Abstract
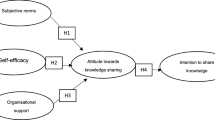
In the organization, the transformation of knowledge is an important issue, and personal motivation for knowledge sharing worth to be investigating. Among them, there are many factors affect that the personal process of knowledge sharing intentions. The individual knowledge sharing intention while often by affects of the environmental factors and individual’s beliefs awareness. Many studies have explored the factors that affect individual action intentions, but few of individual ethical considerations inherent with the views of relevant organizations to analyze the environmental knowledge to the intention. This study reviews of the theory of reasoned action, from perspectives of the social psychological and knowledge sharing while integrative the personal anticipated reciprocal relationship, perceived of ethics and organization culture to seek for the personal impact of the antecedents of knowledge sharing intentions. Moreover, based on existing literature, the author’s observation and inference for develop a conceptual framework to identify the antecedents can be represented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajzen I.: Understanding events—affect and the construction of social-action—Heise, Dr. Contemp. Psychol. 25(10), 775–776 (1980)
Ajzen I., Fishein M.: Understanding Attitudes and Predicting Social Behavior. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ (1980)
Akaah I.: Influence of deontological and teleological factors on research ethics and evaluations. J. Bus. Res. 39, 71–80 (1997)
Ardichvili A., Page V., Wentling T.: Motivation and barriers to participation in virtual knowledge-sharing communities of practice. J. Knowl. Manage. 7(1), 64–77 (2003)
Bagozzi R.P.: The self-regulation of attitudes, intentions, and behavior. Soc. Psychol. Quart. 55(2), 178–204 (1992)
Bagozzi R.P., Schnedlitz P.: Social contingencies in the attitude model: a test of certain interaction hypotheses. Soc. Psychol. Quart. 48, 366–373 (1985)
Bock, G.W., Kim, Y.G.: Breaking the myths of rewards: an exploratory study of attitudes about knowledge sharing. Inf. Resour. Manage. J. April–June, 14–21 (2002)
Bock G.W., Zmud R.W., Kim Y.G., Lee J.N.: Behavioral intention formation in knowledge sharing: examining the roles of extrinsic motivators, social-psychological forces, and organizational climate. MIS Quart. 29(1), 87–111 (2005)
Cabrera A., Cabrera E.F.: Knowledge-sharing dilemmas. Organ. Stud. 23(5), 687–710 (2002)
Calantone R.J., Cavusgil S.T., Zhao Y.: Learning orientation, firm innovation capability, and firm performance. Ind. Market. Manage. 31, 515–524 (2002)
Chang M.K.: Predicting unethical behavior: a comparison of the theory of reasoned action and the theory of planned behavior. J. Bus. Ethics 17(16), 1825–1834 (1998)
Conner K.R., Prahalad C.K.: A resource-based theory of the firm: knowledge versus opportunism. Organ. Sci. 7(5), 477–501 (1996)
Costa P.T. Jr., McCrae R.R.: Manual for the NEO Personality Inventory. Psychological Assessment Resources, Odessa, FL (1985)
Davenport T.H., Prusak L.: Working Knowledge: How Organizations Manage what they Know. Harvard Business School Press, Boston (1998)
Davenprot, T.H., De Long, D.W., Beers, M.C.: Successful knowledge management projects. Sloan Manage. Rev. Winter, 43–57 (1998)
DeConinck J.B., Lewis W.F.: The influence of deontological and teleological considerations and ethical climate on sales managers’intentions to reward or punish sales force behavior. J. Bus. Ethics 16, 497–506 (1997)
Feng L.: A Situational Model of Fast Food Restaurant Consumption: Application of Theory of Reasoned Action. Faculty of graduate studies of the University of Guelph, Guelph (2002)
Fishbein M., Ajzen I.: Belief, Attitude Intention and Behavior: An Introduction to Theory and Research. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA (1975)
Fishbein M., Ajzen I.: On construct-validity—a critique of miniard and cohen paper. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 17(3), 340–350 (1981)
Fraedrich J., Ferrell O.C.: The impact of perceived risk and moral philosophy type on ethical decision-making in business organizations. J. Bus. Res. 24, 283–295 (1992)
Fritzsche D.J., Becker H.: Linking management behavior to ethical philosophy—an empirical investigation. Acad. Manage. J. 27, 166–175 (1984)
Fulk J.: Social construction of communication technology. Acad. Manage. J. 36(5), 921–950 (1993)
Gagné M.: A model of knowledge-sharing motivation. Hum. Resour. Manage. 48(4), 571–589 (2009)
Gellerman S.W.: Managing ethics from the top down. Sloan Manage. Rev. 17(Winter), 73–79 (1989)
Gibbert M., Krause H.: Practice exchange in a best practice marketplace. In: Davenport, T.H., Probst, G.J.B. (eds) Knowledge Management Case Book: Siemens Best Practices, Publicis Corporate Publishing, Eriangen, Germany (2002)
