Abstract
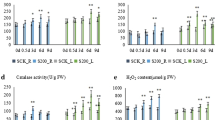
Limonium bicolor, a halophytic species of flowering plant, thrives in saline-alkali soil, demonstrating that it has developed an efficient saline-alkali resistance system and has potential utility as a source of genetic determinants for saline-alkali tolerance. In this study, complementary DNA microarrays containing 1,240 clones of L. bicolor were constructed to have a better view of transcript expression in L. bicolor during saline-alkali (NaHCO3)-induced stress. We obtained transcript profiles of L. bicolor in response to NaHCO3 for 6, 24, and 48 h. A total of 149 transcripts were differentially regulated at least once under the conditions studied. Among these, at least six different patterns of transcript regulation could be distinguished. There were 111, 45, and 51 transcripts that were differentially regulated by NaHCO3 stress for 6, 24, and 48 h, respectively. Of these, nearly 35% were putative novel or functionally unknown genes, and the remainders were involved in a variety of functional areas such as defense, transport, metabolism, and transcription regulation. The microarray analysis demonstrated the complexity of, and differences in, gene expression patterns resulting from different NaHCO3 stress times. This study provides informative preliminary data and a starting point for more in-depth analyses of saline-alkali tolerance in L. bicolor.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAP:
-
cold acclimation proteins
- EST:
-
expressed sequence tags
- LTP:
-
lipid transfer proteins
- MT:
-
metallothionein
- MTLP:
-
metallothionein-like protein
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- GST:
-
glutathione S-transferase
- Rubisco:
-
ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase
References
Chang S, Puryear J, Cairney J. A simple and efficient method for isolating RNA from pine trees. Plant Mol Biol Rep. 1993;11:113–6.
Chao DY, Luo YH, Shi M, Luo D, Lin HX. Salt-responsive genes in rice revealed by cDNA microarray analysis. Cell Res. 2005;15:796–810.
Cho SH, Hoang QT, Kim YY, Shin HY, Ok SH, Bae JM, et al. Proteome analysis of gametophores identified a metallothionein involved in various abiotic stress responses in Physcomitrella patens. Plant Cell Rep. 2006;25:475–88.
de Hoon MJ, Imoto S, Nolan J, Miyano S. Open source clustering software. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:1453–4.
Fu C, Miao W. Cloning and characterization of a new multi-stress inducible metallothionein gene in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Protist. 2006;157:193–203.
Gasmi A, Srairi N, Guermazi S, Karoui H, El Ayeb M. Biological activity of a lectin-like protein purified from Vipera lebetina venom. Toxicon. 1998;36:1738.
Gonorazky AG, Regente MC, Canal LDL. Stress induction and antimicrobial properties of a lipid transfer protein in germinating sunflower seeds. J Plant Physiol. 2005;162:618–24.
Jang CS, Kim DS, Bu SY, Kim JB, Lee SS, Kim JY, et al. Isolation and characterization of lipid transfer protein (LTP) genes from a wheat–rye translocation line. Plant Cell Rep. 2002;20:961–6.
Jin H, Plaha P, Park JY, Hong CP, Lee IS, Yang ZH, et al. Comparative EST profiles of leaf and root of Leymus chinensis, a xerophilous grass adapted to high pH sodic soil. Plant Sci. 2006;170:1081–6.
Jones JT, Mullet JE. A salt-and dehydration-inducible pea gene, Cyp15a, encodes a cell-wall protein with sequence similarity to cysteine proteases. Plant Mol Biol. 1995;28:1055–65.
Ledoigt G, Griffaut B, Debiton E, Vian C, Mustel A, Evray G, et al. Analysis of secreted protease inhibitors after water stress in potato tubers. Int J Biol Macromol. 2006;38:268–71.
Liu XJ, Huang BB, Lin J, Fei J, Chen ZH, Pang YZ, et al. A novel pathogenesis-related protein (SsPR10) from Solanum surattense with ribonucleolytic and antimicrobial activity is stress-and pathogen-inducible. J Plant Physiol. 2006;163:546–56.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001;25:402–8.
Martínez M, Rubio-Somoza I, Carbonero P, Díaz I. A cathepsin B-like cysteine protease gene from Hordeum vulgare (gene CatB) induced by GA in aleurone cells is under circadian control in leaves. J Exp Bot. 2003;384:951–9.
Moons A. Osgstu3 and osgtu4, encoding tau class glutathione S-transferases, are heavy metal- and hypoxic stress-induced and differentially salt stress-responsive in rice roots. FEBS Lett. 2003;553:427–32.
Neven LG, Haskell DW, Hofig A, Li QB, Guy CL. Characterization of a spinach gene responsive to low temperature and water stress. Plant Mol Biol. 1993;21:291–305.
Ouyang B, Yang T, Li H, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Zhang J, et al. Identification of early salt stress response genes in tomato root by suppression subtractive hybridization and microarray analysis. J Exp Bot. 2007;58:507–20.
Pinheiro C, Kehr J, Ricardo CP. Effect of water stress on lupin stem protein analysed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Planta. 2005;221:716–28.
Roxas VP, Lodhi SA, Garrett DK, Mahan JR, Allen RD. Stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco seedlings that overexpress glutathione S-transferase/glutathione peroxidase. Plant Cell Physiol. 2000;41:1229–34.
Roxas VP, Smith RK Jr, Allen ER, Allen RD. Overexpression of glutathione S-transferase/glutathione peroxidase enhances the growth of transgenic tobacco seedlings during stress. Nat Biotechnol. 1997;15:988–91.
Sarowar S, Kim YJ, Kim EN, Kim KD, Hwang BK, Islam R, et al. Overexpression of a pepper basic pathogenesis-related protein 1 gene in tobacco plants enhances resistance to heavy metal and pathogen stresses. Plant Cell Rep. 2005;24:216–24.
Ueda A, Kathiresan A, Bennett J, Takabe T. Comparative transcriptome analyses of barley and rice under salt stress. Theor Appl Genet. 2006;112:1286–94.
Walia H, Wilson C, Zeng L, Ismail AM, Condamine P, Close TJ. Genome-wide transcriptional analysis of salinity stressed japonica and indica rice genotypes during panicle initiation stage. Plant Mol Biol. 2007;63:609–23.
Wong CE, Li Y, Labbe A, Guevara D, Nuin P, Whitty B, et al. Transcriptional profiling implicates novel interactions between abiotic stress and hormonal responses in Thellungiella, a close relative of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006;140:1437–50.
Wu G, Robertson AJ, Liu X, Zheng P, Wilen RW, Nesbitt NT, et al. A lipid transfer protein gene BG-14 is differentially regulated by abiotic stress, ABA, anisomycin, and sphingosine in bromegrass (Bromus inermis). J Plant Physiol. 2004;161:449–58.
Yu L, Wan F, Dutta S, Welsh S, Liu ZH, Freundt E, et al. Autophagic programmed cell death by selective catalase degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:4952–7.
Zhu JK. Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2003;6(5):441–5.
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30571509) and the Key Research Projects of Heilongjiang Province (GB06B303-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Ma, H., Liu, G. et al. Analysis of Gene Expression Profile of Limonium bicolor under NaHCO3 Stress Using cDNA Microarray. Plant Mol Biol Rep 26, 241–254 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-008-0037-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-008-0037-4