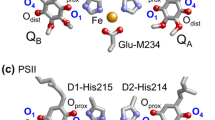
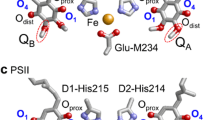
Abstract
Purple, photosynthetic reaction centers from Rhodobacter sphaeroides bacteria use ubiquinone (UQ10) as both primary (QA) and secondary (QB) electron acceptors. Many quinones reconstitute QA function, while a few will act as QB. Nine quinones were tested for their ability to bind and reconstitute QA and QB functions. Only ubiquinone (UQ) reconstitutes both functions in the same protein. The affinities of the non-native quinones for the QB site were determined by a competitive inhibition assay. The affinities of benzoquinones, naphthoquinone (NQ), and 2-methyl-NQ for the QB site are 7 ± 3 times weaker than that at QA site. However, di-ortho-substituted NQs and anthraquinone bind tightly to the QA site (K d ≤ 200 nM), and ≥1,000 times more weakly to the QB site, perhaps setting a limit on the size of the site. With a low-potential electron donor, 2-methyl, 3-dimethylamino-1,4-NQ, (Me-diMeAm-NQ) at QA, QB reduction is 260 meV, more favorable than with UQ as QA. Electron transfer from Me-diMeAm-NQ at the QA site to NQ at the QB site can be detected. In the QB site, the NQ semiquinone is estimated to be ≈60–100 meV higher in energy than the UQ semiquinone, while in the QA site, the semiquinone energy level is similar or lower with NQ than with UQ. Thus, the NQ semiquinone is more stable in the QA than in the QB site. In contrast, the native UQ semiquinone is ≈60 meV lower in energy in the QB than in the QA site, stabilizing forward electron transfer from QA to QB.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RCs:
-
Bacterial photosynthetic reaction centers
- BQ:
-
Benzoquinone
- diMe-BQ:
-
2,6-Dimethyl-benzoquinone
- DQ:
-
Tetramethyl-benzoquinone (duroquinone)
- triMe-BQ:
-
2,3,5-Trimethyl-benzoquinone
- UQ1 :
-
Ubiquinone-1 (2,3-dimethoxy, 5-methyl, 6-prenyl-benzoquinone)
- UQ10 :
-
Ubiquinone-10
- NQ:
-
1,4-Naphthoquinone
- Me-NQ:
-
2-Methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone
- diMe-NQ:
-
2,3-Dimethyl-1,4-naphthoquinone
- Me-diMeAm-NQ:
-
2-Methyl, 3-dimethylamino-1,4-naphthoquinone
- Decyl-diMeAm-NQ:
-
2-Decyl, 3-dimethylamino-1,4-naphthoquinone
- AQ:
-
9,10-Anthraquinone
References
Arata H, Parson WW (1981) Delayed fluorescence from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides reaction centers: enthalpy and free energy changes accompanying electron transfer from P870 to quinones. Biochim Biophys Acta 638:201–209
Ashnagar A, Bruce M, Dutton PL, Prince R (1984) One- and two-electron reduction of hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone and hydroxy-9,10-anthraquinones. The role of internal hydrogen bonding and its bearing on the redox chemistry of the anthracycline antitumour quinones. Biochim Biophys Acta 801:351–359
Baccarini-Melandri A, Gabellini N, Melandri BA, Hurt E, Hauska G (1980) Structural requirements of quinone coenzymes for endogenous and dye-mediated coupled electron transport in bacterial photosynthesis. J Bioenerg Biomembr 12:95–110
Blankenship RE, Parson WW (1979) The involvement of iron and ubiquinone in electron transfer reactions mediated by reaction centers from photosynthetic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta 545:429–444
Cogdell RJ, Brune DC, Clayton RK (1974) Effects of extraction and replacement of ubiquinone upon the photochemical activity of reaction centres and chromatophores from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. FEBS Lett 45:344–347
Cramer WA, Zhang H, Yan J, Kurisu G, Smith JL (2004) Evolution of photosynthesis: time-independent structure of the cytochrome b6f complex. Biochemistry 43:5921–5929
Diner BA, Rappaport F (2002) Structure, dynamics, and energetics of the primary photochemistry of photosystem II of oxygenic photosynthesis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:551–580
Diner BA, Schenck CC, DeVitry C (1984) Effect of inhibitors, redox state and isoprenoid chain length on the affinity of ubiquinone for the secondary acceptor binding site in the reaction centers of photosynthetic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta 766:9–20
