Abstract
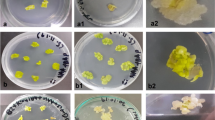
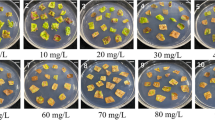
Transgenic hairy roots were induced from petiole and root segments of in vitro plant Aralia elata, a medicinal woody shrub, after co-cultivation with A. rhizogenes ATCC 15834. The percentage of putative hairy root induction from root segments was higher (26.7%) than petiole explants (10.0%). Hairy roots showed active production of lateral roots with vigorous elongation. Transgenic plants were regenerated from hairy roots via somatic embryogenesis. These plants had wrinkled leaves, short petioles and numerous lateral hairy roots. The RT-PCR analysis showed the expression of rol A, B, C, D, aux 1 and 2 genes differed between the transgenic lines. Endogenous IAA level was higher in transgenic than non-transgenic plants. Conclusively, transgenic hairy roots were developed for first time in A. elata and the transgenic hairy root lines showed distinct morphological growth pattern and gene expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbier-Brygoo H, Maurel C, Shen WH, Ephritikhine G, Delbarre A, Guern J, (1990) Use of mutants and transformed plants to study the action of auxins Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 44: 67–77
Brillanceau MH, David C, Tempe J, (1989) Genetic transformation of Catharanthus roseus G. Don by Agrobacterium rhizogenes Plant Cell Rep. 8: 63–66
Cha KC, Myung EJ, (2003) Ethanol fraction of Aralia eleta SEEM. Enhances antioxidant activity and lowers serum lipids in rats when administered with benzo (α) pyrene Biol. Pharm. Bull. 26: 1502–1504
De Cleene M, De Ley J, (1981). The host range of infectious hairy-root Bot. Rev. 47: 147–194
Giri A, Lakshmi Narasu M, (2000) Transgenic hairy roots: recent trends and applications Biotechnol. Adv. 18: 1–22
Godo T, Tsujii O, Ishikawa K, Mii M, (1997) Fertile transgenic plants of Nierembergia scoparia sendtner obtained by mikimopine type strain of Agrobacterium rhizogenes Sci. Hort. 68: 101–111
Gutierrez-Pesce P, Taylor K, Muleo R, Rugini E, (1998) Somatic embryogenesis and shoot regeneration from transgenic roots of the cherry root stock colt (Prunus avium×P. pseudocerasus) mediated by pRi 1855 T-DNA of Agrobacterium rhizogenes Plant Cell Rep. 17: 574–580
Hoshino Y, Mii M, (1998). Bialaphos stimulates shoot regeneration fron hairy roots of snapdragon (Antirrhinum majus L.) transformed by Agrobacterium rhizogenes Plant Cell Rep. 17: 256–261
Kaimori N, (1987). Mass propagation of Japanese Amgelica tree (Aralia eleta S.) through biotechnology Agr. Hort. 61: 75–47
Kim YH, Lee MK, Lee MJ, (1990). Studies on the saponins in the shoot of Aralia eleta (II) Korean J. Dietary Cult. 5: 243–251
Lee MH, Yoon ES, Jeong JH, Choi YE, (2004) Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transformation of Taraxacum platycarpum and changes of morphological characters Plant Cell Rep. 22: 822–827
Mihaljevic SZ, Stipkovic S, Jelaska S, (1996) Increase of root induction in Pinus nigra explants using agrobacteria Plant Cell Rep. 15: 610–614
Moon HK & Youn Y (1999) Somatic embryogenesis from winter buds of 10-year-old Aralia elata. In: Jain SM, Gupta PK & Newton RJ (eds) Somatic Embryogenesis in Woody Plants. Vol 5, Kluwer Academic Publishers (pp 129–134)
Murashige T, Skoog F, (1962). Arevised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497
Nilsson O, Moritz T, Imbault N, Sandberg G, Olsson O, (1993). Hormonal characterization of transgenic tobacco plants expressing the rol C gene of Agrobacterium rhizogenes TL-DNA Plant Physiol. 102: 363–371
Nilsson O, Olsson O, (1997). Getting to the root: the role of the Agrobacterium rhizogenes rol genes in the formation of hairy roots Physiol. Plant. 100: 463–473
Ohara A, Akadaka Y, Daimon H, Mill M, (2000). Plant regeneration from hairy roots induced by infection with Agobacterium rhizogenes in Crotalaria juncea L. Plant Cell Rep. 19: 563–568
Otani M, Mill M, Handa T, Kamada H, Shimadal T, (1993) Transformation of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas Lam.) plants by Agobacterium rhizogenes Plant Sci. 94: 151–159
Pena L, Seguin A, (2001) Recent advances in the genetic transformation of trees Trends Biotech. 19: 500–506
Petit A, David C, Dahl GA, Ellis GJ, Guyon P, (1983) Further extension of the opine concept: Plasmid in Agrobacterium rhizogenes cooperate for opine degradation Mol. Gen. Genet. 190: 204–214
Piispanen R, Aronen T, Chen X, Saranpaa P, Haggman H, (2003). Silver birch (Betula pendula) plants with aux and rol genes show consistent changes in morphology, xylem structure and chemistry Tree Physiol. 23: 721–733
Schaerer S, Pilet PE, (1992). Quantification of indole-3-acetic acid in untransformed and Agrobacterium rhizogenes-transformed pea roots using gas chromatography mass spectrometry Planta 189: 55–59
Spano L, Mariotti D, Pezzotti M, Damiani F, Arcioni S, (1987). Hairy root transformation in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Theo. Appl. Gene. 73(4): 523–530
Tzfira T, Ben-Meir H, Vainstein A, Altman A, (1996) Highly efficient transformation and regeneration of aspen plants through shoot-bud formation in root culture Plant Cell Rep. 15: 566–571
Uozumi N, Ohtake Y, Nakashimada Y, Morikawa Y, Tanaka N, Kobayashi T, (1996). Efficient regeneration from GUS-transformed Ajuga hairy root J. Ferm. Bioeng. 81: 374–378
Weiler EW, (1984). Immunoassay of plant growth regulators Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 35: 85–95
Yoshikawa M, Murakami T, Harada E, Murakami N, Yamahara J, Marsuda H, (1996) Bioactive saponiuns and glycosides VII on the hypoglycemic principles from the root cortex of Aralia eleta Seem.: Structure related hypoglycemic activity of oleanolic acid oligoglycoside Chem. Pharm. Bull. 44: 1923–1927
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Korea Research Foundation (F00007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, H., Anbazhagan, V., You, X. et al. Production of transgenic Aralia elata regenerated from Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transformed roots. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 85, 187–196 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-005-9070-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-005-9070-2