Abstract
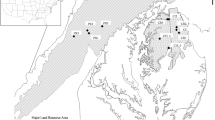
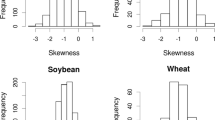
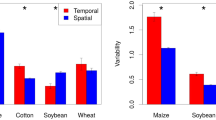
While precision agriculture (PA) technologies are widely used in cropping systems, these technologies have received less attention in mixed farming systems. Little is known about the nature, extent, and temporal stability of spatial variability of pastures in mixed farming systems and the feasibility of managing this variability. This paper describes a technique to create a Stability Index based on both crop grain yield and pasture total green dry matter (TGDM) production over time, using high resolution spatial data in two climatic zones of Australia. Four productivity zones were used to characterise the Stability Index: high and stable, high and unstable, low and stable, and low and unstable. Mapping the indices shows the location and size of the spatial and temporal features of each paddock. The features of the stability zones generally corresponded with soil texture classes. Testing the Stability Indices with a Kruskal–Wallis one-way ANOVA showed significantly different medians for high and low production categories for both grain yield and pasture TGDM (p < 0.01). Crop grain yield stability showed significant differences between medians. In pasture TGDM, the differences between stability medians were not significant, but the technique still separated medians into stable and unstable groupings. This production Stability Index has the potential to be used by farmers to manage spatial variability in mixed farming systems by identifying homogenous areas within a paddock for investigation/amelioration and can also separate out areas of either spatial and/or temporal instability for specific management strategies.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Angus, J. F., & Peoples, M. B. (2013). Nitrogen from Australian dryland pastures. Crop and Pasture Science,63(9), 746–758. https://doi.org/10.1071/cp12161.
Bailey, D. W., & Provenza, F. D. (2008). Mechanisms determining large-herbivore distribution. In H. H. T. Prins & F. Van Langevelde (Eds.), Resource Ecology. Wageningen UR Frontis Series (Vol. 23, pp. 7–28). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer.
Basso, B., Fiorentino, C., Cammarano, D., Cafiero, G., & Dardanelli, J. (2012). Analysis of rainfall distribution on spatial and temporal patterns of wheat yield in mediterranean environment. European Journal of Agronomy,41, 52–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2012.03.007.
Behrens, T., Müller, J., & Diepenbrock, W. (2006). Utilization of canopy reflectance to predict properties of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) and barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) during ontogenesis. European Journal of Agronomy,25(4), 345–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2006.06.010.
Bell, L. W., Hayes, R. C., Pembleton, K. G., & Waters, C. M. (2014a). Opportunities and challenges in Australian grasslands: Pathways to achieve future sustainability and productivity imperatives. Crop and Pasture Science,65(6), 489–507. https://doi.org/10.1071/CP13420.
Bell, L. W., & Moore, A. D. (2011). Mixed crop-livestock businesses reduce price and climate-induced variability in farm returns: a model-derived case study. Paper presented at the 5th World Congress of Conservation Agriculture incorporating 3rd Farming Systems Design Conference Brisbane, Australia, 26–29 September 2011.
Bell, L. W., Moore, A. D., & Kirkegaard, J. A. (2014b). Evolution in crop–livestock integration systems that improve farm productivity and environmental performance in Australia. European Journal of Agronomy,57, 10–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2013.04.007.
Blackmore, S. (2000). The interpretation of trends from multiple yield maps. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture,26(1), 37–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1699(99)00075-7.
Blackmore, S. (2003). The role of yield maps in precision farming. Silsoe, UK: Cranfield University.
Blackmore, S., Godwin, R. J., & Fountas, S. (2003). The analysis of spatial and temporal trends in yield map data over six years. Biosystems Engineering,84(4), 455–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1537-5110(03)00038-2.
Buttafuoco, G., Castrignanò, A., Colecchia, A. S., & Ricca, N. (2010). Delineation of management zones using soil properties and a multivariate geostatistical approach. Italian Journal of Agronomy,5(4), 323–332. https://doi.org/10.4081/ija.2010.323.
Castrignanò, A., Wong, M. T. F., Stelluti, M., De Benedetto, D., & Sollitto, D. (2012). Use of EMI, gamma-ray emission and GPS height as multi-sensor data for soil characterisation. Geoderma,175–176, 78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.01.013.
Chapman, D., Parsons, A., Cosgrove, G., Barker, D. J., Marotti, D., Venning, K., et al. (2007). Impacts of spatial patterns in pasture on animal grazing behavior, intake, and performance. Crop Science,47(1), 399–415. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2006.01.0036.
