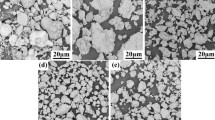
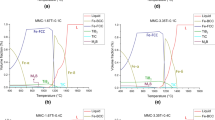
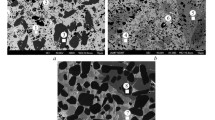
To examine the effect of molybdenum additions on the structurization of TiB2–(Fe–Mo) composite materials, differential thermal analysis of the samples with 8, 13, and 20 wt.% Mo in the metallic phase was carried out and their structure was examined after sintering. It is shown that molybdenum is an active component in the systems with 8 and 13 wt.% Mo and promotes the formation of complex Mo2FeB2 borides, which additionally strengthen the material. When the molybdenum content of the metallic phase increases to 20 wt.%, boride compounds intensively form in the system, making the composite material brittle.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. V. Samsonov and K. I. Portnoy, Alloys Based on Refractory Compounds [in Russian], Obrongiz, Moscow (1961), p. 304.
V. N. Antsiferov, L. D. Sirotenko, A. M. Khanov, and I. V. Yakovlev, Composite Materials and Structures Based on Titanium and Its Compounds [in Russian], Izd. Inst. Gidrodin. SO RAN, Novosibirsk (2001), p. 370.
G. V. Samsonov and I. M. Vinnitsky, Refractory Compounds [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1976).
Koge Ginjutsu Inte, Japanese Patent 50-13128, Method of Producing Sintered Cutting Tools from Titanium Boride [Russian translation], IPC C22C 29/00, publ. July 13 (1975).
I. Noboru, N. Katsuhiro, and I. Nori, Japanese Patent 55-145145, Titanium Boride Solid Alloy [Russian translation], IPC C22C 29/00, publ. November 12 (1980).
I. Sanse, N. Katsuhiro, and I. Nori, Japanese Patent 56-43378, Superhard Titanium Boride Alloy [Russian translation], IPC C22C 29/00, publ. October 12 (1981).
Koge Ginjutsu Inte, Japanese Patent 56-44942, Method of Producing TiB2–Cr–Ni–P Material [Russian translation], IPC C22C 29/00, publ., October 22 (1981).
S. O. Firstov, A. S. Drachinsky, and O. G. Molar, Inventor’s Certificate No. 76060, Metal Ceramic Titanium Diboride Friction Material [in Russian], C22C29/00, publ. June 15 (2006), Bull. No. 6.
R. Gonzalez, M. G. Barandika, D. Ona, et al., “New binder phases for the consolidation of TiB2 hardmetals,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A216, 185–192 (1996).
A. P. Umansky and A. D. Panasyuk, Inventor’s Certificate No. 1295771, Metal Ceramic Titanium Boride Material [in Russian], C22C29/14, publ. November 8 (1986).
A. D. Panasyuk, A. P. Umansky, V. P. Smirnov, and L. P. Isaeva, “Titanium diboride composite material with an iron–nickel binder,” in: Sintering and Hot Pressing of Materials Based on Refractory Compounds [in Russian], Inst. Probl. Materialoved. AN USSR, Kyiv (1986), pp. 75–82.
N. Wu, F. Xue, Q. Yang, et al., “Microstructure and mechanical properties of TiB2-based composites with high volume fraction of Fe-Ni additives prepared by vacuum pressureless sintering,” Ceram. Int., 43, 1394–1401 (2017).
N. V. Bangaru, N. Thirumalai, J. R. Peterson, et al., “Erosion–corrosion-resistant titanium diboride cermets for high-temperature process applications,” Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol., No. 5, 597–609 (2008).
L. Cha, S. Lartigue-Korineka, M. Walls, and L. Mazerolles, “Interface structure and chemistry in a novel steelbased composite Fe–TiB2 obtained by eutectic solidification,” Acta Mater., No. 60 (18), 6382–6389 (2012).
X. Wang, H. Shun, Ch. Li, et al, “The performances of TiB2-contained iron-based coatings at high temperature,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 201, 2500–2504 (2006).
P. Zhang, X. Wang, L. Guo, et al., “Characterization of in situ synthesized TiB2 reinforcements in ironbased composite coating,” Appl. Surf. Sci., 258, 1592–1598 (2011).
J. Lee, J. Y. Jung, E.-S. Lee, et al., “Microstructure and properties of titanium boride dispersed Cu alloys fabricated by spray forming,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A277, 274–283 (2000).
J. Dong, Y. Zhou, Y. W. Shi, and B. H. Chang, “Formation of a TiB2-reinforced copper-based composite by mechanical alloying and hot pressing,” Metall. Mater. Trans., 33A, 1275–1280 (2002).
Ch. Xiao, W. Hong-tao, J. Gang-chang, et al., “Influence of binder phase content on the microstructure and properties of HVOF-sprayed TiB2–Ni coatings,” J. Mater. Eng., No. 3, 34–40 (2014).
H. Wang, H. Li, H. Zhu, et al., “A comparative study of plasma sprayed TiB2–NiCr and Cr3C2–NiCr composite coatings,” Mater. Lett., 153, 110–113 (2015).
A. J. Horlock, D. G. McCartney, P. H. Shipway, and J. V. Wood, “Thermally sprayed Ni(Cr)–TiB2 coatings using powder produced by self-propagating high temperature synthesis: microstructure and abrasive wear behavior,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A336, 88–98 (2002).
