Abstract
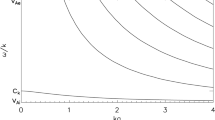
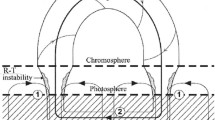
Recent studies show that the parallel heat conduction in the plasma of coronal loops associated with solar flares is controlled by the turbulence-dominated mode, in addition to the free streaming and collision-dominated modes. Using scaling laws, we have studied the relative importance of various modes of parallel heat conduction in the coronal loops of the small (B-class) and large (X-class) solar flares. The scaling laws relate the maximum loop temperature and heating rate to the loop pressure and loop half-length for collision, turbulence, and free streaming dominated modes of the parallel heat conduction. For a set of values of loop half-length \(\approx(2.0 - 3.0)\times10^{9} \) cm, loop pressure \(\approx(6.0 - 20.0)\) erg cm−3 for the small coronal loops, and loop half-length \(\approx(3.0 - 11.0)\times10^{9} \) cm, loop pressure \(\approx(1.0 - 103.0)\) erg cm−3 for the large coronal loops at a constant value of mean free path \(= 10^{7.5} \) cm, our results show that the estimated heating time is ≈ 40–125 s, which represents a fast heating rate. The estimated maximum loop temperature is found to be lower compared to the observed values for the coronal loops of the solar flares. The nature of positive and negative correlation between the scaling parameters show that the collision-dominated heat conduction is a dominant process in the loops of small flares while turbulence-dominated processes suppress the collision-dominated parallel heat conduction in the loops of large solar flares. The instabilities caused by the fast flow of evaporation from the footpoints are discussed as the source of the turbulence.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antiochos, S., Sturrock, P.: 1978, Evaporative cooling of flare plasma. Astrophys. J. 220, 1137. ADS.
Antonucci, E., Gabriel, A., Acton, L., Culhane, J., Doyle, J., Leibacher, J., Machado, M., Orwig, L., Rapley, C.: 1982, Impulsive phase of flares in soft X-ray emission. Solar Phys. 78, 107. DOI. ADS.
Aschwanden, M.J., Stern, R.A., Güdel, M.: 2008, Scaling laws of solar and stellar flares. Astrophys. J. 672, 659. DOI.
Bian, N.H., Kontar, E.P., Emslie, A.G.: 2016, Suppression of parallel transport in turbulent magnetized plasmas and its impact on the non-thermal and thermal aspects of solar flares. Astrophys. J. 824, 78. DOI.
Bradshaw, S.J., Emslie, A.G., Bian, N.H., Kontar, E.P.: 2019, Coronal loop scaling laws for various forms of parallel heat conduction. Astrophys. J. 880, 80. DOI.
Brown, J.C.: 1972, The directivity and polarisation of thick target X-ray bremsstrahlung from solar flares. Solar Phys. 26, 441. DOI. ADS.
Brown, J., Melrose, D., Spicer, D.: 1979, Production of a collisionless conduction front by rapid coronal heating and its role in solar hard X-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. 228, 592. DOI. ADS.
Cargill, P.J., Mariska, J.T., Antiochos, S.K.: 1995, Cooling of solar flares plasmas. I: Theoretical considerations. Astrophys. J. 439, 1034. DOI. ADS.
Culhane, J., Vesecky, J., Phillips, K.: 1970, The cooling of flare produced plasmas in the solar corona. Solar Phys. 15, 394. DOI. ADS.
Dennis, B.R., Emslie, A., Hudson, H.: 2011, Overview of the volume. Space Sci. Rev. 159, 3. DOI.
Fang, X., Yuan, D., Xia, C., Van Doorsselaere, T., Keppens, R.: 2016, The role of Kelvin–Helmholtz instability for producing loop-top hard X-ray sources in solar flares. Astrophys. J. 833, 36. DOI.
Fisher, G.H., Canfield, R.C., McClymont, A.N.: 1984, Chromospheric evaporation velocities in solar flares. Astrophys. J. 281, L79. DOI. ADS.
Fletcher, L., Dennis, B.R., Hudson, H.S., Krucker, S., Phillips, K., Veronig, A., Battaglia, M., Bone, L., Caspi, A., Chen, Q., et al.: 2011, An observational overview of solar flares. Space Sci. Rev. 159, 19. DOI.
Hannah, I., Hudson, H., Battaglia, M., Christe, S., Kašparová, J., Krucker, S., Kundu, M., Veronig, A.: 2011, Microflares and the statistics of X-ray flares. Space Sci. Rev. 159, 263. DOI.
Hirayama, T.: 1974, Theoretical model of flares and prominences. Solar Phys. 34, 323. DOI. ADS.
Holman, G., Kundu, M., Papadopoulos, K.: 1982, Electron pitch angle scattering and the impulsive phase microwave and hard X-ray emission from solar flares. Astrophys. J. 257, 354. DOI. ADS.
Holman, G.D., Aschwanden, M.J., Aurass, H., Battaglia, M., Grigis, P.C., Kontar, E.P., Liu, W., Saint-Hilaire, P., Zharkova, V.V.: 2011, Implications of X-ray observations for electron acceleration and propagation in solar flares. Space Sci. Rev. 159, 107. DOI.
Hudson, H.S.: 2011, Global properties of solar flares. Space Sci. Rev. 158, 5. DOI.
Jain, R., Dave, H., Shah, A., Vadher, N., Shah, V.M., Ubale, G., Manian, K., Solanki, C.M., Shah, K., Kumar, S., et al.: 2005, Solar X-ray spectrometer (SOXS) mission on board GSAT2 Indian spacecraft: The low-energy payload. Solar Phys. 227, 89. DOI.