Gold A.H., Malhotra A., Segars A.H.: Knowledge management: an organizational capabilities perspective. J. Manage. Inform. Syst. 18(1), 185–214 (2001)
Grube J., Morgan M.: Attitude-social support interactions: contingent consistency effects in thee predictions of adolescent smoking, drinking, and drug use. Soc. Psychol. Quart. 53, 329–339 (1990)
Gupta A.K., Govindarajan F.: knowledge management’s social dimension: lessons from Nucor Steel. Sloan Manage. Rev. 42(1), 71–80 (2000)
Hall H.: Input-friendliness: motivating knowledge sharing across intranets. J. Inform. Sci. 27(3), 139–146 (2001)
Hansen R.S.: A multidimensional scale for measuring business ethics. J. Bus. Ethics 11, 523–534 (1992)
Hansen, M., Nohria, N., Tierney, T.: What’s your strategy for managing knowledge. Harvard Bus. Rev. March–April, 106–116 (1999)
Harris J.R., Sutton C.D.: Unravelling the ethical decision-making process: clues from an empirical study comparing Fortune 1000 executives and MBA students. J. Bus. Ethics 14, 805–817 (1995)
Hendriks P.: Why share knowledge? the influence of ICT on the motivation for knowledge sharing. Knowl. Process Manage. 6(2), 91–100 (1999)
Hertzum M.: The importance of trust in software engineers’ assessment and choice if information sources. Inform. Organ. 12, 1–18 (2002)
Hooff B.V.D., De Ridder J.A.: Knowledge sharing in context: the influence of organizational commitment, communication climate and CMC use on knowledge sharing. J. Knowl. Manage. 8(6), 117–130 (2004)
Hunt S., Vasquez-Parraga A.: Organizational consequences, marketing ethics, and salesforce supervision. J. Market. Res. 30, 78–90 (1993)
Hunt S.D., Vitell S.J.: A general theory of marketing ethics. J. Macromarket. 8(Spring), 5–16 (1986)
Hunt S.D., Vitell S.J.: The General Theory of Marketing Ethics: A Retrospective and Revision, Ethics in Marketing. Irwin Inc., Homewood, IL (1993)
Ipe M.: Knowledge sharing in organization: a conceptual framework. Hum. Resour. Dev. Rev. 2(4), 337–359 (2003)
Joe S.-W., Lin S.-Y., Chiu C.-K.: Modeling the unethical intention of software piracy: a qualitative integration of network externalities and information cascades. Qual. Quant. 44(1), 191–198 (2010)
Johnston K., White K.M.: Binge-drinking: a test of the role of group norms in the theory of planned behaviour. Psychol. Health 18, 63–77 (2003)
Knowledge Sharing Steering Committee Holds Initial Meeting in New Delhi. In, 2009/04//, pp. 26-29
Krogh G.: The communal resource and information systems. J. Strategic Inf. Syst. 11, 85–107 (2002)
Lam A.: Tacit knowledge, organizational learning and societal institutions: an integrated framework. Organ. Stud. 21(3), 487–513 (2000)
Lang Y.T., Dickinson J., Buchal R.O.: Cognitive factors in distributed design. Comput. Ind. 48, 89–98 (2002)
Latimer A.E., Ginnis K.A.M.: The importance of subjective norms for people who care what others think of team. Psychol. Health. 20(1), 53–62 (2005)
Lewis W., Agarwal R., Sambamurthy V.: Sources of influence on beliefs about information technology use: an empirical study of knowledge sorkers. MIS Quart. 27(4), 57–678 (2003)
Liao S.H.: Knowledge management technologies and applications—a literature review from 1995 to 2002. Expert Syst. Appl. 25(2), 155–164 (2003)
Liebowitz J.: Knowledge management and its link to artificial intelligence. Expert Syst. Appl. 20, 1–6 (2001)
Lin H.F.: Effects of extrinsic and intrinsic motivation on employee knowledge sharing intentions. J. Inform. Sci. 33(2), 135–149 (2007)
Lin H.F., Lee G.G.: Perceptions of senior managers toward knowledge-sharing behaviour. Manage. Decis. 42(1), 108–125 (2004)
Liska A.E.: A critical examination of the causal structure of the Fishbein/Ajzen attitude-behavior model. Soc. Psychol. Quart. 47, 61–74 (1984)
Mathieson K.: Predicting user intentions: comparing the technology acceptance model with the theory of planned behavior. Inform. Syst. Res. 2(3), 173–191 (1991)
Mayo M.A., Marks L.: An empirical investigation of a general theory of marketing ethics. J. Acad. Market. Sci. 18, 163–171 (1990)
McDermott R., O’Dell C.: Overcoming cultural barriers to sharing knowledge. J. Knowl. Manage. 5(1), 76–85 (2001)
Miniard P.W., Cohen J.B.: An examination of the Fishbein-Ajzen behavioral-intention model’s concepts and measures. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 17, 303–309 (1981)
Mooradian T., Renzl B., Matzler K.: Who trusts? Personality, trust and knowledge sharing. Manage. Learn. 37(4), 523–540 (2006)
Murphy P.E.: Creating ethical corporate structure. Sloan Manage. Rev. 17(Winter), 81–87 (1989)
Nahapiet J., Ghoshal S.: Social capital, intellectual capital, and the organizational advantage. Acad. Manage. Rev. 40(2), 242–266 (1998)
