Abstract
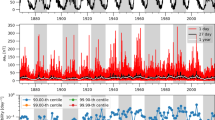
Near-Earth solar winds are separated into two groups: slow solar wind (SSW) with plasma speed [\(V_{\mathrm{sw}}\)] \(< 500\) km s−1 and high-speed solar wind (HSW) with \(V_{\mathrm{sw}} > 700\) km s−1. A comparative study is performed on the plasma and interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) properties of the near-Earth SSW and HSW, using solar wind measurements propagated to Earth’s bow shock nose from 1963 through 2022. On average, HSW is characterized by higher alpha-to-proton density ratio [\(N_{\mathrm{a}}/N_{\mathrm{p}}\)] (67%), ram pressure [\(P_{ \mathrm{sw}}\)] (95%), proton temperature [\(T_{\mathrm{p}}\)] (370%), reconnection electric field [\(VB_{\mathrm{s}}\)] (141%), Alfvén speed [\(V_{\mathrm{A}}\)] (76%), magnetosonic speed [\(V_{\mathrm{ms}}\)] (65%), and lower proton density [\(N_{\mathrm{p}}\)] (52%) and plasma-\(\beta\) (54%) than SSW. In \(VB_{\mathrm{s}}\), \(V = V_{\mathrm{sw}}\), \(B_{\mathrm{s}}\) is the southward component of IMF. \(V_{\mathrm{A}} = B_{0}/\sqrt{\mu_{0}\rho}\), \(V_{\mathrm{ms}} = \sqrt{V_{\mathrm{A}}^{2}+V_{\mathrm{S}}^{2}}\), where \(B_{0}\) is the IMF magnitude, \(\mu_{0}\) is the free space permeability, \(\rho\) is the solar wind mass density, and \(V_{\mathrm{S}}\) is the sound speed. \(\beta\) is defined as the plasma pressure to the magnetic-pressure ratio. The geomagnetic activity is found to be enhanced during HSW, as reflected in higher average auroral electrojet index [AE] (213%) and stronger geomagnetic Dst index (367%) compared to those during SSW. The SSW characteristic parameters \(N_{\mathrm{a}}/N_{\mathrm{p}}\), \(T_{\mathrm{p}}\), \(B_{0}\), \(V_{\mathrm{A}}\), and \(V_{\mathrm{ms}}\) exhibit medium to strong correlations (correlation coefficients \(r = 0.51\) to 0.87) with the \(F_{\mathrm{10.7}}\) solar flux, while \(\beta\) and Mach numbers exhibit strong anti-correlations (\(r = -0.82\) to −0.90) with \(F_{\mathrm{10.7}}\). The associations are weaker or insignificant for HSW.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The Ulysses solar wind data are obtained from COHOWeb (omniweb.gsfc.nasa.gov/coho/). The near-Earth solar wind and IMF measurements are obtained from OMNIWeb (omniweb.gsfc.nasa.gov/). The geomagnetic indices are obtained from the World Data Center for Geomagnetism, Kyoto, Japan (wdc.kugi.kyoto-u.ac.jp/). The \(F_{10.7}\) solar flux data are obtained from the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) Interactive Solar Irradiance Data Center (lasp.colorado.edu/lisird/).
References
Abbo, L., Ofman, L., Antiochos, S.K., Hansteen, V.H., Harra, L., Ko, Y.-K., Lapenta, G., Li, B., Riley, P., Strachan, L., von Steiger, R., Wang, Y.-M.: 2016, Slow solar wind: observations and modeling. Space Sci. Rev. 201, 55. DOI.
Belcher, J.W., Davis, L. Jr.: 1971, Large-amplitude Alfvén waves in the interplanetary medium, 2. J. Geophys. Res. 76, 3534. DOI.
Burlaga, L.F.: 1974, Interplanetary stream interfaces. J. Geophys. Res. 79, 3717. DOI.
Burlaga, L.F., Behannon, K.W., Hansen, S.F., Pneuman, G.W., Feldman, W.C.: 1978, Sources of magnetic fields in recurrent interplanetary streams. J. Geophys. Res. 83, 4177. DOI.
Burton, R.K., McPherron, R.L., Russell, C.T.: 1975, An empirical relationship between interplanetary conditions and Dst. J. Geophys. Res. 80, 4204. DOI.
Carrington, R.C.: 1859, Description of a Singular Appearance seen in the Sun on September 1, 1859. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 20, 13. DOI.
