Abstract
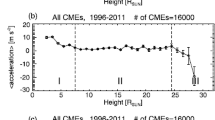
We report kinematic properties of slow interplanetary coronal mass ejections (ICMEs) identified by SOHO/LASCO, interplanetary scintillation, and in situ observations and propose a modified equation for the ICME motion. We identified seven ICMEs between 2010 and 2011 and compared them with 39 events reported in our previous work. We examined 15 fast (V SOHO−V bg>500 km s−1), 25 moderate (0 km s−1≤V SOHO−V bg≤500 km s−1), and 6 slow (V SOHO−V bg<0 km s−1) ICMEs, where V SOHO and V bg are the initial speed of ICMEs and the speed of the background solar wind. For slow ICMEs, we found the following results: i) They accelerate toward the speed of the background solar wind during their propagation and reach their final speed by 0.34±0.03 AU. ii) The acceleration ends when they reach 479±126 km s−1; this is close to the typical speed of the solar wind during the period of this study. iii) When γ 1 and γ 2 are assumed to be constants, a quadratic equation for the acceleration a=−γ 2(V−V bg)|V−V bg| is more appropriate than a linear one a=−γ 1(V−V bg), where V is the propagation speed of ICMEs, while the latter gives a smaller χ 2 value than the former. For the motion of the fast and moderate ICMEs, we found a modified drag equation a=−2.07×10−12(V−V bg)|V−V bg|−4.84×10−6(V−V bg). From the viewpoint of fluid dynamics, we interpret this equation as indicating that ICMEs with 0 km s−1≤V−V bg≤2300 km s−1 are controlled mainly by the hydrodynamic Stokes drag force, while the aerodynamic drag force is a predominant factor for the propagation of ICME with V−V bg>2300 km s−1.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asai, K., Ishida, Y., Kojima, M., Maruyama, K., Misawa, H., Yoshimi, N.: 1995, Multi-station system for solar wind observations using the interplanetary scintillation method. J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 47, 1107 – 1112.
Borgazzi, A., Lara, A., Romero-Salazar, L., Ventura, A.: 2008, Transport in the interplanetary medium of coronal mass ejections. Geofis. Int. 47, 301 – 310.
Borgazzi, A., Lara, A., Echer, E., Alves, M.: 2009, Dynamics of coronal mass ejections in the interplanetary medium. Astron. Astrophys. 498, 885 – 889.
Brueckner, G.E., Howard, R.A., Koomen, M.J., Korendyke, C.M., Michels, D.J., Moses, J.D., et al.: 1995, The Large Angle Spectroscopic Coronagraph (LASCO). Solar Phys. 162, 357 – 402.
Brueckner, G., Delaboudiniere, J., Howard, R., Paswaters, S., St. Cyr, O.C., Schwenn, R., Lamy, P., Simnett, G., Thompson, B., Wang, D.: 1998, Geomagnetic storms caused by coronal mass ejections (CMEs): March 1996 through June 1997. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 3019 – 3022.
Byrne, J.P., Maloney, S.A., McAteer, R.J., Refojo, J.M., Gallagher, P.T.: 2010, Propagation of an earth-directed coronal mass ejection in three dimensions. Nature Commun. 1, 74.
Cane, H., Richardson, I., St. Cyr, O.C.: 2000, Coronal mass ejections, interplanetary ejecta and geomagnetic storms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 3591 – 3594.
Cargill, P.: 2004, On the aerodynamic drag force acting on interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Solar Phys. 221, 135 – 149.
Chen, J.: 1996, Theory of prominence eruption and propagation: Interplanetary consequences. J. Geophys. Res. 101, 27499 – 27520.
Gapper, G., Hewish, A., Purvis, A., Duffett-Smith, P.: 1982, Observing interplanetary disturbances from the ground. Nature 296, 633 – 636.
Gloeckler, G., Cain, J., Ipavich, F.M., Tums, E.O., Bedini, P., Fisk, L.A., et al.: 1998, Investigation of the composition of solar and interstellar matter using solar wind and pickup ion measurements with SWICS and SWIMS on the ACE spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev. 86, 497 – 539.
Gopalswamy, N., Lara, A., Lepping, R., Kaiser, M., Berdichevsky, D., St. Cyr, O.C.: 2000, Interplanetary acceleration of coronal mass ejections. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 145 – 148.
Gopalswamy, N., Lara, A., Yashiro, S., Kaiser, M., Howard, R.: 2001, Predicting the 1-AU arrival times of coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 29207 – 29218.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Michalek, G., Stenborg, G., Vourlidas, A., Freeland, S., Howard, R.: 2009, The SOHO/LASCO CME catalog. Earth Moon Planets 104, 295 – 313.
Gosling, J., McComas, D., Phillips, J., Bame, S.: 1991, Geomagnetic activity associated with Earth passage of interplanetary shock disturbances and coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 96, 7831 – 7839.
Guhathakurta, M., Fisher, R.: 1998, Solar wind consequences of a coronal hole density profile: Spartan 201-03 coronagraph and Ulysses observations from 1.15 R ⊙ to 4 AU. Astrophys. J. Lett. 499, L215 – L218.
Hewish, A., Scott, P.F., Wills, D.: 1964, Interplanetary scintillation of small diameter radio sources. Nature 203, 1214 – 1217.
Howard, T.: 2011, Coronal Mass Ejections: An Introduction, Springer, New York, 4.
Iju, T., Tokumaru, M., Fujiki, K.: 2013, Radial speed evolution of coronal mass ejections during solar cycle 23. Solar Phys. 288, 331 – 353 (Paper I).
Kojima, M., Kakinuma, T.: 1990, Solar cycle dependence of global distribution of solar wind speed. Space Sci. Rev. 53, 173 – 222.