Nonaka I., Takeuchi H.: The Knowledge-Creating Company. Oxford University Press, New York (1995)
Rabow J., Neuman C.A., Hemandez A.C.R.: Contingent consistency in attitudes, social support and the consumption of alcohol: additive and interactive effects. Soc. Psychol. Quart. 50, 56–63 (1987)
Robin D.P., Reidenbach R.E.: A framework for analyzing ethical issues in marketing. Bus. Prof. Ethics J. 5, 3–22 (1988)
Ruppel C.P., Harrington S.J.: Sharing knowledge through Intranets: a study of organizational culture and Intranet implementation. IEEE Trans. Prof. Commun. 44(1), 37–52 (2001)
Ryan M.J.: Behavioral lntention formation: the interdependency of attitudinal and social infiuence variables. J. Consum. Res. 9, 263–278 (1982)
Ryu S., Ho S.H., Han I.: Knowledge sharing behavior of physicians in hospital. Expert Syst. Appl. 25(1), 113–122 (2003)
Salancik G., Pfeffer J.: A social information processing approach to job attitudes and task design. Admin. Sci. Quart. 23, 224–253 (1978)
Schein E.H.: Organizational culture. Am. Psychol. 45(2), 109–119 (1990)
Schminke M., Ambrose M., Noel T.: The effect of ethical frameworks on perceptions of organizational justice. Acad. Manage. J. 40, 1190–1207 (1997)
Schmitz J., Fulk J.: Organizational colleagues, media richness, and electronic mail: a test of the social infiuence model of technology use. Commun. Res. 18(4), 487–523 (1991)
Sheppherd G.J., O’Keefe D.J.: Separability of attitudinal and normative influences on behavioral intentions in the Fishbein-Ajzen model. J. Soc. Psychol. 122, 287–288 (1984)
Shimp T.A., Kavas A.: The theory of reasoned action applied to coupon usage. J. Consum. Res. 11, 795–809 (1984)
Stevens B.: An analysis of corporate ethical code studies: where do we go from here?. Acad. Manage. Rev. 11(3), 601–617 (1994)
Taylor S., Todd P.: Understanding information technology usage: a test of competing models. Inform. Syst. Res. 6(2), 144–176 (1995)
Terry D.H., Hogg M.A.: Group norms and the attitude-behaviour relationship: a role for group identification. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 22, 776–793 (1996)
Thompson R.L., Higgins C.A., Howell J.M.: Personal computing: toward a conceptual model of utilization. MIS Quart. 16(1), 125–143 (1991)
Thong J., Yap C.: Testing an ethical decision-making theory: the case of shoplifting. J. Manage. Inform. Syst. 15, 213–237 (1998)
Trafimow D., Fishbein M.: The importance of risk in determining the extent to which attitudes affect intentions to wear seat belts. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 24, 1–24 (1994a)
Trafimow D., Fishbein M.: The moderating effect of behavior type on the subjective norm-behavior relationship. J. Soc. Psychol. 134(6), 755–763 (1994b)
Vallerand R.J., Bissonnette R.: Intrinsic, extrinsic, and amotivational styles as predictors of behavior: a prospective study. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 60, 599–620 (1992)
Vallerand R.J., Deshaies P., Currier J.P., Pelletier L.G., Mongeau C.: Ajzen and Fishbein’s theory of reasoned action as applied to moral behavior: a confirmatory analysis. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 62, 98–109 (1992)
Venkatesh V., Davis F.D.: A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: four longitudinal field studies. Manage. Sci. 46, 186–204 (2000)
Venkatesh V., Morris M.G.C.: Why don’t men ever stop to ask for directions? Gender, social influence, and their role in technology acceptance and usage behavior. MIS Quart. 24(1), 115–137 (2000)
Verlegh P.W., Candel M.J.J.M.: The consumption of convenience foods: reference groups and eating situations. Food Qual. Prefer. 10, 457–464 (1999)
Vitell S., Hunt S.D.: The general theory of marketing ethics: a partial test of the model. Res. Market. 10, 237–265 (1990)
Vroom V.H.: Work and Motivation. John Wiley, New York (1964)
Wang C.C.: The influence of ethical and self-interest concerns on knowledge sharing intentions among managers: an empirical study. Int. J. Manage. 21(3), 370–381 (2004)
Weiss L.: Collection and connection: the anatomy of knowledge sharing in professional service. Organ. Dev. J. 17(4), 61–72 (1999)
Yoo, Y., Torrey, B.: National culture and knowledge management in a global learning organization. In: Choo, C.W., Bontis, N. (eds.) The Strategic Management of Intellectual Capital and Organizational Knowledge. Oxford University Press, pp. 421–435. Oxford University Press, New York (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, MT., Chen, KS. & Chien, JL. The factors impact of knowledge sharing intentions: the theory of reasoned action perspective. Qual Quant 46, 1479–1491 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-011-9462-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-011-9462-9