Chen, P.F.: 2011, Coronal mass ejections: models and their observational basis. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 8, 1. DOI.
Cliver, E.W., Feynman, J., Garrett, H.B.: 1990, An estimate of the maximum speed of the solar wind, 1938-1989. J. Geophys. Res. 95, 17103. DOI.
D’Amicis, R., Perrone, D., Bruno, R., Velli, M.: 2021, On Alfvénic slow wind: a journey from the Earth back to the Sun. J. Geophys. Res. 126, e2020JA028996. DOI.
Davis, L. Jr.: 1966, Models of interplanetary fields and plasma flow. In: Mackin, R.J., Neugebauer, M. (eds.) The Solar Wind, Pergamon Press, New York, 147.
Davis, L. Jr., Smith, E.J., Coleman, P.J., Sonett, C.P.: 1966, Interplanetary magnetic measurements. In: Mackin, R.J., Neugebauer, M. (eds.) The Solar Wind, Pergamon Press, New York, 35.
Gosling, J.T., Hundhausen, A.J., Bame, S.J.: 1976, Solar wind stream evolution at large heliocentric distances: experimental demonstration and the test of a model. J. Geophys. Res. 81, 2111. DOI.
Gosling, J.T., Asbridge, J.R., Bame, S.J., Feldman, W.C.: 1978, Solar wind stream interfaces. J. Geophys. Res. 83, 1401. DOI.
Gosling, J.T., Borrini, G., Asbridge, J.R., Bame, S.J., Feldman, W.C., Hansen, R.T.: 1981, Coronal streamers in the solar wind at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 5438. DOI.
Grandin, M., Aikio, A.T., Kozlovsky, A.: 2019, Properties and geoeffectiveness of solar wind high-speed streams and stream interaction regions during solar cycles 23 and 24. J. Geophys. Res. 124, 3871. DOI.
Hajra, R.: 2021a, Variation of the interplanetary shocks in the inner heliosphere. Astrophys. J. 917, 91. DOI.
Hajra, R.: 2021b, September 2017 space-weather events: a study on magnetic reconnection and geoeffectiveness. Solar Phys. 296, 50. DOI.
Hajra, R.: 2021c, Weakest solar cycle of the space age: a study on solar wind–magnetosphere energy coupling and geomagnetic activity. Solar Phys. 296, 33. DOI.
Hajra, R., Sunny, J.V.: 2022, Corotating interaction regions during solar cycle 24: a study on characteristics and geoeffectiveness. Solar Phys. 297, 30. DOI.
Hajra, R., Tsurutani, B.T.: 2018, Interplanetary shocks inducing magnetospheric supersubstorms (\({SML} <-2500\) nT): unusual auroral morphologies and energy flow. Astrophys. J. 858, 123. DOI.
Hajra, R., Tsurutani, B.T.: 2022, Near-Earth sub-Alfvénic solar winds: interplanetary origins and geomagnetic impacts. Astrophys. J. 926, 135. DOI.
Hajra, R., Echer, E., Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D.: 2013, Solar cycle dependence of high-intensity long-duration continuous AE activity (HILDCAA) events, relativistic electron predictors? J. Geophys. Res. 118, 5626. DOI.
Hajra, R., Tsurutani, B.T., Echer, E., Gonzalez, W.D., Santolik, O.: 2015, Relativistic (\(E >0.6\), \(>2.0\), and \(>4.0\) MeV) electron acceleration at geosynchronous orbit during high-intensity, long-duration, continuous AE activity (HILDCAA) events. Astrophys. J. 799, 39. DOI.
Hajra, R., Henri, P., Myllys, M., Héritier, K.L., Galand, M., Simon Wedlund, C., Breuillard, H., Behar, E., Edberg, N.J.T., Goetz, C., Nilsson, H., Eriksson, A.I., Goldstein, R., Tsurutani, B.T., Moré, J., Vallières, X., Wattieaux, G.: 2018, Cometary plasma response to interplanetary corotating interaction regions during 2016 June–September: a quantitative study by the Rosetta Plasma Consortium. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 480, 4544. DOI.
Krieger, A.S., Timothy, A.F., Roelof, E.C.: 1973, A coronal hole and its identification as the source of a high velocity solar wind stream. Solar Phys. 29, 505. DOI.
Lamy, P.L., Floyd, O., Boclet, B., Wojak, J., Gilardy, H., Barlyaeva, T.: 2019, Coronal mass ejections over solar cycles 23 and 24. Space Sci. Rev. 215, 39. DOI.
McComas, D.J., Barraclough, B.L., Funsten, H.O., Gosling, J.T., Santiago-Muñoz, E., Skoug, R.M., Goldstein, B.E., Neugebauer, M., Riley, P., Balogh, A.: 2000, Solar wind observations over Ulysses’ first full polar orbit. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 10419. DOI.
Nakagawa, Y., Nozawa, S., Shinbori, A.: 2019, Relationship between the low-latitude coronal hole area, solar wind velocity, and geomagnetic activity during solar cycles 23 and 24. Earth Planets Space 71, 24. DOI.
Ness, N.F., Wilcox, J.M.: 1964, Solar origin of the interplanetary magnetic field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 13, 461. DOI.
Neugebauer, M., Snyder, C.W.: 1966, Mariner 2 observations of the solar wind: 1. Average properties. J. Geophys. Res. 71, 4469. DOI.
Parker, E.N.: 1965, Dynamical theory of the solar wind. Space Sci. Rev. 4, 666. DOI.
Phillips, J.L., Bame, S.J., Feldman, W.C., Gosling, J.T., Hammond, C.M., McComas, D.J., Goldstein, B.E., Neugebauer, M., Scime, E.E., Suess, S.T.: 1995, Ulysses solar wind plasma observations at high southerly latitudes. Science 268, 1030. DOI.
Pizzo, V.J.: 1985, In: Tsurutani, B.T., Stone, R.G. (eds.) Interplanetary Shocks on the Large Scale: A Retrospective on the Last Decade’s Theoretical Efforts 35, AGU, Washington, 51.
Press, W.H., Teukolsky, S.A., Vetterling, W.T., Flannery, B.P.: 1992, Numerical Recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 0521431085.
Reiff, P.H.: 1990, The use and misuse of statistics in space physics. J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 42, 1145. DOI.
Richardson, I.G., Cliver, E.W., Cane, H.V.: 2000, Sources of geomagnetic activity over the solar cycle: relative importance of coronal mass ejections, high-speed streams, and slow solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 18203. DOI.
Sanchez-Diaz, E., Rouillard, A.P., Lavraud, B., Segura, K., Tao, C., Pinto, R., Sheeley, N.R. Jr, Plotnikov, I.: 2016, The very slow solar wind: properties, origin and variability. J. Geophys. Res. 121, 2830. DOI.
Sarabhai, V.: 1963, Some consequences of nonuniformity of solar wind velocity. J. Geophys. Res. 68, 1555. DOI.
Schwabe, H.: 1844, Sonnen — Beobachtungen im Jahre 1843. Astron. Nachr. 21, 234. DOI.
Scolini, C., Messerotti, M., Poedts, S., Rodriguez, L.: 2018, Halo coronal mass ejections during Solar Cycle 24: reconstruction of the global scenario and geoeffectiveness. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 8, A09. DOI.
Sheeley, N.R., Harvey, J.W.: 1981, Coronal holes, solar wind streams, and geomagnetic disturbances during 1978 and 1979. Solar Phys. 70, 237. DOI.
Sheeley, N.R., Harvey, J.W., Feldman, W.C.: 1976, Coronal holes, solar wind streams, and recurrent geomagnetic disturbances: 1973-1976. Solar Phys. 49, 271. DOI.
Smith, E.J., Tsurutani, B.T., Rosenberg, R.L.: 1978, Observations of the interplanetary sector structure up to heliographic latitudes of \(16^{\circ}\): pioneer 11. J. Geophys. Res. 83, 717. DOI.
Smith, E.J., Wolfe, J.H.: 1976, Observations of interaction regions and corotating shocks between one and five AU: pioneers 10 and 11. Geophys. Res. Lett. 3, 137. DOI.
Suess, S.T., Ko, Y.-K., von Steiger, R., Moore, R.L.: 2009, Quiescent current sheets in the solar wind and origins of slow wind. J. Geophys. Res. 114, A04103. DOI.
Sunny, J.V., Nair, A.G., Babu, M., Hajra, R.: 2023, A comparative study on geoeffective and non-geoeffective corotating interaction regions. Adv. Space Res. 71, 268. DOI.
Syed Ibrahim, M., Joshi, B., Cho, K.-S., Kim, R.-S., Moon, Y.-J.: 2019, Interplanetary coronal mass ejections during solar cycles 23 and 24: Sun-Earth propagation characteristics and consequences at the near-Earth region. Solar Phys. 294, 54. DOI.
