Abstract
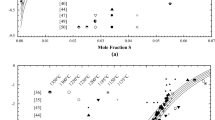
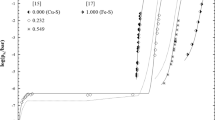
All phase equilibria and thermodynamic data available in the literature on the copper sulfides high- and low-temperature chalcocite, djurleite and anilite have been critically analyzed for optimization of the solid-state phase diagram of the Cu-S system at 1 bar total pressure. A two-sublattice approach derived from a recently developed Gibbs energy model for digenite enables the consideration of the solid solution nature of both modifications of chalcocite and for the first time of djurleite. Anilite is considered as stoichiometric compound. The sulfur solubility of metallic copper is described by a substitutional approach. The obtained Gibbs energy functions for high- and low-temperature chalcocite, djurleite, anilite and copper alloy phase allow computations and predictions of phase equilibria and thermodynamic properties in good accordance with experimental data of the Cu-S solid-state system.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.J. Chakrabarti and D.E. Laughlin, The Cu-S (Copper–Sulfur) System, Phase Diagrams of Binary Copper Alloys, P.R. Subramanian, Ed., ASM International, Materials Park, 1994, p 355–371
H. Rau, Defect Equilibria in Cubic High Temperature Cu-Sulfide (Digenite), J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 1967, 28(6), p 903–916
H. Rau, Homogeneity Range of Cubic High Temperature Cuprous Sulfide (Digenite), J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 1974, 35(10), p 1415–1424
N. Nagamori, A Thermodynamic Study of Digenite Solid Solution (Cu2-δS) at 600 to 1000 °C and a Statistical Thermodynamic Critique on General Nonstochiometry, Metall. Trans. B, 1976, 7B(1), p 67–80
R.C. Sharma and Y.A. Chang, A Thermodynamic Analysis of Cu-S System, Metall. Trans., 1980, 11B(4), p 575–583
A.T. Dinsdale, T.G. Chart, T.I. Barry, and J.R. Taylor, Phase Equilibria and Thermodynamic Data for the Cu-S System, High Temp. High Press., 1982, 14(6), p 633–640
B.J. Lee, B. Sundman, S.Il. Kim, and K.G. Chin, Thermodynamic Calculation on the Stability of Cu2S in Low Carbon Steels, ISIJ Int., 2007, 47(1), p 163–171
P. Waldner and W. Sitte, Digenite Cu2-xS: Thermodynamic Analysis of Sulfur Activities, Chem. Mon., 2012, 143(9), p 1215–1218
D. Shishin and S.A. Decterov, Critical Assessment and Thermodynamic Modeling of the Cu-O and Cu-O-S Systems, CALPHAD, 2012, 38, p 59–70
T. Jantzen, K. Hack, E. Yazhenskikh, and M. Mueller, Evaluation of Thermodynamic Data and Phase Equilibria in the System Ca-Cr-Cu-Fe-Mg-Mn-S Part I: Binary and Quasi-Binary Subsystems, CALPHAD, 2017, 56, p 270–285
P. Waldner, Gibbs Energy Modeling of Digenite and Adjacent Solid-State Phases, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2017, 48B(4), p 2157–2166
J.S. Smart and A.A. Smith, Effect of P, As, S and Se on Some Properties of High Purity Cu, Trans. AIME, 1946, 166, p 144–155
W. Ruehl and E. Saur, Röntgenographische Untersuchung zum Zustandsdiagramm des Systems Cu2S-CuS (X-ray Study on the Phase Diagram of the Cu2S-CuS System), Ber.Oberhess. Ges. Natur- u. Heilk Gießen, Naturw. Abt, 1957, 28, p 35–47, in German
J. Oudar, Étude de la solubilité du soufre dans le cuivre aux températures élevées, C. R., 1959, 249(2), p 259–261, in French
V. Wehefritz, Untersuchungen am System Kupfer–Schwefel (Study on the Copper–Sulfur System), Z. Phys. Chem. NF, 1960, 26(5–6), p 339–358, in German
E.H. Roseboom, An Investigation of the Cu-S System and some Natural Copper Sulfides between 25 and 700 °C, Econ. Geol., 1966, 61(4), p 641–672
W.R.Cook, The Copper–Sulfur Phase Diagram, Ph.D. Thesis, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland OH, 1971
H.J. Mathieu and H. Rickert, Elektrochemische-thermodynamische Untersuchungen am System Kupfer–Schwefel bei Temperaturen T = 15–90°C (Electrochemical–Thermodynamic Investigation of the Cu-S System at Temperatures between 15 and 90°C), Z. Phys. Chem. N.F., 1972, 79(5–6), p 315–330, in German