Lara, A., Flandes, A., Borgazzi, A., Subramanian, P., México, C.U.: 2011, Velocity profile of interplanetary coronal mass ejections beyond 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 116, A12102.
Lindsay, G.M., Luhmann, J.G., Russell, C.T., Gosling, J.T.: 1999, Relationships between coronal mass ejection speeds from coronagraph images and interplanetary characteristics of associated interplanetary coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 12515 – 12524.
Lynch, B.J., Li, Y., Thernisien, A.F.R., Robbrecht, E., Fisher, G.H., Luhmann, J.G., Vourlidas, A.: 2010, Sun to 1 AU propagation and evolution of a slow streamer-blowout coronal mass ejection. J. Geophys. Res. 115, A07106.
Maloney, S.A., Gallagher, P.T.: 2010, Solar wind drag and the kinematics of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. Lett. 724, L127 – L132.
Manoharan, P.K.: 2006, Evolution of coronal mass ejections in the inner heliosphere: A study using white-light and scintillation images. Solar Phys. 235, 345 – 368.
Reiner, M.J., Kaiser, M.L., Bougeret, J.L.: 2003, On the deceleration of CMEs in the corona and interplanetary medium deduced from radio and white-light observations. In: Velli, M., Bruno, R., Malara, F. (eds.) Solar Wind Ten: Proceedings of the Tenth International Solar Wind Conference, AIP Conf. Proc. 679, 152 – 155.
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V.: 2010, Near-Earth interplanetary coronal mass ejections during solar cycle 23 (1996–2009): Catalog and summary of properties. Solar Phys. 264, 189 – 237.
Rollett, T., Möstl, C., Temmer, M., Veronig, A.M., Farrugia, C.J., Biernat, H.K.: 2012, Constraining the kinematics of coronal mass ejections in the inner heliosphere with in-situ signatures. Solar Phys. 276, 1 – 22.
Schwenn, R., Mühlhäuser, K., Marsch, E., Rosenbauer, H.: 1981, Two states of the solar wind at the time of solar activity minimum II. Radial gradient of plasma parameters in fast and slow streams. In: Rosenbauer, H. (ed.) Solar Wind Four. Max-Plank-Institute für Aeronomie, Katlenburg-Lindau, 126 – 130.
Shanmugaraju, A., Moon, Y.J., Vrsnak, B., Vrbanec, D.: 2009, Radial evolution of well-observed slow CMEs in the distance range 2 – 30 R ⊙. Solar Phys. 257, 351 – 361.
Sheeley, N. Jr., Wang, Y.M., Hawley, S., Brueckner, G., Dere, K., Howard, R., et al.: 1997, Measurements of flow speeds in the corona between 2 and 30 R ⊙. Astrophys. J. 484, 472 – 478.
Shen, C., Wang, Y., Gui, B., Ye, P., Wang, S.: 2011, Kinematic evolution of a slow CME in corona viewed by STEREO-B on 8 October 2007. Solar Phys. 269, 389 – 400.
Stone, E., Frandsen, A., Mewaldt, R., Christian, E., Margolies, D., Ormes, J., Snow, F.: 1998, The Advanced Composition Explorer. Space Sci. Rev. 86, 1 – 22.
Tappin, S.: 2006, The deceleration of an interplanetary transient from the Sun to 5 AU. Solar Phys. 233, 233 – 248.
Temmer, M., Rollett, T., Möstl, C., Veronig, A., Vršnak, B., Odstrčil, D.: 2011, Influence of the ambient solar wind flow on the propagation behavior of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J. 743, 101 – 112.
Tokumaru, M., Kojima, M., Fujiki, K., Maruyama, K., Maruyama, Y., Ito, H., Iju, T.: 2011, A newly developed UHF radiotelescope for interplanetary scintillation observations: Solar wind imaging facility. Radio Sci. 46, RS0F02.
Vourlidas, A., Buzasi, D., Howard, R., Esfandiari, E.: 2002, Mass and energy properties of LASCO CMEs. In: Wilson, A. (ed.) Solar Variability: From Core to Outer Frontiers, ESA SP-506, 91 – 94.
Vršnak, B., Gopalswamy, N.: 2002, Influence of the aerodynamic drag on the motion of interplanetary ejecta. J. Geophys. Res. 107, 1019.
Vršnak, B., Žic, T., Falkenberg, T., Möstl, C., Vennerstrom, S., Vrbanec, D.: 2010, The role of aerodynamic drag in propagation of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Astron. Astrophys. 512, A43.
Vršnak, B., Žic, T., Vrbanec, D., Temmer, M., Rollett, T., Möstl, C., et al.: 2013, Propagation of interplanetary coronal mass ejections: The drag-based model. Solar Phys. 285, 295 – 315.
Yashiro, S., Gopalswamy, N., Michalek, G., St. Cyr, O.C., Plunkett, S., Rich, N., Howard, R.: 2004, A catalog of white light coronal mass ejections observed by the SOHO spacecraft. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A07105.
Acknowledgements
The IPS observations were carried out under the solar wind program of the Solar-Terrestrial Environment Laboratory (STEL) of Nagoya University. We acknowledge use of the SOHO/LASCO CME catalog; this CME catalog is generated and maintained at the CDAW Data Center by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and the Catholic University of America in cooperation with the Naval Research Laboratory. SOHO is a project of international cooperation between the European Space Agency and NASA. We thank the Space Physics Data Facility of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center for use of OMNIWeb service and OMNI data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iju, T., Tokumaru, M. & Fujiki, K. Kinematic Properties of Slow ICMEs and an Interpretation of a Modified Drag Equation for Fast and Moderate ICMEs. Sol Phys 289, 2157–2175 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-014-0472-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-014-0472-3