Diner BA, Petrouleas V, Wendoloski JJ (1991) The iron–quinone electron–acceptor complex of photosystem II. Physiol Plant 81:423–436
Dutton PL, Petty KM, Bonner HS, Morse SD (1975) Cytochrome c2 and reaction center of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides Ga. membranes. Extinction coefficients, content, half-reduction potentials, kinetics and electric field alterations. Biochim Biophys Acta 387:536–556
Franzen S, Boxer SG (1993) Temperature dependence of the electric field modulation of electron-transfer rates: charge recombination in photosynthetic reaction centers. J Phys Chem 97:6304–6318
Fromme P, Jordan P, Krauß N (2001) Structure of photosystem I. Biochim Biophys Acta 1507:5–31
Giangiacomo KM, Dutton PL (1989) In photosynthetic reaction centers, the free energy difference for electron transfer between quinones bound at the primary and secondary quinone-binding sites governs the observed secondary site specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2658–2662
Goldsmith JO, Boxer SG (1996) Rapid isolation of bacterial photosynthetic reaction centers with an engineered poly-histidine tag. Biochim Biophys Acta 1276:171–175
Graige MS, Feher G, Okamura MY (1998) Conformational gating of the electron transfer reaction Q −•A QB → QAQ −•B in bacterial reaction centers of Rhodobacter sphaeroides determined by a driving force assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:11679–11684
Graige MS, Paddock ML, Feher G, Okamura MY (1999) Observation of the protonated semiquinone intermediate in isolated reaction centers from Rhodobacter sphaeroides: implications for the mechanism of electron and proton transfer in proteins. Biochemistry 38:11465–11473
Gunner MR, Dutton PL (1989) Temperature and −∆G° dependence of the electron transfer from BPh− to QA in reaction center protein from Rhodobacter sphaeroides with different quinones as QA. J Am Chem Soc 111:3400–3412
Gunner MR, Tiede DM, Prince RC, Dutton PL (1982) Quinones as prosthetic groups in membrane electron-transfer proteins I: systematic replacement of the primary ubiquinone of photochemical reaction centers with other quinones. In: Trumpower BL (ed) Function of quinones in energy conserving systems. Academic Press, New York, pp 265–269
Gunner MR, Braun BS, Bruce JM, Dutton PL (1985) The characterization of the QA binding site of the reaction center of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. In: Michel-Beyerle ME (ed) Antenna and reaction centers of photosynthetic bacteria. Springer, New York, pp 298–305
Gunner MR, Braun BS, Bruce JM, Dutton PL (1986a) The characterization of the QA binding site of the reaction center of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. In: Michel-Beyerle ME (ed) Antennas and reaction centers of photosynthetic bacteria. Springer, Berlin, pp 298–305
Gunner MR, Robertson DE, Dutton PL (1986b) Kinetic studies on the reaction center protein from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides: the temperature and free energy dependence of electron transfer between various quinones in the QA site and the oxidized bacteriochlorophyll dimer. J Phys Chem 90:3783–3795
Gunner MR, Madeo J, Zhu Z (2008) Modification of quinone electrochemistry by the proteins in the biological electron transfer chains: examples from photosynthetic reaction centers. J Bioenerg Biomembr 40:509–519
Heathcote P (2002) Reaction centers: the structure and evolution of biological solar power. Trends Biochem Sci 27:79–86
Herrmann KW (1962) Non-ionic–cationic micellar properties of dimethyldodecylamine oxide. J Phys Chem 66(1962):295–300
Hunte C, Palsdottir H, Trumpower BL (2003) Protonmotive pathways and mechanisms in the cytochrome bc1 complex. FEBS Lett 545:39–46
Ishikita H, Knapp EW (2003) Redox potential of quinones in both electron transfer branches of photosystem I. J Biol Chem 278:52002–52011
Kirmaier C, Holten D, Parson WW (1985) Temperature and detection-wavelength dependence of the picosecond electron transfer kinetics measured in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides reaction centers. Resolution of new spectral and kinetic components in the primary charge separation process. Biochim Biophys Acta 810:33–48