Cook, S., & Bramley, R. G. V. (2001). Is agronomy being left behind by precision agriculture? Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 10th Australian agronomy conference Hobart, Tasmania, Australia, 29 January - 1 February 2001.
Corder, G. W., & Foreman, D. I. (2014). Nonparametric statistics: A step-by-step approach (2nd ed.). Hoboken, New Jersey, USA: Wiley.
Diacono, M., Castrignanò, A., Troccoli, A., De Benedetto, D., Basso, B., & Rubino, P. (2012). Spatial and temporal variability of wheat grain yield and quality in a Mediterranean environment: A multivariate geostatistical approach. Field Crops Research,131, 49–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2012.03.004.
Dobermann, A., Ping, J. L., Adamchuk, V. I., Simbahan, G. C., & Ferguson, R. B. (2003). Classification of crop yield variability in irrigated production fields. Agronomy Journal,95(5), 1105–1120. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2003.1105.
Edirisinghe, A., Hill, M. J., Donald, G. E., & Hyder, M. (2011). Quantitative mapping of pasture biomass using satellite imagery. International Journal of Remote Sensing,32(10), 2699–2724. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161003743181.
Ewing, M. A., & Flugge, F. (2004). The benefits and challenges of crop-livestock integration in Australian agriculture. Paper presented at the 4th International Crop Science Congress 26 September–1 October 2004, Brisbane, Australia.
Farid, H. U., Bakhsh, A., Ahmad, N., Ahmad, A., & Mahmood-Khan, Z. (2016). Delineating site-specific management zones for precision agriculture. The Journal of Agricultural Science,154(02), 273–286. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859615000143.
Glenn, E. P., Huete, A. R., Nagler, P. L., & Nelson, S. G. (2008). Relationship between remotely-sensed vegetation indices, canopy attributes and plant physiological processes: What vegetation indices can and cannot tell us about the landscape. Sensors,8(4), 2136–2160. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8042136.
Goel, N. S., & Qin, W. (1994). Influences of canopy architecture on relationships between various vegetation indices and LAI and FPAR: A computer simulation. Remote Sensing Reviews,10(4), 309–347. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757259409532252.
Gong, P., Pu, R., Biging, G. S., & Larrieu, M. R. (2003). Estimation of forest leaf area index using vegetation indices derived from Hyperion hyperspectral data. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,41(6), 1355–1362. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2003.812910.
Gourley, C. J. P., Peverill, K. I., & Dougherty, W. J. (2007). Making better fertiliser decisions for grazed pastures in Australia, accounting for nutrients and fertcare. Paper presented at the Australian Fertilizer Industry Conference Hamilton Island, Queensland, Australia, 6–10 August 2007.
Heberger, M. (2011). Australia’s Millennium drought: impacts and responses. In P. H. Gleick (Ed.), The world’s water: The Biennial report on freshwater resources (pp. 97–125). Washington DC, USA: Island Press/Center for Resource Economics.
Hill, M. J., Donald, G. E., Vickery, P. J., Moore, A. D., & Donnelly, J. R. (1999). Combining satellite data with a simulation model to describe spatial variability in pasture growth at a farm scale. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture,39(3), 285–300. https://doi.org/10.1071/EA98109.
Holland, K. H., Schepers, J. S., Shanahan, J. F., Horst, G. L., & Mulla, D. J. (2004). Plant canopy sensor with modulated polychromatic light source. Paper presented at the 7th International Conference on precision agriculture and other precision resources management, Minneapolis, USA, 25–28 July 2004.
Huete, A. R. (1988). A soil-adjusted vegetation index (SAVI). Remote Sensing of Environment,25(3), 295–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-4257(88)90106-X.
Huete, A. R., Didan, K., Miura, T., Rodriguez, E. P., Gao, X., & Ferreira, L. G. (2002). Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sensing of Environment,83(1–2), 195–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0034-4257(02)00096-2.
Inchbold, A., Whelan, B., & Baines, P. (2009). Making money out of precision agriculture. Improving winter cropping systems in the Riverine Plains. Yarrawonga, VIC, Australia: Riverine Plains Inc.
Isbell, R. (2016). The Australian soil classification. Collingwood, VIC, Australia: CSIRO Publishing.
Jeffrey, S. J., Carter, J. O., Moodie, K. B., & Beswick, A. R. (2001). Using spatial interpolation to construct a comprehensive archive of Australian climate data. Environmental Modelling & Software,16(4), 309–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1364-8152(01)00008-1.
