Abstract
The directivity and polarisation of solar hard X-ray bursts is discussed in terms of two bremsstrahlung source models. These involve continuous and impulsive injection of electrons respectively, as described widely in the literature.
A detailed analysis is made of the continuous injection model in which electrons are accelerated downward into the dense chromosphere where their velocity distribution is greatly modified by collisions. This thick target scattering is described by a simple analytical model. Directivity and polarisation of the bremsstrahlung emission are calculated in detail for a thick target model in which the guiding magnetic field is vertical.
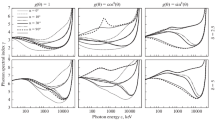
It is predicted for this model that X-ray sources should brighten from the centre to the limb of the solar disk, while the degree of polarisation should rise from zero to around 30 % near the limb. The plane of maximum intensity for any source is that containing the source and the disk centre. Both the directivity and polarisation should increase with increasing photon energy.
Very recent observations agree with these predictions though they suggest that the field is significantly non-vertical. If scattering is not included in the model, or if an impulsive injection model is taken, agreement with observations is not obtained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acton, L. W.: 1968, Astrophys. J. 152, 305.
Benz, A. O. and Gold, T.: 1971, Solar Phys. 21, 157.
Brown, J. C.: 1971, Solar Phys. 18, 489.
Brown, J. C.: 1972, Solar Phys. 25, 158.
Cheng, C. C.: 1972, Solar Phys. 22, 178.
Cline, T. L., Holt, S. S., and Hones, E. W.: 1968, J. Geophys. Res. 73, 434.
Darwin, C. G.: 1913, Phil. Mag. 25, 201.
Drake, J. F.: 1971, Solar Phys. 16, 152.
Elwert, G.: 1939, Ann. Physik. 34, 178.
Elwert, G.: 1968, in K. O. Kiepenheuer (ed.), ‘Structure and Development of Solar Active Regions’, IAU Symp. 35, 144.
Elwert, G. and Haug, E.: 1970, Solar Phys. 15, 234.
Elwert, G. and Haug, E.: 1971, Solar Phys. 20, 413.
Frost, K. J.: 1969, Astrophys. J. 158, L 159.
Gluckstern, R. L. and Hull, M. H.: 1953, Phys. Rev. 90, 1030.
Haug, E.: 1972a, Solar Phys. 25, 425.
Haug, E.: 1972b, private communications.
Hudson, H. S.: 1971, private communication.
de Jager, C. and Kundu, M. R.: 1963, Space Res. 3, 836.
Kahler, S. W. and Kreplin, R. W.: 1971, Astrophys. J. 168, 531.
Kane, S. R. and Anderson, K. A.: 1970, Astrophys. J. 162, 1003.
Koch, H. W. and Motz, J. W.: 1959, Rev. Mod. Phys. 31, 920.
Korchak, A. A.: 1967a, Soviet Astron.-AJ 11, 258.
Korchak, A. A.: 1967b, Soviet Phys. Doklady 12, 192.
Lin, R. P. and Hudson, H. S.: 1971, Solar Phys. 17, 412.
Ohki, K.: 1969, Solar Phys. 7, 260.
Pinter, Š.: 1969, Solar Phys. 8, 142.
Schatzman, E.: 1965, in C. de Jager (ed.), The Solar Spectrum, D. Reidel Publishing Company, p. 313.
Spitzer, L.: 1962, Physics of Fully Ionised Gases, Interscience.
Strauss, F. M. and Papagiannis, M. D. A.: 1971, Astrophys. J. 164, 369.
Sturrock, P. A.: 1968, in K. O. Kiepenheuer (ed.), ‘Structure and Development of Solar Active Regions’, IAU Symp. 35, 471.
Sweet, P. A.: 1969, Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 7, 149.
Syrovatskii, S. I. and Shmelva, O. P.: 1972, to appear in Soviet Astron.-AJ.
Takakura, T. and Kai, K.: 1966, Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 18, 57.
Takakura, T. and Scalise, E.: 1970, Solar Phys. 11, 434.
Tindo, I. P., Ivanov, V. D., Mandelstam, S. L., and Shuryghin, A. I.: 1970, Solar Phys. 14, 204.
Tindo, I. P., Ivanov, V. D., Mandelstam, S. L., and Shuryghin, A. I.: 1972a, Solar Phys. 24, 429.
Tindo, I. P., Valniček, B., Livshits, M. A., Ivanov, V. D.: 1972b, Lebedev Physical Institute, Laboratory of Spectroscopy, - Preprint No. 43.
Zirin, H., Pruss, G., and Vorpahl, J.: 1971, Solar Phys. 19, 463.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Temporarily at the Lehrstuhl für Theoretische Astrophysik der Universität Tübingen, West Germany.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brown, J.C. The directivity and polarisation of thick target X-ray bremsstrahlung from solar flares. Sol Phys 26, 441–459 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00165286
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00165286