Abstract
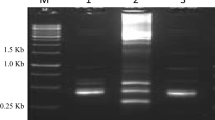
To understand the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the salt response and to isolate differentially expressed genes, we constructed a forward subtractive cDNA library from Salsola ferganica treated with 600 mM NaCl for different lengths of time (0, 4, 8, 12, 16, 24, 36 h) using the suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) technique. This SSH library contained approximately 2,200 positive clones, with the insert size ranging from 250 to 700 bp. Eighty clones were selected for further study based on results from reverse Northern blotting and sequencing and, these cDNAs are the first reported expressed sequence tags (ESTs) of Salsola ferganica listed in GenBank. Among these 80 differentially expressed genes, 32 are genes with known function that display a high homology (between 68 and 100% identity) to known sequences, 47 have an unknown function, showing no homology with known sequences, and one is a novel gene that does not match any previously reported genes. Five cDNA fragments, sf3d8, sf6d8, sf4a8, sf8d6, and sf6c7, were randomly chosen from the 80 differentially expressed genes for reverse transcription-PCR analysis. The expression of sf8d6 was entirely induced by salt stress and that of sf3d8, sf6d8, sf4a8, and sf6c7 was increased from a relatively lower level. The isolated ESTs reported here may enable us to find new genes involved in salt tolerance in Salsola ferganica.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DIG:
-
Digoxygenin
- EST:
-
Expressed sequence tag
- RT–PCR:
-
Reverse transcription PCR
- SSH:
-
Suppression subtractive hybridization
References
Agarie S, Cushman MA, Kore-eda S, Deyholos M, Galbraith D, Cushman JC (2001) Gene expression profiling of salinity stress responses using expressed sequence tag (EST)-based microarrays in the common ice plant, Mesembryanthemum crystallinum. Nippon Shokubutsu Seiri Gakkai Nenkai oyobi Shinpojiumu Koen Yoshishu 41:199
Deng Y, Jiang Y, Liu J (1998) The xeromorphic and salinemorphic structure of leaves and assimilating branches in ten Chenopodiacea species in xinjiang. Acta Anaesthesiol Sin 22(2):164–170
Diedhiou CJ, Popova OV, Golldack D (2009) Transcript profiling of the salt-tolerant Festuca rubra ssp. litoralis reveals a regulatory network controlling salt acclimatization. J Plant Physiol 166(7):697–711
Flowers TJ, Yeo AR (1995) Breeding for salinity resistance in crop plants: where next? Aust J Plant Physiol 22:875–884
Flowers TJ, Hajibagheri MA, Clipson NJW (1986) Halophytes. Q Rev Biol 61:313–337
Hanson AD, Rathinasabapathi B, Chamberlain B, Gage DA (1991) Comparative physiological evidence that β-alanine betaine and choline-O-sulfate act a scompatible osmolytes in halophytic Limonium species. Plant Physiol 97:1199–1205
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohnert HJ (2000) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 51:463–499
Hedley PE, Hein I, Morris WL, et al (2000) Characterisation of resistance pathways to Rhynchosporium secalis in barley using suppression subtractive hybridization. In: Proc 6th Int Congress Plant Molecular Biology. Quebec City, pp S22–S36
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Circular 347. The College of Agriculture, University of California, Berkeley
Huang JH (2005) Geographical distribution of Salsola L. in China. Arid Land Geography 28:325–329
Jansen C, Korell M, Eckey C, Biedenkopf D, Kogel KH (2005) Identification and transcriptional analysis of powdery mildew-induced barley genes. Plant Sci 168:373–380
Jin H, Sun Y, Yang Q, Chao Y, Kang J, Jin H, Li Y, Margaret G (2010) Screening of genes induced by salt stress from Alfalfa. Mol Biol Rep 37(2):745–753
Li HY, Wang YC, Jiang J, Liu GF, Gao CQ, Yang CP (2009) Identification of genes responsive to salt stress on Tamarix hispida roots. Gene 433:65–71
Munns M (2005) Genes and salt tolerance: bringing them together. New Phytol 167:645–663
Namasivayam P, Hanke D (2006) Identification of differentially expressed sequences in pre-embryogenic tissue of oilseed rape by suppression subtractive hybridisation (SSH). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 86:417–421
Ok SH, Park HM, Kim JY (2003) Identification of differentially expressed genes during flower development in carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus). Plant Sci 165:291–297
Ouyang B, Yang T, Li H, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Fei Z, Ye Z (2007) Identification of early salt stress response genes in tomato root by suppression subtractive hybridization and microarray analysis. J Exp Bot 58(3):507–520