Kirkegaard, J. A., Conyers, M. K., Hunt, J. R., Kirkby, C. A., Watt, M., & Rebetzke, G. J. (2014). Sense and nonsense in conservation agriculture: Principles, pragmatism and productivity in Australian mixed farming systems. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment,187, 133–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2013.08.011.
Kirkegaard, J. A., & Lilley, J. M. (2007). Root penetration rate: A benchmark to identify soil and plant limitations to rooting depth in wheat. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture,47(5), 590–602. https://doi.org/10.1071/EA06071.
Kirkegaard, J. A., Peoples, M. B., Angus, J. F., & Unkovich, M. J. (2011). Diversity and evolution of rainfed farming systems in southern Australia. In P. Tow, I. Cooper, I. Partridge, & C. Birch (Eds.), Rainfed farming systems (pp. 715–754). Dordrecht, Netherlands: Springer.
Kruskal, W. H., & Wallis, W. A. (1952). Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. Journal of the American statistical Association,47(260), 583–621. https://doi.org/10.2307/2280779.
Laca, E. A. (2009). New approaches and tools for grazing management. Rangeland Ecology & Management,62(5), 407–417. https://doi.org/10.2111/08-104.1.
Li, G. D., Dear, B., Casburn, G., Walker, J., Bowden, P., & Hayes, R. (2010). A survey of the current and future use of lucerne, chicory and perennial grasses in pasture-crop rotations in southern New South Wales. Paper presented at the Food Security from Sustainable Agriculture: 15th Australian Agronomy Conference Lincoln, New Zealand, 15–18 November 2010.
Lilley, J. M., & Kirkegaard, J. A. (2016). Farming system context drives the value of deep wheat roots in semi-arid environments. Journal of Experimental Botany,67(12), 3665–3681. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw093.
Marques da Silva, J. R. (2006). Analysis of the spatial and temporal variability of irrigated maize yield. Biosystems Engineering,94(3), 337–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2006.03.006.
Marques da Silva, J. R., Peça, J. O., Serrano, J. M., de Carvalho, M. J., & Palma, P. M. (2008). Evaluation of spatial and temporal variability of pasture based on topography and the quality of the rainy season. Precision Agriculture,9(4), 209–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-008-9066-0.
McBratney, A. B., Whelan, B. M., & Shatar, T. M. (1997). Variability and uncertainty in spatial, temporal and spatiotemporal crop yield and related data. Paper presented at the Precision Agriculture: Spatial and Temporal Variability of Environmental Quality Conference, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 21–23 January 1997.
Meehl, P. E. (1990). Why summaries of research on psychological theories are often uninterpretable. Psychological Reports,66(1), 195–244. https://doi.org/10.2466/pr0.1990.66.1.195.
Moral, F. J., Terrón, J. M., & Marques da Silva, J. R. (2010). Delineation of management zones using mobile measurements of soil apparent electrical conductivity and multivariate geostatistical techniques. Soil and Tillage Research,106(2), 335–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2009.12.002.
Murray, R. I., Yule, I. J., & Gillingham, A. G. (2007). Developing variable rate application technology: Modelling annual pasture production on hill country. New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research,50(1), 41–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-6850-8_2.
Mutanga, O., & Skidmore, A. K. (2004). Narrow band vegetation indices overcome the saturation problem in biomass estimation. International Journal of Remote Sensing,25(19), 3999–4014. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160310001654923.
Nichols, P. G. H., Loi, A., Nutt, B. J., Evans, P. M., Craig, A. D., Pengelly, B. C., et al. (2007). New annual and short-lived perennial pasture legumes for Australian agriculture: 15 years of revolution. Field Crops Research,104(1–3), 10–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2007.03.016.
Oliver, Y. M., & Robertson, M. J. (2009). Quantifying the benefits of accounting for yield potential in spatially and seasonally responsive nutrient management in a mediterranean climate. Australian Journal of Soil Research,47(1), 114–126. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR08099.
Ollinger, S. V. (2011). Sources of variability in canopy reflectance and the convergent properties of plants. New Phytologist,189(2), 375–394. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03536.x.
Peverill, K., Sparrow, L., & Reuter, D. (Eds.). (1999). Soil analysis: An interpretation manual. Collingwood, VIC, Australia: CSIRO Publishing.