Kleinfeld D, Okamura MY, Feher G (1984) Electron transfer in reaction centers of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides: I. Determination of the charge recombination pathway of D+QAQ −B and free energy and kinetic relations between Q −A QB and QAQ −B . Biochim Biophys Acta 766:126–140
Kurisu G, Zhang H, Smith JL, Cramer WA (2003) Structure of the cytochrome b6f complex of oxygenic photosynthesis: tuning the cavity. Science 302:1009–1014
Labahn A, Paddock ML, McPherson PH, Okamura MY, Feher G (1994) Direct charge recombination from D+QAQ −B to DQAQB in bacterial reaction centers from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Phys Chem 98:3417–3423
Labahn A, Bruce JM, Okamura MY, Feher G (1995) Direct charge recombination from D+QAQ −B to DQAQB in bacterial reaction centers from Rhodobacter sphaeroides containing low potential quinone in the QA site. Chem Phys 97:355–366
Lancaster CRD (1998) Ubiquinone reduction and protonation in photosynthetic reaction centres from Rhodopseudomonas viridis: X-ray structures and their functional implications. Biochim Biophys Acta 1365:143–150
Li J, Gilroy D, Tiede DM, Gunner MR (1998) Kinetic phases in the electron transfer from P+Q −A QB to P+QAQ −B and the associated processes in Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26 reaction centers. Biochemistry 37:2818–2829
Li J, Coleman WJ, Youvan DC, Gunner MR (2000a) Characterization of a symmetrized mutant RC with 42 residues from the QA site replacing residues in the QB site. Photosynth Res 64:41–52
Li J, Takahashi E, Gunner MR (2000b) −∆G °AB and pH dependence on the electron transfer from P+Q −A QB to P+QAQ −B in Rhodobacter sphaeroides reaction centers. Biochemistry 39:7445–7454
Liang Y, Nagus DK, Hochstrasser RM, Gunner MR, Dutton PL (1981) Picosecond kinetics: absorption studies of an iron porphyrin and bacteriopheophytin using a streak camera. Chem Phys Lett 84:236–240
Loach PA, Sekura SL (1968) Primary photochemistry and electron transport in Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochemistry 7:2642–2649
Madeo J, Gunner MR (2005) Modeling binding kinetics at the QA site in bacterial reaction centers. Biochemistry 44:10994–11004
Madeo J, Mihajlovic M, Lazaridis T, Gunner MR (2011) Slow dissociation of a charged ligand: analysis of the primary quinone (QA) site of photosynthetic bacterial reaction centers. J Am Chem Soc 133:17375–17385
Mancino LJ, Dean DP, Blankenship RE (1984) Kinetics and thermodynamics of the P870+Q −A → P870+Q −B reaction in isolated reaction centers from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Biochim Biophys Acta 764:46–54
McComb JC, Stein RR, Wraight CA (1990) Investigations on the influence of headgroup substitution and isoprene side-chain length in the function of primary and secondary quinones of bacterial reaction centers. Biochim Biophys Acta 1015:156–171
McElroy JD, Feher G, Mauzerall DC (1969) On the nature of the free radical formed during the primary process of bacterial photosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 172:180–183
McPherson PH, Okamura MY, Feher G (1990) Electron transfer from the reaction center of Rb. sphaeroides to the quinone pool: doubly reduced QB leaves the reaction center. Biochim Biophys Acta 1016:289–292
Mitchell P (1975) The protonmotive Q cycle: a general formulation. FEBS Lett 59:137–139
Nonella M, Boullais C, Mioskowski C, Nabedryk E, Breton J (1999) Vibrational spectrum and torsional potential of 2-methoxy-3-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone. J Phys Chem 103:6363–6370
Okamura MY, Isaacson RA, Feher G (1975) The primary acceptor in bacterial photosynthesis: obligatory role of ubiquinone in photoactive reaction centers of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:3492–3496
Okamura MY, Paddock ML, Graige MS, Feher G (2000) Proton and electron transfer in bacterial reaction centers. Biochim Biophys Acta 1458:148–163
Paddock ML, Feher G, Okamura MY (2003) Proton transfer pathways and mechanism in bacterial reaction centers. FEBS Lett 555:45–50
Prince RC, Dutton PL, Bruce JM (1983) Electrochemistry of ubiquinones, menaquinones and plastoquinones in aprotic solvents. FEBS Lett 160:273–276
Prince RC, Halbert TR, Upton TH (1988) Structural influences on the electrochemistry of ubiquinone. In: Kim CH, Tedeschi H, Diwan J, Salerno J (eds) Advances in membrane biochemistry and bioenergetics. Plenum Publishing Corporation, New York
Remy A, Boers RB, Egorova-Zachernyuk T, Gast P, Lugtenberg J, Gerwert K (2003) Does different orientation of the methoxy groups of ubiquinone-10 in the reaction center of Rhodobacter sphaeroides cause different binding at QA and QB. Eur J Biochem 270:3603–3609
Rinyu L, Martin EW, Takahashi E, Maroti P, Wraight CA (2004) Modulation of the free energy of the primary quinone acceptor QA in reaction centers from Rhodobacter sphaeroides: contributions from the protein and protein–lipid (cardiolipin) interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1655:93–101
Sadekar S, Raymond J, Blankenship RE (2006) Conservation of distantly related membrane proteins: photosynthetic reaction centers share a common structural core. Mol Biol Evol 23:2001–2007
Salmon-Chemin L, Buisine E, Yardley V, Kohler S, Bebreu M-A, Landry V, Sergheraert C, Croft SL, Srauth-Siegel L, Davioud-Carvet E (2001) 2- and 3-substituted 1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives as subversive substrates of trypanothione reductase and lipoamide dehydrogenase from Trypanosoma cruzi: synthesis and correlation between redox cycling activities and in vitro cytotoxicity. J Med Chem 44:548–565
Schmid R, Labahn A (2000) Temperature and free energy dependence of the direct charge recombination rate from the secondary quinone in bacterial reaction centers from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Phys Chem B 104:2928–2936
Sebban P, Wraight CA (1989) Heterogeneity of the P+Q −A recombination kinetics in reaction centers from Rhodopseudomonas viridis: the effect of pH and temperature. Biochim Biophys Acta 974:54–65
Shopes RJ, Wraight CA (1987) Charge recombination from the P+Q −A state in reaction centers from Rhodopseudomonas viridis. Biochim Biophys Acta 893:409–425
Sinning I, Koepke J, Schiller B, Mathis P, Rutherford AW, Michel H (1990) The herbicide resistant mutants T1 from Rhodopseudomonas viridis. Curr Res Photosynth 1:173–176
Slooten L (1972) Electron acceptors in reaction center preparations from photosynthetic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta 275:208–218
Stowell MHB, McPhillips TM, Rees DC, Soltis SM, Abresch E, Feher G (1997) Light-induced structural changes in photosynthetic reaction center: implications for mechanism of electron–proton transfer. Science 276:812–816
Stroebel D, Choquet Y, Popot JL, Picot D (2003) An atypical haem in the cytochrome b6f complex. Nature 426:413–418
Takahashi E, Wraight CA (1990) A crucial role for AspL213 in the proton transfer pathway to the secondary quinone of reaction centers from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Biochim Biophys Acta 1020:107–111
Takahashi E, Wells TA, Wraight CA (1998) Environmental control of the redox potential of QA in Rb. sphaeroides reaction centers: polar replacement of IleM260 causes marked change in QA and QB function. In: Garab G (ed) Proceedings of the XIth international photosynthesis congress. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 17–22
Tiede DM, Vazquez J, Cordova J, Marone AP (1996) Time-resolved electrochromism associated with the formation of quinone anions in the Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26 reaction center. Biochemistry 35:10763–10775
Warncke K, Dutton PL (1993a) Experimental resolution of the free energies of aqueous solvation contributions to ligand–protein binding: quinone–QA site interactions in the photosynthetic reaction center protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:2920–2924
Warncke K, Dutton PL (1993b) Influence of QA site redox cofactor structure on equilibrium binding, in situ electrochemistry, and electron-transfer performance in the photosynthetic reaction center protein. Biochemistry 32:4769–4779
