) Genetic manipulation of Japonica rice using the OsBADH1 gene from Indica rice to improve salinity tolerance. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 104:79–89
He ZP (1993) A laboratory guide to chemical control technology on field crop. Beijing Agricultural University Press, Beijing
He SZ, Han YF, Wang YP, Zhai H, Liu QC (2009) In vitro selection and identification of sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) plants tolerant to NaCl. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 96:69–74
He C, Yang AF, Zhang WW, Gao Q, Zhang JR (2010) Improved salt tolerance of transgenic wheat by introducing betA gene for glycine betaine synthesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 101:65–78
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif Agric Exp Stn Circ 347:1–39
Huai JL, Zheng J, Wang GY (2009) Overexpression of a new Cys2/His2 zinc finger protein ZmZF1 from maize confers salt and drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 99:117–124
Huang PM, Chen JY, Wang SJ (2009) Tissue-specific regulation of rice molybdenum cofactor sulfurase gene in response to salt stress and ABA. Acta Physiol Plant 31:545–551
Ikegami K, Okamoto M, Seo M, Koshiba T (2009) Activation of abscisic acid biosynthesis in the leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana in response to water deficit. J Plant Res 122:235–243
Jin TC, Chang Q, Li WF, Yin DX, Li ZJ, Wang DL, Liu B, Liu LX (2010) Stress-inducible expression of GmDREB1 conferred salt tolerance in transgenic alfalfa. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 100:219–227
Kimura T, Otani M, Noda T, Ideta O, Shimada T, Saito A (2001) Absence of amylose in sweetpotato [Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.] following the introduction of granule-bound starch synthase I cDNA. Plant Cell Rep 20:663–666
Kishor PBK, Hong ZLM, Miao GH, Hu CAA, Verma DPS (1995) Overexpression of Delta 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase increases proline production and confers osmotolerance in transgenic plants. Plant Physiol 108:1387–1394
Koca H, Ozdemir F, Turkan I (2006) Effect of salt stress on lipid peroxidation and superoxide dismutase and peroxidase activities of Lycopersicon esculentum and L. pennellii. Biol Plant 50(4):745–748
Kumar V, Shriram V, Kavi Kishor PB, Jawali N, Shitole MG (2010) Enhanced proline accumulation and salt stress tolerance of transgenic indica rice by over-expressing P5CSF129A gene. Plant Biotechnol Rep 4:37–48
Li YH, Zhang YZ, Feng FJ, Liang D, Cheng LL, Ma FW, Shi SG (2010) Overexpression of a Malus vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene (MdNHX1) in apple rootstock M.26 and its influence on salt tolerance. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 102:337–345
Lim S, Kim YH, Kim SH, Kwon SY, Lee HS, Kim JS, Cho KY, Paek KY, Kwak SS (2007) Enhanced tolerance of transgenic sweetpotato plants that express both CuZnSOD and APX in chloroplasts to methyl viologen-mediated oxidative stress and chilling. Mol Breeding 19:227–239
Liu QC, Zhai H, Wang Y, Zhang DP (2001) Efficient plant regeneration from embryogenic suspension cultures of sweetpotato. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 37:564–567
Morán R, García R, López A, Zaldúa Z, Mena J, García M, Armas R, Somonte D, Rodríguez J, Gómez M, Pimentel E (1998) Transgenic sweet potato plants carrying the delta-endotoxin gene from Bacillus thuringiensis var. tenebrionis. Plant Sci 139:175–184
Munns R (2002) The impact of salinity stress. http://www.plantstress.com/Articles/index.asp
Newell CA, Lowe JM, Merryweather A, Rooke LM, Hamilton WDO (1995) Transformation of sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) with Agrobacterium tumefaciens and regeneration of plants expressing cowpea trypsin inhibitor and snowdrop lectin. Plant Sci 107:215–227
Okada Y, Saito A, Nishiguchi M, Kimura T, Mori M, Hanada K, Sakai J, Miyazaki C, Matsuda Y, Murata T (2001) Virus resistance in transgenic sweetpotato [Ipomoea batatas L. (Lam.)] expressing the coat protein gene of sweetpotato feathery mottle virus. Theor Appl Genet 103:743–751
Otani M, Wakita Y, Shimada T (2003) Production of herbicide-resistant sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) plants by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. Breeding Sci 53:145–148
