Abstract
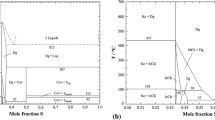
Thermodynamic evaluation of the Cu-Ni system within the CALPHAD approach is based on values of mixing enthalpies and activities of components in liquid and solid solutions, as well as parameters of phase transformations. The excess Gibbs free energy of phases is described by the following equations: ΔGL, ex = xNi(1 − xNi)(14259 + 0.45T) J/mole for liquid alloy and ΔG(Cu, Ni), ex = xNi(1 − xNi) × × (6877.12 + 4.6T + (1–2xNi)(−2450.1 + 1.87T)) J/mole for fcc solution. For the Gibbs free energy of the (Cu, Ni) phase, the magnetic effect is described by the Hillert-Jarl method. The thermodynamic model of the system generates a self-consistent description of all thermodynamic values and phase equilibria. The calculated binodale of fcc solid solution is in satisfactory agreement with experimental data. The critical point have coordinates 605 K and xNi = 0.6.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Hansen and K. Anderko, Constitution of Binary Alloys, McGraw Hill, New York (1958).
B. D. Bastow and D. H. Kirkwood, “Solid/liquid equilibrium in the Copper-Nickel-Tin system determined by microprobe analysis,” J. Inst. Metals, 99, No. 9, 277–283 (1971).
E. A. Feest and R. D. Doherty, “The Cu-Ni equilibrium phase diagram,” J. Inst. Metals, No. 3, 102–103.
B. Predel and R. Mohs, “Thermodynamische Untersuchung flussiger Nickel-Kupfer Legierungen,” Arch Eisenhut, 42, No. 8, 575–579 (1971).
E. Schurmann and E. Schultz, “Untersuchengen zum Verlauf der Liquidus und Solidus linien in den Systemen Kupfer-Mangan und Kupfer-Nickel,” Z. Metallkd., 62, No. 10, 758–762 (1971).
F. A. Shunk (ed.), Constitution of Binary Alloys, McGraw-Hill, New York (1969).
D. J. Chakrabarti, D. E. Laughlin, S. W. Chen, et al., “Cu-Ni (copper-nickel),” in: Phase Diagrams of Binary Copper Alloys, ASM International, Ohio, OH (1994), pp. 276–286.
B. Mozer, D. T. Keating, and S. C. Moss, “Neutron measurement of clustering in the alloy CuNi [copper-nickel],” Physical Review, 175, No. 3, 868–876 (1968).
M. F. Ebel, “X-ray measurements on spinodal decomposition in copper-nickel alloys,” Physica Status Solidi A, 5, No. 1, 91–94 (1971).
J. Vrijen and Radelaar, “Clustering in copper-nickel alloys: a diffuse neutron-scattering studyd,” Physical Review B, 17, No. 2, 409–421 (1978).
W. Wagner, R. Poerschke, A. Axmann, et al., “Neutron-scattering studies on an electron-irradiated (nickel-62)-41.4 at.% (copper-65) alloy,” Physical Review B, 21, No. 8, 3087–3099 (1980).
T. Tsakalakos, “Spinodal decomposition in copper-nickel alloys by artificial composition modulation technique,” Scripta Metallurgica, 15, No. 3, 255–258 (1981).
R. E. Pawel and E. E. Stansbury, “The specific heat copper, nickel and copper-nickel alloys,” J. Phys. Chem. Sol., 26, No. 3, 607–613 (1965).
M. G. Benz and J. F. Elliott, High Temperature Heats of Mixing for the Liquid Copper-Tin System and the Liquid Copper-Nickel System, U.S. At. Energy Comm., NYO-4691, 1963, p. 36.
R. N. Dokken and J. F. Elliott, “Calorimetry at 1100°C to 1200°C: The copper-nickel, copper-silver, copper-cobalt systems,” Trans. Metal. Soc. AIME, 233, 1351–1358 (1965).
Abu El Hasan, Abdelazis, and A. A. Vertman, “Thermal chemistry of iron-and nickel-based melts,” Izv. AN SSSR. Metally, No. 3, 19–30 (1966).
Y. Tozaki, Y. Iguchi, Ban-ya-Shiro, et al., “Heat of mixing of iron alloys,” in: Int. Symp. Met. Chemistry: Appl. errous Met. (July 19–21, 1971), Shaffield (1971), pp. 130–132.
Y. Iguchi, Y. Tozaki, M. Kakizaki, et al., “Calorimetric examination of mixing heats of nickel and cobalt alloys,” J. Iron and Steel Inst. Jap., 63, 953–961 (1977).
S. Sato and O. J. Kleppa, “Enthalpies of formation of borides of iron, cobalt and nickel by solution calorimetry in liquid copper,” Metal. Trans., B13, 251–257 (1982).
U. K. Stolz, I. Arpshofen, F. Sommer, et al., “Determination of the enthalpy of mixing of liquid alloys using a high-temperature mixing calorimeter,” J. Phase Equilibria, 14, No. 4, 473–478 (1993).