Tang, F., Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D., Akasofu, S.I., Smith, E.J.: 1989, Solar sources of interplanetary southward Bz events responsible for major magnetic storms (1978-1979). J. Geophys. Res. 94, 3535. DOI.
Tsurutani, B.T., Echer, E., Gonzalez, W.D.: 2011, The solar and interplanetary causes of the recent minimum in geomagnetic activity (MGA23): a combination of midlatitude small coronal holes, low IMF BZ variances, low solar wind speeds and low solar magnetic fields. Ann. Geophys. 29, 839. DOI.
Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D.: 1987, The cause of high-intensity long-duration continuous AE activity (HILDCAAs): interplanetary Alfvén wave trains. Planet. Space Sci. 35, 405. DOI.
Tsurutani, B.T., Hajra, R.: 2022, Extremely slow (\(V_{\mathrm{sw}} <300\) km s−1) solar winds (ESSWs) at 1 au: causes of extreme geomagnetic quiet at Earth. Astrophys. J. 936, 155. DOI.
Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D., Tang, F., Lee, Y.T.: 1992, Great magnetic storms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 19, 73. DOI.
Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D., Lakhina, G.S., Alex, S.: 2003, The extreme magnetic storm of 1-2 September 1859. J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1268. DOI.
Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D., Zhou, X.-Y., Lepping, R.P., Bothmer, V.: 2004, Properties of slow magnetic clouds. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 66, 147. DOI.
Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, W.D., Gonzalez, A.L.C., Guarnieri, F.L., Gopalswamy, N., Grande, M., Kamide, Y., Kasahara, Y., Lu, G., Mann, I., McPherron, R., Soraas, F., Vasyliunas, V.: 2006, Corotating solar wind streams and recurrent geomagnetic activity: a review. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A07S01. DOI.
Tsurutani, B.T., Hajra, R., Tanimori, T., Takada, A., Remya, B., Mannucci, A.J., Lakhina, G.S., Kozyra, J.U., Shiokawa, K., Lee, L.C., Echer, E., Reddy, R.V., Gonzalez, W.D.: 2016, Heliospheric plasma sheet (HPS) impingement onto the magnetosphere as a cause of relativistic electron dropouts (REDs) via coherent EMIC wave scattering with possible consequences for climate change mechanisms. J. Geophys. Res. 121, 10130. DOI.
Verbanac, G., Bandić, M., Krauss, S.: 2022, Influence of the solar wind high-speed streams on the thermospheric neutral density during the declining phase of solar cycle 23. Adv. Space Res. 69, 4335. DOI.
Verbanac, G., Vršnak, B., Veronig, A., Temmer, M.: 2011a, Equatorial coronal holes, solar wind high-speed streams, and their geoeffectiveness. Astron. Astrophys. 526, A20. DOI.
Verbanac, G., Vršnak, B., Živković, S., Hojsak, T., Veronig, A.M., Temmer, M.: 2011b, Solar wind high-speed streams and related geomagnetic activity in the declining phase of solar cycle 23. Astron. Astrophys. 533, A49. DOI.
Verbanac, G., Živković, S., Vršnak, B., Bandić, M., Hojsak, T.: 2013, Comparison of geoeffectiveness of coronal mass ejections and corotating interaction regions. Astron. Astrophys. 558, A85. DOI.
Vršnak, B., Temmer, M., Veronig, A.M.: 2007, Coronal holes and solar wind high-speed streams: II. Forecasting the geomagnetic effects. Solar Phys. 240, 331. DOI.
Vršnak, B., Dumbović, M., Čalogović, J., Verbanac, G., Poljanı̌ć–Beljan, I.: 2017, Geomagnetic effects of corotating interaction regions. Solar Phys. 292, 140. DOI.
Winterhalter, D., Smith, E.J., Burton, M.E., Murphy, N., McComas, D.J.: 1994, The heliospheric plasma sheet. J. Geophys. Res. 99, 6667. DOI.
Acknowledgments
The work is funded by the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB, grant no. SB/S2/RJN-080/2018), a statutory body of the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India through the Ramanujan Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
I am the sole author of this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hajra, R. Near-Earth High-Speed and Slow Solar Winds: A Statistical Study on Their Characteristics and Geomagnetic Impacts. Sol Phys 298, 53 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-023-02141-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-023-02141-6