Qiao GR, Zhou J, Jiang J, Sun YH, Pan LY, Song HG, Jiang JM, Zhuo RY, Wang XJ, Sun ZX (2010) Transformation of Liquidambar formosana L. via Agrobacterium tumefaciens using a mannose selection system and recovery of salt tolerant lines. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 102:163–170
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barly: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci 81:8014–8018
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C T method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Shen YY, Huang CL, Zhang XH, Cao MQ (2002) Plant drought tolerance molecular mechanism. Chin J Eco-Agric 10:30–34
Shimada T, Otani M, Hamada T, Kim SH (2006) Increase of amylose content of sweetpotato starch by RNA interference of the starch branching enzyme II gene (IbSBEII). Plant Biotechnol 23:85–90
Subramanyam K, Sailaja KV, Subramanyam K, Rao DM, Lakshmidevi K (2010) Ectopic expression of an osmotin gene leads to enhanced salt tolerance in transgenic chilli pepper (Capsicum annum L.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult doi:10.1007/s11240-010-9850-1
Ushimaru T, Nakagawa T, Fujioka Y, Daicho K, Naito M, Yamauchi Y, Nonaka H, Amako K, Yamawaki K, Murata N (2006) Transgenic Arabidopsis plants expressing the rice dehydroascorbate reductase gene are resistant to salt stress. J Plant Physiol 163:1179–1184
Verbruggen N, Villarroel R, Montagu MV (1993) Osmoregulation of a pyrrilone-5-carboxylate reductase gene in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 103:171–181
Wakita Y, Otani M, Hamada T, Mori M, Iba K, Shimada T (2001) A tobacco microsomal ω-3 fatty acid desaturase gene increases the linolenic acid content in transgenic sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas). Plant Cell Rep 20:244–249
Watad AEA, Reinhold L, Lerner HR (1983) Comparison between a stable NaCl-selected Nicotiana cell line and the wild type. Plant Physiol 73:624–629
Wei Q, Guo YJ, Cao HM, Kuai BK (2010) Cloning and characterization of an AtNHX2-like Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Ammopiptanthus mongolicus (Leguminosae) and its ectopic expression enhanced drought and salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult doi:10.1007/s11240-010-9869-3
Xie ZY, Yang GS (2003) Advances in salt tolerance of forage plants. Pratacultural Sci 20:11–17
Xiong LM, Ishitani M, Lee H, Zhu JK (2001) The arabidopsis LOS5/ABA3 locus encodes a molybdenum cofactor sulfurase and modulates cold stress- and osmotic stress-responsive gene expression. Plant Cell 13:2063–2083
Yi G, Shin YM, Choe G, Shin B, Kim YS, Kim KM (2007) Production of herbicide-resistant sweet potato plants transformed with the bar gene. Biotechnol Lett 29:669–675
Yu B, Zhai H, Wang YP, Zang N, He SZ, Liu QC (2007) Efficient Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation using embryogenic suspension cultures in sweetpotato Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 90:265–273
Zang N, Zhai H, Gao S, Chen W, He SZ, Liu QC (2009) Efficient production of transgenic plants using the bar gene for herbicide resistance in sweetpotato. Sci Hortic 122:649–653
Zhang HX, Hodson JN, Wlliams JP, Blumwald E (2001) Engineering salt-tolerant Brassica plants: characterization of yield and seed oil quality in transgenic plants with increased vacuolar sodium accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:12832–12836
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Gong ZZ, College of Biological Sciences, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, and Prof. Wang T, State Key Laboratory of Agrobiotechnology, Beijing, China, for providing LOS5 gene and Strain EHA 105, respectively. We also thank Dr. Michael Portereiko, Ceres, Inc. USA, for English improvement. This work was supported by China Agro-industry Research System (Sweetpotato), the National High-Tech Research and Development Project of China (no. 2009AA10Z102) and the National Transgenic Plants Project of China (no. 2009ZX08009-064B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shang Gao and Li Yuan contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, S., Yuan, L., Zhai, H. et al. Transgenic sweetpotato plants expressing an LOS5 gene are tolerant to salt stress. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 107, 205–213 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-9971-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-9971-1