A. P. Umansky, I. Hussainova, M. S. Storozhenko, et al., “Structure, phase composition, and wear mechanisms of plasma-sprayed NiCrSiB–20 wt.% TiB2 coatings,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 53, Nos. 11–12, 663–671 (2015).
O. Umanskyi, M. Storozhenko, I. Hussainova, et al., “Effect of TiB2 additives on wear behavior of NiCrSiB-based plasma sprayed coatings,” Mater. Sci., 22, 15–19 (2016).
A. P. Umansky, A. E. Terentiev, M. S. Storozhenko, and I. S. Martsenyuk, “Effect of fine TiB2 additions on the structure and phase composition of composite powders and coatings in the (Ni–Cr–Si–B)–TiB2 system,” in: Scientific Papers, Lutsk (2013), Issue 41, Part 2, pp. 213–221.
O. Umanskyi, O. Poliarus, M. Ukrainets, and M. Antonov, “Physical–chemical interaction in NiAI–MeB2 systems intended for tribological applications,” Weld. J., 94, 225–230 (2015).
O. Umanskyi, O. Poliarus, M. Ukrainets, and I. Martsenyuk, “Effect of ZrB2, CrB2 and TiB2 additives on the tribological characteristics of NiAl-based gas-thermal coatings,” Key Eng. Mater., 604, 20–23 (2014).
A. Hirose, M. Hasegawa, and K. F. Kobayashi, “Microstructures and mechanical properties of TiB2 particle reinforced TiAl composites by plasma arc melting process,” Mater. Sci. Eng., A239–240, 46–54 (1997).
V. N. Eremenko and Yu. V. Naidich, Wetting of Refractory Compounds with Liquid Metals [in Ukrainian], Vyd. Akad. Nauk URSR, Lviv (1958), p. 60.
A. Panasyuk and A. Umansky, “Physicochemical principles of formation of composite materials based on titanium diboride,” J. Less-Common Met., 117, 335–339 (1986).
I. M. Spiridonova, A. D. Panasyuk, E. V. Sukhovaya, and A. P. Umansky, Stability of Composite Materials [in Russian], Svidler A. L., Dnepropetrovsk (2011), p. 244.
A. P. Umansky, V. P. Konoval, A. D. Panasyuk, et al., “Plasma coatings of TiCrC–FeCr composite powder alloys: structure and properties,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 46, No. 3–4, 133–138 (2007).
V. G. Samsonov, A. D. Panasyuk, and M. S. Borovikova, “Contact relation between refractory compounds and liquid metals,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 12, No. 6, 476–480 (1973).
G. V. Samsonov, A. D. Panasyuk, G. V. Kozina, and M. S. Borovikova, “Effect of boron, carbon, molybdenum, and chromium additions on interface interaction in the refractory compound–liquid alloy systems,” in: Physical Chemistry of Melt Surfaces and Soldering [in Russian], Metsniereba, Tbilisi (1977), pp. 183–188.
A. P. Umansky, A. D. Panasyuk, N. N. Sereda, et al., “Studying the interface interaction in the (TiC–Mo2C)–(Ni-Mo) systems with microprobe analysis,” Adgez. Raspl. Paika Mater., Issue 26, 41–45 (1991).
M. S. Storozhenko, “Effect of molybdenum additions on the structurization of Fe–Mo alloys and contact interaction in the TiB2–(Fe–Mo) systems,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 55, No. 9–10, 617–624 (2017).
A. P. Umansky, M. S. Storozhenko, and V. V. Akopyan, “Studying the contact interaction of TiB2 with Fe–Mo alloys,” Adgez. Raspl. Paika Mater., Issue 44, 38–45 (2011).
A. Panasyuk, O. Umanskyi, M. Storozhenko, and V. Akopyan, “Development of TiB2-based cermets with Fe–Mo binder,” Key Eng. Mater., 527, 9–13 (2013).
E. I. Gladyshevsky, T. F. Fedorov, Yu. B. Kuzma, and Z. V. Skolozdra, “Isothermal section of the molybdenum–iron–boron system,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 5, No. 4, 305–309 (1966).
K. Takagi, “Development and application of high strength ternary boride base cermets,” J. Solid State Chem., No. 9, 2809–2818 (2006).
O. A. Bannykh, N. P. Lyakishev, and L. L. Rokhlin, Phase Diagrams of Binary Metallic Systems: Handbook [in Russian], in 3 Vols., Mashinostroenie, Moscow (1996), Vol. 2, p. 992.
V. V. Chernienko, V. A. Grametski, and E. G. Pavlyshko, “Multilayer bulk boriding of iron-based composite materials,” Tr. Odess. Politekh. Univ., No. 1 (21), 1–3 (2004).
H. Yu, W. Liu, and Y. Zheng, “Effect of carbon content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mo2FeB2 based cermets,” Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., No. 29, 724–728 (2011).
H. Yu, W. Liu, and Y. Zheng, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of liquid phase sintered Mo2FeB2 based cermets,” Mater. Des., No. 6, 3521–3525 (2011).
Q. F. Wang, Y. J. Pan, B. Hu, and L. Zhou, “Effects of alloys on microstructure and properties of Mo2FeB2-based cermets,” Adv. Mater. Res., 399–401, 399–402 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Poroshkova Metallurgiya, Vol. 57, Nos. 3–4 (520), pp. 96–107, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Storozhenko, M.S., Umanskyi, O.P., Stelmach, O.U. et al. Effect of Molybdenum Additions on the Structure of TiB2–(Fe–Mo) Composite Materials. Powder Metall Met Ceram 57, 200–208 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-018-9969-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-018-9969-x