Abstract
Solar flares are one of the most energetic events in the solar system, their impact on Earth at ground level and its atmosphere remains under study. The repercussions of this phenomenon in our technological infrastructure includes radio blackouts and errors in geopositional and navigation systems that are considered natural hazards in ever more countries. Occurrence frequency and intensity of the most energetic solar flares are being taken into account in national programs for civil protection in order to reduce the risk and increase the resilience from space weather events. In this work we use the statistical theory of extreme values as well as other statistical methods in order to assess the magnitudes of the most extreme solar-flare events expected to occur in a given period of time. We found that the data set under study presents a dual tail behavior. Our results show that on average we can expect one solar flare greater than X23 each 25 years, that is to say, one such event each two solar cycles.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The data can be found in https://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/stp/space-weather/solar-data/solar-features/solar-flares/x-rays/goes/xrs/ .
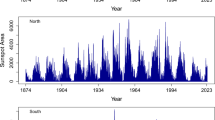
In terms of Figure 4, the set \(S_{59}\) would be a combination of data points on the left and on the right of the dashed vertical line in the figure.
For the generation of these synthetic samples, we used both, \(G_{1}\) and \(G_{2}\) as the parent distribution.
References
Ackermann, M., Ajello, M., Albert, A., Allafort, A., Baldini, L., Barbiellini, G., Bastieri, D., Bechtol, K., Bellazzini, R., Bissaldi, E., Bonamente, E., Bottacini, E., Bouvier, A., Brandt, T.J., Bregeon, J., Brigida, M., Bruel, P., Buehler, R., Buson, S., Caliandro, G.A., Cameron, R.A., Caraveo, P.A., Cecchi, C., Charles, E., Chekhtman, A., Chen, Q., Chiang, J., Chiaro, G., Ciprini, S., Claus, R., Cohen-Tanugi, J., Conrad, J., Cutini, S., D’Ammando, F., de Angelis, A., de Palma, F., Dermer, C.D., Desiante, R., Digel, S.W., Di Venere, L., Silva, E.d.C.e., Drell, P.S., Drlica-Wagner, A., Favuzzi, C., Fegan, S.J., Focke, W.B., Franckowiak, A., Fukazawa, Y., Funk, S., Fusco, P., Gargano, F., Gasparrini, D., Germani, S., Giglietto, N., Giordano, F., Giroletti, M., Glanzman, T., Godfrey, G., Grenier, I.A., Grove, J.E., Guiriec, S., Hadasch, D., Hayashida, M., Hays, E., Horan, D., Hughes, R.E., Inoue, Y., Jackson, M.S., Jogler, T., Jóhannesson, G., Johnson, W.N., Kamae, T., Kawano, T., Knödlseder, J., Kuss, M., Lande, J., Larsson, S., Latronico, L., Lemoine-Goumard, M., Longo, F., Loparco, F., Lott, B., Lovellette, M.N., Lubrano, P., Mayer, M., Mazziotta, M.N., McEnery, J.E., Michelson, P.F., Mizuno, T., Moiseev, A.A., Monte, C., Monzani, M.E., Moretti, E., Morselli, A., Moskalenko, I.V., Murgia, S., Murphy, R., Nemmen, R., Nuss, E., Ohno, M., Ohsugi, T., Okumura, A., Omodei, N., Orienti, M., Orlando, E., Ormes, J.F., Paneque, D., Panetta, J.H., Perkins, J.S., Pesce-Rollins, M., Petrosian, V., Piron, F., Pivato, G., Porter, T.A., Rainò, S., Rando, R., Razzano, M., Reimer, A., Reimer, O., Ritz, S., Schulz, A., Sgrò, C., Siskind, E.J., Spandre, G., Spinelli, P., Takahashi, H., Takeuchi, Y., Tanaka, Y., Thayer, J.G., Thayer, J.B., Thompson, D.J., Tibaldo, L., Tinivella, M., Tosti, G., Troja, E., Tronconi, V., Usher, T.L., Vandenbroucke, J., Vasileiou, V., Vianello, G., Vitale, V., Werner, M., Winer, B.L., Wood, D.L., Wood, K.S., Wood, M., Yang, Z. (Fermi LAT Collaboration): 2014, High-energy gamma-ray emission from solar flares: Summary of Fermi large area telescope detections and analysis of two M-class flares. Astrophys. J. 787, 15. DOI . ADS .
Aschwanden, M.J., Freeland, S.L.: 2012, Automated solar flare statistics in soft x-rays over 37 years of goes observations: The invariance of self-organized criticality during three solar cycles. Astrophys. J. 754(2), 112.
Benz, A.O., Güdel, M.: 2010, Physical processes in magnetically driven flares on the Sun, stars, and young stellar objects. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 48, 241. DOI . ADS .
