Abstract
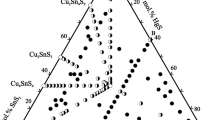
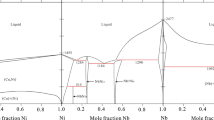
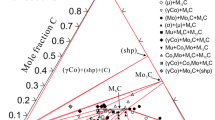
The Co-Cu-Sn ternary system has been modeled based on reported phase equilibrium data in the literature using the CALPHAD (CALculation of PHAse Diagrams) method. The excess Gibbs energies of solution phases, including liquid, Bcc, Fcc and Hcp, are expressed by the Redlich-Kister polynomial. The two-sublattice model (Co,Cu)m(Sn)n is used to describe the solid solution of binary intermetallic compounds, i.e. CoSn3, CoSn2 Cu3Sn and βCu6Sn5 in the Co-Cu-Sn ternary system. Co3Sn2 was described using the four-sublattice model (Co,Cu,Sn)1(Cu,Sn)1(Co,Va)0.5(Co,Va)0.5. The ternary stoichiometric compound Co2Cu8Sn3 is modeled by the stoichiometric model, Co2Cu7.5Sn3. Finally, a set of self-consistent parameters which can describe the thermodynamics of the Co-Cu-Sn ternary system was obtained. Based on the calculated thermodynamic parameters, the liquidus projection and reaction scheme are also derived in the present work.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.S. Węglowski, S. Błacha, and A. Phillips, Electron Beam Welding – Techniques and Trends – Review, Vacuum, 2016, 130, p 72–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2016.05.004
H. Kuroki, K. Nezaki, T. Wakabayashi, and K. Nakamura, Application of Linear Friction Welding Technique to Aircraft Engine Parts, IHI Engineering Reviews, 2014, 47, p 40–43.
A. Anand, and A. Khajuria, Welding Processes in Marine Application: A Review, International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Robotics Research, 2015, 2(1), p 215–225.
H.R. Kotadia, P.D. Howes, and S.H. Mannan, A Review: On the Development of Low Melting Temperature Pb-Free Solders, Microelectron. Reliab., 2014, 54(6–7), p 1253–1273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2014.02.025
S.F. Cheng, C.M. Huang, and M. Pecht, A Review of Lead-Free Solders for Electronics Applications, Microelectron. Reliab., 2017, 75, p 77–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2017.06.016
N.C. Lee, Getting Ready for Lead-Free Solders, Soldering and Surface Mount Technol, 1997, 9(2), p 65–69. https://doi.org/10.1108/09540919710800656
P. Sun, C. Andersson, X. Wei, Z. Cheng, Z. Lai, D. Shangguan, J. Liu. High temperature aging study of intermetallic compound formation of Sn-3.5Ag and Sn-4.0Ag-0.5Cu solders on electroless Ni (P) metallization; proceedings of the 56th Electronic Components and Technology Conference 2006, F, (2006). IEEE. https://doi/org/https://doi.org/10.1109/ECTC.2006.1645850
N. Dariavach, P. Callahan, J. Liang, and R. Fournelle, Intermetallic Growth Kinetics for Sn-Ag, Sn-Cu, and Sn-Ag-Cu Lead-Free Solders on Cu, Ni, and Fe-42Ni Substrates, J. Electron. Mater., 2006, 35(7), p 1581–1592. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-006-0152-7
F. Cheng, H. Nishikawa, and T. Takemoto, Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Sn–Ag–Cu Lead-Free Solders with Minor Addition of Ni and/or Co, J. Mater. Sci., 2008, 43, p 3643–3648. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2580-7
I.E. Anderson, B.A. Cook, J. Harringa, and R.L. Terpstra, Microstructural Modifications and Properties of Sn-Ag-Cu Solder Joints Induced by Alloying, J. Electron. Mater., 2002, 31(11), p 1166–1174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-002-0006-x
Z.L. Ma, S.A. Belyakov, and C.M. Gourlay, Effects of Cobalt on the Nucleation and Grain Refinement of Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu Solders, J. Alloys and Compound., 2016, 682, p 326–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.04.265
M.G.M. Miranda, E. Estévez-Rams, G. Martinez, and M.N. Baibich, Phase Separation in Cu90Co10 High-Magnetoresistance Materials, Phys. Rev. B, 2003, 68, p 1014434. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.68.014434
T. Nishizawa, and K. Ishida, The Co−Cu (Cobalt-Copper) System, Bull. Alloy Phase Diagram., 1984, 5(2), p 161–165.
S. Curiotto, L. Battezzati, E. Johnson, and N. Pryds, Thermodynamics and Mechanism of Demixing in Undercooled Cu–Co–Ni Alloys, Acta Mater., 2007, 55(19), p 6642–6650.