Plant, R. (2001). Site-specific management: the application of information technology to crop production. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture,30(1), 9–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1699(00)00152-6.
Price, G. H. H. (2006). Australian soil fertility manual (3rd ed.). Collingwood, VIC, Australia: CSIRO Publishing.
Price, R. J., & Hacker, R. B. (2009). Grain and Graze: an innovative triple bottom line approach to collaborative and multidisciplinary mixed-farming systems research, development and extension. Animal Production Science,49(10), 729–735. https://doi.org/10.1071/EA08306.
Pullanagari, R. R., Yule, I. J., Tuohy, M. P., Hedley, M. J., Dynes, R. A., & King, W. M. (2012). Proximal sensing of the seasonal variability of pasture nutritive value using multispectral radiometry. Grass and Forage Science. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2494.2012.00877.x.
R Core Team (2017). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. (Vol. 3.3.3). Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing.
Reuter, D., & Robinson, J. B. (1997). Plant analysis: An interpretation manual. Collingwood, VIC, Australia: CSIRO publishing.
Rook, A. J., Dumont, B., Isselstein, J., Osoro, K., WallisDeVries, M. F., Parente, G., et al. (2004). Matching type of livestock to desired biodiversity outcomes in pastures: A review. Biological Conservation,119(2), 137–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2003.11.010.
Schellberg, J., Hill, M. J., Gerhards, R., Rothmund, M., & Braun, M. (2008). Precision agriculture on grassland: Applications, perspectives and constraints. European Journal of Agronomy,29(2–3), 59–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2008.05.005.
Schirrmann, M., Gebbers, R., Kramer, E., & Seidel, J. (2011). Soil pH mapping with an on-the-go sensor. Sensors,11(1), 573–598. https://doi.org/10.3390/s110100573.
Schmer, M. R., Mitchell, R. B., Vogel, K. P., Schacht, W. H., & Marx, D. B. (2009). Spatial and temporal effects on switchgrass stands and yield in the great plains. BioEnergy Research,3(2), 159–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-009-9045-y.
Schnyder, H., Locher, F., & Auerswald, K. (2009). Nutrient redistribution by grazing cattle drives patterns of topsoil N and P stocks in a low-input pasture ecosystem. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems,88(2), 183–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-009-9334-z.
Serrano, J., Marques da Silva, J., & Shahidian, S. (2014). Spatial and temporal patterns of potassium on grazed permanent pastures—Management challenges. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment,188, 29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2014.02.012.
Serrano, J. M., Peça, J. O., Marques da Silva, J. R., & Shahidian, S. (2011). Spatial and temporal stability of soil phosphate concentration and pasture dry matter yield. Precision Agriculture,12(2), 214–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-010-9170-9.
Serrano, J. M., Peça, J. O., Marques da Silva, J. R., & Shaidian, S. (2010). Mapping soil and pasture variability with an electromagnetic induction sensor. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture,73(1), 7–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2010.03.008.
Shen, M., Chen, J., Zhu, X., & Tang, Y. (2009). Yellow flowers can decrease NDVI and EVI values: Evidence from a field experiment in an alpine meadow. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing,35(2), 99–106. https://doi.org/10.5589/m09-003.
Shen, M., Chen, J., Zhu, X., Tang, Y., & Chen, X. (2010). Do flowers affect biomass estimate accuracy from NDVI and EVI? International Journal of Remote Sensing,31(8), 2139–2149. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160903578812.
Simeoni, M. A., Galloway, P. D., O’Neil, A. J., & Gilkes, R. J. (2009). A procedure for mapping the depth to the texture contrast horizon of duplex soils in south-western Australia using ground penetrating radar, GPS and kriging. Soil Research,47(6), 613–621. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR08241.
Soder, K. J., Gregorini, P., Scaglia, G., & Rook, A. J. (2009). Dietary selection by domestic grazing ruminants in temperate pastures: Current state of knowledge, methodologies, and future direction. Rangeland Ecology & Management,62(5), 389–398. https://doi.org/10.2111/08-068.1.
Sudduth, K. A., Kitchen, N., & Drummond, S. (2010). Comparison of three canopy reflectance sensors for variable-rate nitrogen application in corn. Paper presented at the 10th International Conference on Precision Agriculture Denver, Colorado, USA, 18–21 July, 2010.
Sudduth, K. A., Kitchen, N. R., & Kremer, R. J. (2009). VNIR spectroscopy estimation of soil quality indicators. Paper presented at the American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers Annual International Meeting, Reno, Nevada, USA, 21–24 June, 2009.