Canfield, R.C., de La Beaujardiere, J.-F., Fan, Y., Leka, K.D., McClymont, A.N., Metcalf, T.R., Mickey, D.L., Wuelser, J.-P., Lites, B.W.: 1993, The morphology of flare phenomena, magnetic fields, and electric currents in active regions. I – Introduction and methods. Astrophys. J. 411, 362. DOI . ADS .
Castillo, E., Hadi, A.S., Balakrishnan, N., Sarabia, J.-M.: 2005, Extreme Value and Related Models with Applications in Engineering and Science, Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics. John Wiley & Sons, New York. ISBN: 978-0471671725.
Chakrabarty, A., Samorodnitsky, G.: 2012, Understanding heavy tails in a bounded world or, is a truncated heavy tail heavy or not? Stoch. Models 28(1), 109.
Chamberlin, P.C., Woods, T.N., Eparvier, F.G., Jones, A.R.: 2009, Next generation X-ray sensor (XRS) for the NOAA GOES-R satellite series. In: Solar Physics and Space Weather Instrumentation III, Proceedings of the SPIE 7438, 743802. DOI . ADS .
Chertok, I.M., Belov, A.V.: 2017, Long- and mid-term variations of the soft X-ray flare type in solar cycles. Solar Phys. 292, 144. DOI . ADS .
Chinnery, M.A., North, R.G.: 1975, The frequency of very large earthquakes. Science 190, 1197.
Clauset, A., Shalizi, C.R., Newman, M.E.: 2009, Power-law distributions in empirical data. SIAM Rev. 51(4), 661.
Cliver, E.W., Dietrich, W.F.: 2013, The 1859 space weather event revisited: Limits of extreme activity. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 3(27), A31. DOI . ADS .
Coles, S.: 2001, An Introduction to Statistical Modeling of Extreme Values, Springer Series in Statistics. Springer, Bristol.
de Haan, L., Ferreira, A.: 2007, Extreme Value Theory: An Introduction, Springer Series in Operations Research and Financial Engineering. Springer, New York, ISBN 9780387344713.
Diaconis, P., Efron, B.: 1983, Computer-intensive methods in statistics. Sci. Am. 248(5), 116.
DiCiccio, T.J., Efron, B.: 1996, Bootstrap confidence intervals. Stat. Sci. 11, 189.
Gold, T., Hoyle, F.: 1960, On the origin of solar flares. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 120, 89. DOI . ADS .
Grabchak, M.: 2016, Tempered stable distributions. In: Tempered Stable Distributions, Springer, Charlotte.
Jonas, S., McCarron, E.D.: 2016, White House releases national space weather strategy and action plan. Space Weather 14(2), 54. DOI .
Kane, S.R., McTiernan, J.M., Hurley, K.: 2005, Multispacecraft observations of the hard X-ray emission from the giant solar flare on 2003 November 4. Astron. Astrophys. 433, 1133. DOI . ADS .
Katsova, M.M., Kitchatinov, L.L., Livshits, M.A., Moss, D.L., Sokoloff, D.D., Usoskin, I.G.: 2018, Can superflares occur on the Sun? A view from dynamo theory. Astron. Rep. 62(1), 72. DOI .
Koons, H.C.: 2001, Statistical analysis of extreme values in space science. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 10915. DOI . ADS .
Leadbetter, M.R., Lindgren, G., Rootzén, H.: 2012, Extremes and Related Properties of Random Sequences and Processes, Springer, New York.
Meerschaert, M.M., Roy, P., Shao, Q.: 2012, Parameter estimation for exponentially tempered power law distributions. Commun. Stat., Theory Methods 41(10), 1839. DOI .
Riley, P.: 2012, On the probability of occurrence of extreme space weather events. Space Weather 10(2), 02012. DOI . ADS .
Stumpf, M.P.H., Porter, M.A.: 2012, Critical truths about power laws. Science 335(6069), 665. DOI .
Toriumi, S., Schrijver, C.J., Harra, L.K., Hudson, H., Nagashima, K.: 2017, Magnetic properties of solar active regions that govern large solar flares and eruptions. Astrophys. J. 834, 56. DOI . ADS .
Wheatland, M.S.: 2010, Evidence for departure from a power-law flare size distribution for a small solar active region. Astrophys. J. 710, 1324. DOI . ADS .
Acknowledgements
The authors thank projects for Catedras Conacyt (Conacyt Fellow), Repositorios Institucionales (268273) and Ciencia Basica (254497).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De la Luz, V., Balanzario, E.P. & Tsiftsi, T. Estimating the Maximum Intensities of Soft X-Ray Flares Using Extreme Value Theory. Sol Phys 293, 119 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-018-1342-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-018-1342-1