Z.-K. Liu, Computational Thermodynamics and its Applications, Acta Mater., 2020, 200, p 745–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.008
Y.K. Chen, C.M. Hsu, S.W. Chen, C.M. Chen, and Y.C. Huang, Phase Equilibria of Sn-Co-Cu Ternary System, Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 2012, 43(10), p 3586–3595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1192-7
J.M. Liu, W. Zhai, K. Zhou, D.L. Geng, and B.B. Wei, Thermophysical Properties and Liquid-Solid Transition Mechanisms of Ternary (Co0.5Cu0. 5)(100–x) Snx Alloys, Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65, p 22–228101. https://doi.org/10.7498/aps.65.228101
M. Palumbo, S. Curiotto, and L. Battezzati, Thermodynamic Analysis of the Stable and Metastable Co-Cu and Co-Cu-Fe Phase Diagrams, Calphad, 2006, 30(2), p 171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.calphad.2005.10.007
H.Q. Dong, S. Jin, L.G. Zhang, J.S. Wang, X.M. Tao, H.S. Liu, and Z.P. Jin, Thermodynamic Assessment of the Au-Co-Sn Ternary System, J. Electron. Mater., 2009, 38(10), p 2158–2169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-009-0874-4
M. Jiang, J. Sato, I. Ohnuma, R. Kainuma, and K. Ishida, A Thermodynamic Assessment of the Co-Sn System, Calphad, 2004, 28(2), p 213–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.calphad.2004.08.001
J.H. Shim, C.S. Oh, B.J. Lee, and D.N. Lee, Thermodynamic Assessment of the Cu-Sn System, Int. J. Mater. Res., 1996, 87(3), p 205–212. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijmr-1996-870310
J.A. Wang, C.L. Liu, C. Leinenbach, U.E. Klotz, P.J. Uggowitzer, and J.F. Loffler, Experimental Investigation and Thermodynamic Assessment of the Cu-Sn-Ti Ternary System, Calphad, 2011, 35(1), p 82–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.calphad.2010.12.006
E.A. Owen, and D.M. Jones, Effect of Grain Size on the Crystal Structure of Cobalt, Proceed. Phys. Soc. Sect. B, 1954, 67, p 456–466. https://doi.org/10.1088/0370-1301/67/6/302
H.W. King, Crystal Structures of the Elements at 25° C, Bulletin of alloy phase diagrams, 1981, 2(3), p 401–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02868307
H. Fjellvág, and A. Kjekshus, Structural Properties of Co3Sn2, Ni3Sn2 and Some Ternary Derivatives. Acta Chemica Scandinavica, Series A: Phys. Inorgan. Chem., 1986, 40, p 23–30.
A.K. Larsson, M. Haeberlein, S. Lidin, and U. Schwarz, Single Crystal Structure Refinement and High-Pressure Properties of CoSn, J. Alloy. Compd., 1996, 240(1–2), p 79–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/0925-8388(95)02189-2
M. Armbrüster, M. Schmidt, R. Cardoso-Gil, H. Borrmann, and Y. Grin, Crystal Structures of Iron Distannide, FeSn2, and Cobalt Distannide, CoSn2, Zeitschrift für Kristallographie-New Crystal Structures, 2007, 222(2), p 83–84. https://doi.org/10.1524/ncrs.2007.0033
A. Lang, and W. Jeitschko, Two New Phases in the System Cobalt-tin: the Crystal Structures of α-and β-CoSn3, Z. Metallkd., 1996, 87(10), p 759–764.
J.K. Brandon, W.B. Pearson, and D.J.N. Tozer, A Single-Crystal X-ray Diffraction Study of the ζ bronze Structure, Cu20Sn6, Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B: Struct. Crystallogr. Cryst. Chem., 1975, 31(3), p 774–779. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0567740875003780
M.H. Booth, J.K. Brandon, R.Y. Brizard, C.T. Chieh, and W.B. Pearson, γ-Brasses with F cells, