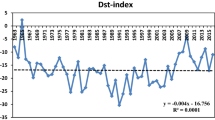
Abstract
An updated catalog is created of 303 well-defined high-speed solar wind streams that occurred in the time period 2009 – 2016. These streams are identified from solar and interplanetary measurements obtained from the OMNIWeb database as well as from the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) database. This time interval covers the deep minimum observed between the last two Solar Cycles 23 and 24, as well as the ascending, the maximum, and part of the descending phases of the current Solar Cycle 24. The main properties of solar-wind high-speed streams, such as their maximum velocity, their duration, and their possible sources are analyzed in detail. We discuss the relative importance of all those parameters of high-speed solar wind streams and especially of their sources in terms of the different phases of the current cycle. We carry out a comparison between the characteristic parameters of high-speed solar wind streams in the present solar cycle with those of previous solar cycles to understand the dependence of their long-term variation on the cycle phase. Moreover, the present study investigates the varied phenomenology related to the magnetic interactions between these streams and the Earth’s magnetosphere. These interactions can initiate geomagnetic disturbances resulting in geomagnetic storms at Earth that may have impact on technology and endanger human activity and health.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aslam, O.P.M., Badruddin: 2017, Study of the geoeffectiveness and galactic cosmic-ray response of VarSITI-ISEST campaign events in Solar Cycle 24. Solar Phys. 292, 17. DOI .
Badruddin, Falak, Z.: 2016, Study of the geo-effectiveness of coronal mass ejections, corotating interaction regions and their associated structures observed during Solar Cycle 23. Astrophys. Space Sci. 361, 253. DOI .
Badruddin, Kumar, A.: 2015, Study of the Forbush decreases, geomagnetic storms, and ground-level enhancements in selected intervals and their space weather implications. Solar Phys. 290, 127. DOI .
Badruddin, Singh, Y.P.: 2009, Geoeffectiveness of magnetic cloud, shock/sheath, interaction region, high-speed stream and their combined occurrence. Planet. Space Sci. 57, 318. DOI .
Bame, S.J., Asbridge, J.R., Feldman, W.C., Gosling, J.T.: 1976, Solar cycle evolution of high-speed solar wind streams. Astrophys. J. 207, 977.
Belov, A., Baisultanova, L., Eroshenko, E., Mavromichalaki, H., Yanke, V., Pchelkin, V., Plainaki, C., Mariatos, G.: 2005, Magnetospheric effects in cosmic rays during the unique magnetic storm on November 2003. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A09S20. DOI .
Bothmer, V., Zhukov, A.N.: 2007, The Sun as the prime source of space weather. In: Daglis, J. (ed.) Space Weather – Physics and Effects. DOI . Chapter 3.
Cane, H.V.: 2000, Coronal mass ejections and Forbush decreases. Space Sci. Rev. 93, 55. DOI .
Crooker, N.U., Shodhah, S., Gosling, J.T., Simmerer, J., Steinberg, J.T., Kahler, S.W.: 2000, Density extremes in the solar wind. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 3769. DOI .
de Toma, G.: 2011, Evolution of coronal holes and implications for high-speed solar wind during the minimum between Cycles 23 and 24. Solar Phys. 274, 19. DOI .
Eroshenko, E., Belov, A., Mavromichalaki, H., Mariatos, G., Oleneva, V., Plainaki, C., Yanke, V.: 2004, Cosmic ray variations during the two great bursts of solar activity in the 23rd solar cycle. Solar Phys. 224, 345. DOI .
Friedel, R.H.W., Reeves, G.D., Obara, T.: 2002, Relativistic electron dynamics in the 612 inner magnetosphere – a review. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 64, 265.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S.: 2007, Geoeffectiveness of halo coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 112, A06112. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Xie, H., Mäkelä, P., Michalek, G.: 2014, Anomalous expansion of coronal mass ejections during Solar Cycle 24 and its space weather implications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 41, 2673. DOI .
Gosling, J.T., Asbridge, J.R., Bame, S.J., Feldman, W.C.: 1976, Solar wind speed variations: 1962 – 1974. J. Geophys. Res. 81, 5061. DOI .
Gupta, V., Badruddin: 2009, Interplanetary structures and solar wind behavior during major geomagnetic perturbations. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 71, 885.
Gupta, V., Badruddin: 2010, High-speed solar wind streams during 1996 – 2007: sources, statistical distribution, and plasma/field properties. Solar Phys. 264, 165. DOI .
Jian, L., Russell, C.T., Luhmann, J.G., Skoug, R.M.: 2006, Properties of interplanetary coronal mass ejections at one AU during 1995 – 2004. Solar Phys. 239, 393. DOI .
Kane, R.P.: 2007, Solar terrestrial effects of two district types. Adv. Space Res. 39, 1890. DOI .