Sun, W., Whelan, B. M., Minasny, B., & McBratney, A. B. (2012). Evaluation of a local regression kriging approach for mapping apparent electrical conductivity of soil (ECa) at high resolution. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science,175(2), 212–220. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201100005.
Taylor, J. A., McBratney, A. B., & Whelan, B. M. (2007). Establishing management classes for broadacre agricultural production. Agronomy Journal,99(5), 1366–1376. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2007.0070.
Thenkabail, P. S., Smith, R. B., & De Pauw, E. (2000). Hyperspectral vegetation indices and their relationships with agricultural crop characteristics. Remote Sensing of Environment,71(2), 158–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(99)00067-X.
Trotter, M. G., Lamb, D. W., Hinch, G. N., & Guppy, C. N. (2010a). Global navigation satellite system livestock tracking: System development and data interpretation. Animal Production Science,50(6), 616–623. https://doi.org/10.1071/AN09203.
Trotter, M. G., Lamb, D. W., Hinch, G. N., & Guppy, C. N. (2010b). GNSS tracking of livestock: towards variable fertilizer strategies for the grazing industry. Paper presented at the 10th International Conference on Precision Agriculture, Denver, Colorado, USA, 18–21 July 2010.
Tucker, C. J. (1979). Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sensing of Environment,8(2), 127–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-4257(79)90013-0.
van Dijk, A. I. J. M., Beck, H. E., Crosbie, R. S., de Jeu, R. A. M., Liu, Y. Y., Podger, G. M., et al. (2013). The Millennium drought in southeast Australia (2001–2009): Natural and human causes and implications for water resources, ecosystems, economy, and society. Water Resources Research,49(2), 1040–1057. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrcr.20123.
Viña, A., Gitelson, A. A., Nguy-Robertson, A. L., & Peng, Y. (2011). Comparison of different vegetation indices for the remote assessment of green leaf area index of crops. Remote Sensing of Environment,115(12), 3468–3478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2011.08.010.
Waller, N. G. (2004). The fallacy of the null hypothesis in soft psychology. Applied and Preventive Psychology,11(1), 83–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appsy.2004.02.015.
Whelan, B. M., & McBratney, A. B. (2003). Definition and interpretation of potential management zones in Australia. Paper presented at the 11th Australian Agronomy Conference: “Solutions for a better environment” Geelong, VIC, 2–5 February 2003.
Whelan, B. M., McBratney, A. B., & Minasny, B. (2001). Vesper 1.5 –spatial prediction software for precision agriculture. Paper presented at the 3rd European Conference on Precision Agriculture Montpellier, France, 18–20 June 2001.
Whelan, B. M., & Taylor, J. A. (2013). Precision agriculture for grain production systems. Collingwood, VIC, Australia: CSIRO Publishing.
Wong, M. T. F., & Asseng, S. (2006). Determining the causes of spatial and temporal variability of wheat yields at sub-field scale using a new method of upscaling a crop model. Plant and Soil,283(1–2), 203–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-006-0012-5.
Wong, M. T. F., Wittwer, K., Oliver, Y. M., & Robertson, M. J. (2010). Use of EM38 and gamma ray spectrometry as complementary sensors for high-resolution soil property mapping. In R. Viscarra-Rossel (Ed.), Proximal soil sensing (pp. 343–349). New York: Springer.
Xu, H. W., Wang, K., Bailey, J. S., Jordan, C., & Withers, A. (2006). Temporal stability of sward dry matter and nitrogen yield patterns in a temperate grassland. Pedosphere,16(6), 735–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(06)60109-4.
Ziliak, S., & McCloskey, D. N. (2008). The cult of statistical significance: How the standard error costs (4th ed.). Ann Arbour: University of Michigan Press.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Mr. Murray Hall (“Milroy”) and Mr. Adam Inchbold (“Grandview”) for allowing this study to be conducted on their properties and for their technical input. We also wish to thank Mr. Simon McDonald from Charles Sturt University Thurgoona for his statistical advice and Ms. Deanna Duffy for assistance with ArcGIS.
Funding
This work was supported by the Australian Grains Research and Development Corporation through a Grains Research Scholarship (GRDC Project No 10042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McEntee, P.J., Bennett, S.J. & Belford, R.K. Mapping the spatial and temporal stability of production in mixed farming systems: an index that integrates crop and pasture productivity to assist in the management of variability. Precision Agric 21, 77–106 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-019-09658-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-019-09658-6