H. Luquet, F. Guastavino, J. Bougnot, and J.C. Vaissiere, Étude Du Système Cu-S Dans le Domaine Cu1.78S-Cu2.1S par Analyse Thermique Differentielle, Mater. Res. Bull., 1972, 7(9), p 955–962, in French
A. Dumon, A. Lichanot, and S. Gromb, Étude Du Diagramme des Phases Du Système Cu-S Dans L’Intervalle de Compoition Cu2,000S-Cu1,960S, J. Chim. Phys., 1974, 71(3), p 407–414, in French
J.C. Vaissière, F.M. Roche, and J. Bougnot, Contribution a l’Etude Du Diagramme de Phase Du System CuxS (1.75 ≤ x ≤ 2) Entre 10 °C and 200 °C, Mater. Res. Bull., 1976, 11(7), p 851–856, in French
R.W. Potter, II, An Electrochemical Investigation of the System Cu-S, Econ. Geol., 1977, 72(8), p 1524–1542
M.J. Ferrante, J.M. Stuve, and L.B. Pankratz, Thermodynamic Properties of Cuprous and Cupric Sulfides, High Temp. Science, 1981, 14(2), p 77–90
F. Grønvold and E.F. Westrum, Jr., Thermodynamics of Copper Sulfides I. Heat Capacity and Thermodynamic Properties of Copper(I) Sulfide, Cu2S, from 5 to 950 K, J. Chem. Thermodyn., 1987, 19(11), p 1183–1198
F. Grønvold, S. Stølen, E.F. Westrum, Jr., and C.G. Galeas, Thermodynamics of Copper Sulfides III. Heat Capacities and Thermodynamic Properties of Cu1.75S, Cu1.80S, and Cu1.85S from 5 to about 700 K, J. Chem. Thermodyn., 1987, 19(2), p 1305–1324
L. Cemič and O.J. Kleppa, High Temperature Calorimetry of Sulfide Systems III. Standard Enthalpies of Formation of Phases in the Systems Fe-Cu-S and Co-S, Phys. Chem. Miner., 1988, 16(2), p 172–179
S. Stølen, F. Grønvold, and E.F. Westrum, Jr., Thermodynamics of Copper Sulfides IV. Heat Capacity and Thermodynamic Properties of Cu1.90S from 5 K 750 K, Cu1.95S from 5 K to 1000 K, Cu1.98S from 300 K to 1000 K, and Cu1.995S from 300 K to 750 K, J. Chem. Thermodyn., 1990, 22(1), p 1035–1057
J.A. Schmidt, A.E. Sagua, and G. Lescano, Electrochemical Investigation of the Equilibria (Covelitte + Anilite) and (Covellite + Digenite), J. Chem. Thermodyn., 1998, 30(3), p 283–290
C.W. Bale, E. Belisle, P. Chartrand, S.A. Degterov, G. Eriksson, K. Hack, I.-H. Jung, Y.-B. Kang, J. Melançon, A.D. Pelton, C. Robelin, and S. Petersen, FactSage Thermochemical Software and Databases, CALPHAD, 2009, 33(2), p 295–311
M.J. Buerger and B.J. Wuensch, Distribution of Atoms in High Chalcocite, Cu2S, Science, 1963, 141(3577), p 276–277
H.T. Evans, Jr., Copper Coordination in Low Chalcocite and Djurlite and other Copper-Rich Sulfides, Am. Mineral., 1981, 66(7–8), p 807–818
M. Hillert and L.I. Staffanson, Regular Solution Model for Stoichiometric Phases and Ionic Melts, Acta Chem. Scand., 1970, 24(10), p 3618–3626
B. Sundman and J. Ågren, A Regular Solution Model for Phases with Several Components and Sublattices, Suitable for Computer Applications, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 1981, 42(4), p 297–301
P. Waldner and A.D. Pelton, Thermodynamic Modeling of the Ni-S System, Z. Metallk., 2004, 95(8), p 672–681
P. Waldner and A.D. Pelton, Thermodynamic Modeling of the Fe-S System, J. Phase Equilibria Diffus., 2005, 26(1), p 23–38
A.T. Dinsdale, SGTE Data for Pure Elements, CALPHAD, 1991, 15(4), p 317–425
M.W. Chase, Jr., C.A. Davies, J.R. Downey, Jr., D.J. Frurip, R.A. McDonald, and A.N. Syverud, JANAF Thermochemical Tables, 3rd ed., Supplement No. 1, J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 1985, 14, p 1774–1777
K.C. Mills, Thermodynamic Data for Sulphides, Selenides and Tellurides, NPL, Teddington, 1974, p 244–251
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waldner, P. Solid-State Phase Equilibria of the Cu-S System: Thermodynamic Modeling. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 39, 810–819 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-018-0670-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-018-0670-z