Kudela, K., Brenkus, R.: 2004, Cosmic ray decreases and geomagnetic activity: list of events 1982 – 2002. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 66, 1121. DOI .
Kumar, A., Badruddin: 2014, Cosmic ray modulation due to high speed solar wind streams of different sources, speed and duration. Solar Phys. 289, 4267. DOI .
Lakhina, G., Tsurutani, B.T.: 2016, Geomagnetic storms: historical perspective to modern view. Geosci. Lett. 3, 5. DOI .
Lindblad, A., Lundstedt, H.: 1981, A catalogue of high-speed plasma streams in the solar wind. Solar Phys. 74, 197. DOI .
Lindblad, B.A., Lundstedt, H.: 1983, A catalogue of high speed plasma streams in 1975 – 1978. Solar Phys. 88, 377. DOI .
Lindblad, B.A., Lundstedt, H., Larsson, B.: 1989, A third catalogue of high-speed plasma streams in the solar wind – data for 1978 – 1982. Solar Phys. 120, 145. DOI .
Maris, O., Maris, G.: 2005, Specific features of the high-speed plasma stream cycles. Adv. Space Res. 35, 2129.
Mavromichalaki, H., Vassilaki, A.: 1998, Fast plasma streams recorded near the Earth during 1985 – 1996. Solar Phys. 183, 181. DOI .
Mavromichalaki, H., Vassilaki, A., Marmatsouri, E.: 1988, A catalogue of high-speed solar wind streams – further evidence of their relationship to \(A_{p}\)-index. Solar Phys. 115, 345. DOI .
Melkumyan, A.A., Belov, A.V., Abunina, M.A., Abunin, A.A., Eroshenko, E.A., Oleneva, V.A., Yanke, V.G.: 2018, Main properties of Forbush effects related to high-speed streams from coronal holes. Geomagn. Aeron. 58, 154. DOI .
Muntean, G.M., Besliu-Ionescu, D., Dobrica, V.: 2018, Complex catalogue of high speed streams and geomagnetic storms during solar cycle 24 (2009 – 2016). VarSITI Newsletter 17, 5.
Paouris, E., Gerontidou, M., Mavromichalaki, H.: 2016, The geomagnetic storms of 2015: statistical analysis and forecasting results. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 18, EGU2016-11753.
Paouris, E., Mavromichalaki, H.: 2017, Interplanetary coronal mass ejections resulting from Earth-directed CMEs using SOHO and ACE combined data during Solar Cycle 23. Solar Phys. 292, 30. DOI .
Papaioannou, A., Belov, A., Mavromichalaki, H., Eroshenko, E., Oleneva, V.: 2009a, The unusual cosmic ray variations in July 2005 resulted from western and behind the limb solar activity. Adv. Space Res. 43, 582. DOI .
Papaioannou, A., Mavromichalaki, H., Eroshenko, E., Belov, A., Oleneva, V.: 2009b, The burst of solar and geomagnetic activity in August – September 2005. Ann. Geophys. 27, 1019.
Parker, E.: 1959, Extension of the solar corona into interplanetary. J. Geophys. Res. 64, 1675.
Richardson, I.G.: 2013, Geomagnetic activity during the rising phase of solar cycle. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 3, A08. DOI .
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V., Cliver, E.W.: 2002, Sources of geomagnetic activity during nearly three solar cycles (1972 – 2000). J. Geophys. Res. 107, SSH 8-1. DOI .
Sabbah, I.: 2000, The role of interplanetary magnetic field and solar wind in modulating both galactic cosmic rays and geomagnetic activity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 1823. DOI .
Wang, Y.M.: 2010, On the relative constancy of the solar wind mass flux at 1 AU. Astrophys. J. Lett. 715(2), 121. DOI .
Watari, S.: 2018, Intense geomagnetic storms associated with coronal holes under the weak solar-wind conditions of cycle 24. Solar Phys. 293, 23. DOI .
Xystouris, G., Sigala, E., Mavromichalaki, H.: 2014, A complete catalogue of high-speed solar wind streams during solar cycle 23. Solar Phys. 289, 995. DOI .
Yermolaev, Y.I., Ladkina, I.G., Nikolaeva, N.S., Yermolaev, M.Y.: 2014, Influence of the interplanetary driver type on the durations of the main and recovery phases of magnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. 119, 8126. DOI .
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the contribution of the OMNI Web database of NASA/GSFC providing the necessary data for the definition of the HSSWSs. The websites http://www.olen.info/solar/coronal_holes.html and http://cdaw.gsfc.nasa.gov/CME_list/ , providing data for the coronal holes and for the coronal mass ejections, respectively, are also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors indicate that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerontidou, M., Mavromichalaki, H. & Daglis, T. High-Speed Solar Wind Streams and Geomagnetic Storms During Solar Cycle 24. Sol Phys 293, 131 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-018-1348-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-018-1348-8