M. A. Turchanin, S. V. Porokhnya, L. V. Belevtsov, et al., “Thermodynamic properties of liquid copper-nickel alloys,” Rasplavy, No. 4, 8–12 (1994).
H. O. Samson-Himmelstjerna, “Heat content and heat of formation of molten alloys,” Z. Metallkd., 28, No. 7, 197–202 (1936).
C. W. Schultz, G. R. Zellars, S. L. Payne, et al., “Activities of copper and nickel in liquid copper-nickel alloys,” Bureau of Mines Report of Investigations, 6410, No. 4, 9 (1964).
A. D. Kulkarni and R. E. Johnson, “Thermodynamic studies of liquid copper alloys by electromotive force method. II. Copper-nickel-oxygen and copper-nickel systems,” Metal. Trans., 4, No. 7, 1723–1727 (1973).
V. V. Berezutskii and G. M. Lukashenko, “Thermodynamic properties of liquid nickel-copper alloys,” Ukr. Khim. Zh., No. 10, 1029–1032 (1987).
J. Tomiska and A. Neckel, “Knudsen-cell mass spectrometry for the determination of the thermodynamic properties of liquid copper-nickel alloys,” Int. J. Mass Spectrometry and Ion Physic, 47, 223–226 (1983).
O. Kubaschewski, W. A. Dench, and V. A. Genta, “A High temperature calorimeter for slow reactions,” in: The Physical Chemistry of Metallic Solutions and Intermetallic Compounds, Vol. 1, His Majesty’s Stationery Office, London (1958), pp. 1–8.
J. S. L. Leach and M. B. Bever, “On the heats of formation of copper-nickel alloys,” Trans. Met. Soc. AIME, 215, No. 4, 728–729 (1959 (1960)).
R. J. Oriani and U. K. Murphy, “Heats of formation of solid nickel-copper and nickel-gold alloys,” Acta Met., 8, 23–25 (1960).
L. Elford, F. Muller, and O. Kubaschewski, “Thermodynamic properties of copper-nickel alloys,” Ber. Bunsengesellschaft, 73, 601–605 (1968).
A. A. Vecher and Ya. I. Gerasimov, “Studying the thermodynamic properties of binary metal systems with the emf method. VIII. Solid copper-nickel solutions,” Zh. Fiz. Khim., 37, No. 3, 490–498 (1963).
R. A. Rapp and F. Maak, “Thermodynamic properties of solid copper-nickel alloys,” Acta Metallurgica, 10, No. 1, 63–69 (1962).
A. Kontopoulos, “Thermodynamic activities in copper-nickel-iron solid solutions,” Praktika tes Akademias Athenon, 52, No. A-D, B607–B619 (1978).
J. C. Gachon, M. Notin, C. Cunat, et al., “Enthalpy of formation and excess entropy for dulite copper-based alloys: experimental and theoretical study,” Acta Metallurgica, 28, 489–497 (1980).
Z. Moser, W. Zakulski, P. Spencer, et al., “Thermodynamic investigations of solid Cu-Ni and Fe-Ni alloys and calculation of the solid state miscibility gap in the Cu-Fe-Ni system,” CALPHAD, 9, No. 3, 257–269 (1985).
Ya. I. Gerasimov, A. A. Vecher, and V. A. Geiderikh, “Thermodynamic properties of solid copper-nickel and iron-cobalt solutions,” Dokl. AN SSSR, 122, 834–836 (1958).
I. Katayama, H. Shimatani, and Z. Kozuka, “Thermodynamic study of solid Cu-Ni and Ni-Mo alloys by E.M.F. measurements using solid electrolyte,” J. Jap. Inst. Met., 37, No. 5, 509–515 (1973).
L. Kaufman, “Coupled phase diagrams and thermochemical data for transition metal binary systems. III,” CALPHAD, 2, No. 2, 117–146 (1978).
R. C. Sharma, “Thermodynamic Analysis of Cu-Ni System,” Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 35, 372–375 (1982).
A. A. Jansson, Thermodynamic Evaluation of the Cu-Fe-Ni System, Trita-mac 0340, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm (1987), pp. 1–10.
G. Inden, “Determination of chemical and magnetic interchange energies in bcc alloys. III. Application to ferromagnetic alloys,” Z. Metallkd., 68, 529–534 (1977).
M. Hillert and M. Jarl, “A model for alloying effects in ferromagnetic metals,” CALPHAD, 2, 227–238 (1978).
J.-O. Andersson, T. Helander, L. Hoglund. et al., “Thermo-Calc & DICTRA, computational tools for materials science,” CALPHAD, 26, No. 2, 273–313 (2003).
A. T. Dinsdale, “SGTE data for pure elements,” CALPHAD, 15, 317–425 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
__________
Translated from Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, Vol. 46, No. 9–10 (457), pp. 65–77, 2007.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turchanin, M.A., Agraval, P.G. & Abdulov, A.R. Phase equilibria and thermodynamics of binary copper systems with 3d-metals. VI. Copper-nickel system. Powder Metall Met Ceram 46, 467–477 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-007-0073-x
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-007-0073-x