Ozturk ZN, Talamé V, Deyholos M, Michalowski C, Galbraith DW, Gozukirmizi N, Tuberosa R, Bohnert HJ (2002) Monitoring large-scale changes in transcript abundance in drought- and salt-stressed barley. Plant Mol Biol 48:551–573
Qia YH, Yamauchia YS, Lingb JQ (2005) The submergence-induced gene OsCTP in rice (Oryza sativa L.) is similar to Eschcerichia coli cation transport protein ChaC. Plant Sci 168:15–22
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Schroeyers K, Chaparro C, Goormachtig S, Holsters M (2004) Nodulation-enhanced sequences from the water stress-tolerant tropical legume Sesbania rostrata. Plant Sci 167:207–216
Shi OC, Ingvardsen C, Thummler F, Albrecht E (2005) Identification by suppression subtractive hybridization of genes that are differentially expressed between near-isogenis maize lines in association with sugarcane Moasic virus resistance. Mol Gen Genomics 273:450–461
Summers PS, Weretilnyk EA (1993) Choline synthesis in spinach in relation to salt stress. Plant Physiol 103:1269–1276
Türkana I, Demiral T (2009) Recent developments in understanding salinity tolerance. Environ Exp Bot 67:2–9
Van den Berg N, Crampton BG (2004) High-throughput screening of suppression subtractive hybridization cDNA libraries using DNA microarray analysis. Bio-Techniques 38:818–824
Varin L, Deluca V, Ibrahim R, Brisson N (1992) Molecular characterization of two plant flavonol sulfotransferases (Flavera chloraefolia). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:1286–1290
Vinocur B, Altman A (2005) Recent advances in engineering plant tolerance to abiotic stress: achievements and limitations. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16:1–10
Wang P, Yin L, Li J (1997) Ecological distribution and physiological adaptation to saline-alkali environment of C3 and C4 plants in Northeastern China prairie area. Chinese J Appl Ecol 8:407–411
Wang RZ (2002) The C4 photosynthetic pathway and life forms in grassland species from North China. Photosynthetica 40(1):97–102
Wang W, Vinocur B, Altman A (2003) Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218:1–14
Wang Y, Ma H, Liu G, Xu C, Zhang D, Ban Q (2008) Analysis of gene expression profile of Limonium bicolor under NaHCO3 stress using cDNA microarray. Plant Mol Biol Rep 26:241–254
Wang ZL, Li PH, Fredricksen M, Gong ZZ, Kimd CS, Zhang CQ, Bohnert HJ, Zhu JK, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM, Zhao YX, Zhang H (2004) Expressed sequence tags from Thellungiella halophila, a new model to study plant salt-tolerance. Plant Sci 166:609–616
Weretilnyk EA, Smith DN, Wilch GA, Summers PS (1995) Enzymes of choline synthesis in spinach: response of phospho-base N-methyltransferase activities to light and salinity. Plant Physiol 109:1085–1091
Wong CE, Li Y, Labbe A, Guevara D, Nuin P, Whitty B, Diaz C, Golding GB, Gray GR, Weretilnyk EA, Griffith M, Moffatt BA (2006) Transcriptional profiling implicates novel interactions between abiotic stress and hormonal responses in Thellungiella, a close relative of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 140:1437–1450
Wyn Jones RG, Storey R, Leigh RA, Ahmad N, Pollard A (1977) A hypothesis on cytoplasmic osmoregulation. In: Marré ZnE, Cifem O (eds) Regulation of cell membrane activities in plants. Elsevier-North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 121–136
Yao YG, Ni ZF (2005) Identification of differentially expressed genes in leaf and root between wheat hybrid and its parental inbreds using PCR-based cDNA subtraction. Plant Mol Biol 58:367–384
Yokoi S, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (2002) Salt stress tolerance of plants. JIRCAS working report. Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences, Tsukuba, pp 25–33
Zhang L, Ma XL, Zhang Q, Ma CL, Wang PP, Sun YF, Zhao YX, Zhang H (2001) Expressed sequence tags from a NaCl-treated Suaeda salsa cDNA library. Gene 267:193–200
Zhu JK (2001) Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 6:66–71
Acknowledgments
The research reported here was supported by the Educational Natural Science Foundation for Young teachers of China (No.XJEDU-2009S04). We would like to thank Dr Hai-yan Lan for her comments on this experiment. We also would like to acknowledge Dr. Ji Ma for her helpful suggestions on this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, B., Jiang, Gq., Wang, Yx. et al. Identification of differentially expressed transcripts involved in the salt-stress response of Salsola ferganica by suppression subtractive hybridization. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 103, 343–352 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9787-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9787-4