Warncke K, Gunner MR, Dutton PL (1987) Effect of hydrocarbon tail structure on the affinity of substituted quinones for the QA site in reaction centers of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides R-26. In: Biggins J (ed) Progress in photosynthesis research. Martinus Nijhoff, Dordrecht, pp 217–220
Warncke K, Gunner MR, Braun BS, Gu L, Yu C, Bruce JM, Dutton PL (1994) Influence of hydrocarbon tail structure on quinone binding and electron-transfer performance at the QA and QB sites of the photosynthetic reaction center protein. Biochemistry 33:7830–7841
Williams JC, Steiner LA, Feher G (1986) Primary structure of the reaction center from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Proteins Struct Funct Genet 1:312–325
Woodbury NWT, Parson WW (1984) Nanosecond fluorescence from isolated photosynthetic reaction centers from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Biochim Biophys Acta 767:345–361
Woodbury NW, Becker M, Middendorf D, Parson WW (1985) Picosecond kinetics of the initial photochemical electron-transfer reaction in bacterial photosynthetic reaction centers. Biochemistry 24:7516–7521
Woodbury NW, Parson WW, Gunner MR, Prince RC, Dutton PL (1986) Radical-pair energetics and decay mechanisms in reaction center containing anthraquinones or benzoquinones in place of ubiquinone. Biochim Biophys Acta 851:6–22
Wraight CA (1979) The role of quinones in bacterial photosynthesis. Photochem Photobiol 30:767–776
Wraight CA (2004) Proton and electron transfer in the acceptor quinone complex of photosynthetic reaction centers from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Front Biosci 9:309–337
Wraight CA, Clayton RK (1973) The absolute quantum efficiency of bacteriochlorophyll photoxidation in reaction centers. Biochim Biophys Acta 333:246–260
Wraight C, Gunner MR (2009) The acceptor quinones of purple photosynthetic bacteria—structure and spectroscopy. In: Hunter NC, Daldal F, Thurnauer MC, Beatty JT (eds) The purple phototropic bacteria. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 379–405
Wraight CA, Stein RR (1980) Redox equilibrium in the acceptor quinone complex of isolated reaction centers and the mode of action of o-phenanthroline. FEBS Lett 113:73–77
Wraight CA, Stein RR (1983) Bacterial reaction centers as a model for photosystem II: turn over of the secondary acceptor quinone. In: Inoue Y, Crofts AR, Govindjee, Murata N, Renger G, Satoh K (eds) The oxygen evolving system of photosynthesis. Academic Press, New York, pp 383–393
Wraight CA, Vakkasoglu AS, Poluektov Y, Mattis AJ, Nihan D, Lipshutz BH (2008) The 2-methoxy group of ubiquinone is essential for function of the acceptor quinones in reaction centers from Rba. sphaeroides. Biochim Biophys Acta 1777:631–636
Xu Q, Gunner MR (2000) Temperature dependence of the free energy, enthalpy and entropy of P+Q −A charge recombination in photosynthetic reaction centers. J Phys Chem B 104:8035–8043
Xu Q, Gunner MR (2002) Exploring the energy profile of the Q −A to QB electron transfer reaction in bacterial photosynthetic reaction centers: pH dependence of the conformational gating step. Biochemistry 41:2694–2701
Zhu Z, Gunner MR (2005) Energetics of quinone-dependent electron and proton transfers in Rhodobacter sphaeroides photosynthetic reaction centers. Biochemistry 44:82–96
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. Mahesh Lakshman (City College of New York) for his help with quinone synthesis, to Dr. Philip Laible (Argonne National Laboratory) for the His-tagged bacteria and his helpful advice on their cultivation, and to Drs. Jennifer Madeo and Pierre Seban for their helpful discussions. This study has been supported by the National Science Foundation Grant MCB 1022208, with infrastructure support from the National Center for Research Resources (G12RR03060), and the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities (G12MD007603) from the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Gunner, M.R. Affinity and activity of non-native quinones at the QB site of bacterial photosynthetic reaction centers. Photosynth Res 120, 181–196 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-013-9850-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-013-9850-1