Jiang, Y.W., Liu, S., Liu, W., Petrosian, V.: 2006, Evolution of the loop-top source of solar flares: Heating and cooling processes. Astrophys. J. 638, 1140. DOI.
Kontar, E., Brown, J., Emslie, A., Hajdas, W., Holman, G., Hurford, G., Kašparová, J., Mallik, P., Massone, A., McConnell, M.L., et al.: 2011, Deducing electron properties from hard X-ray observations. Space Sci. Rev. 159, 301. DOI.
Kontar, E.P., Bian, N.H., Emslie, A.G., Vilmer, N.: 2013, Turbulent pitch-angle scattering and diffusive transport of hard X-ray-producing electrons in flaring coronal loops. Astrophys. J. 780, 176. DOI.
Kontar, E., Perez, J., Harra, L., Kuznetsov, A., Emslie, A., Jeffrey, N., Bian, N., Dennis, B.: 2017, Turbulent kinetic energy in the energy balance of a solar flare. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 155101. DOI.
Korablev, L., Rudakov, L.: 1966, Quasilinear theory of current instability in a plasma (quasilinear current instability in two-temperature plasma for Coulomb collision and free electron acceleration). Sov. Phys. JETP 23, 145.
Krucker, S., Battaglia, M., Cargill, P., Fletcher, L., Hudson, H., MacKinnon, A., Masuda, S., Sui, L., Tomczak, M., Veronig, A., et al.: 2008, Hard X-ray emission from the solar corona. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 16, 155. DOI.
Kumar, P., Jain, R., Bhatt, Y., Shishodia, Y.: 2019, Characteristics of solar microflares as seen in soft X-ray emission. Pramāna 92, 32. DOI.
Kumar, P., Choudhary, R., Sampathkumaran, P., Mandal, S.: 2020, A comparative study of non-thermal parameters of the X-class solar flare plasma obtained from cold and warm thick-target models; error estimation by Monte Carlo simulation method. Astrophys. Space Sci. 365, 1. DOI.
Lin, R.P., Dennis, B.R., Hurford, G., Smith, D., Zehnder, A., Harvey, P., Curtis, D., Pankow, D., Turin, P., Bester, M., et al.: 2003, The Reuven–Ramaty High-Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager (RHESSI), Springer, Dordrecht, 3. DOI.
Mariska, J.T., Emslie, A.G., Li, P.: 1989, Numerical simulations of impulsively heated solar flares. Astrophys. J. 341, 1067. DOI. ADS.
Melrose, D.: 1990, Particle beams in the solar atmosphere: General overview. Solar Phys. 130, 3. DOI.
Parker, E.N.: 1957, Sweet’s mechanism for merging magnetic fields in conducting fluids. J. Geophys. Res. 62, 509. DOI.
Reale, F.: 2007, Diagnostics of stellar flares from X-ray observations: From the decay to the rise phase. Astron. Astrophys. 471, 271. DOI.
Rosner, R., Tucker, W.H., Vaiana, G.: 1978, Dynamics of the quiescent solar corona. Astrophys. J. 220, 643. DOI. ADS.
Ruan, W., Xia, C., Keppens, R.: 2019, Extreme-ultraviolet and X-ray emission of turbulent solar flare loops. Astrophys. J. Lett. 877, L11. DOI.
Ryan, D.F., Chamberlin, P.C., Milligan, R.O., Gallagher, P.T.: 2013, Decay-phase cooling and inferred heating of M- and X-class solar flares. Astrophys. J. 778, 68. DOI.
Sagdeev, R.Z., Galeev, A.: 1969, Nonlinear Plasma Theory, Benjamin, New York. ADS.
Schwartz, R., Csillaghy, A., Tolbert, A., Hurford, G., Mc Tiernan, J., Zarro, D.: 2002, RHESSI data analysis software: Rationale and methods. Solar Phys. 210, 165. DOI.
Shibata, K., Yokoyama, T.: 1999, Origin of the universal correlation between the flare temperature and the emission measure for solar and stellar flares. Astrophys. J. 526, L49. DOI
Shibata, K., Yokoyama, T.: 2002, A Hertzsprung–Russell-like diagram for solar/stellar flares and corona: Emission measure versus temperature diagram. Astrophys. J. 577, 422. DOI.
Simões, P.J., Kontar, E.P.: 2013, Implications for electron acceleration and transport from non-thermal electron rates at looptop and footpoint sources in solar flares. Astron. Astrophys. 551, A135. DOI.
Smith, D., Brown, J.: 1980, Limits on the streaming and escape of electrons in thermal models for solar hard X-ray emission. Astrophys. J. 242, 799. DOI. ADS.
Spitzer, L.: 1962, Physics of Fully Ionized Gases, Courier Corporation, Mineola.
Zaumen, W., Acton, L.: 1974, Cooling of solar flare plasmas. Solar Phys. 36, 139. DOI.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the anonymous referee for his/her valuable comments, which greatly improved this paper. The authors also wish to thank Prof. Rajmal Jain (former professor, PRL Ahmedabad) for providing SSWIDL software. The authors wish to acknowledge RHESSI and SOXS missions for the availability of their open X-ray data of various classes of solar flares.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Declarations
The authors have no relevant financial or nonfinancial interests to disclose.
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, P., Choudhary, R.K. A Study on the Various Modes of Parallel Heat Conduction in the Coronal Loops of Small and Large Solar Flares Using Scaling Laws. Sol Phys 296, 147 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-021-01884-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-021-01884-4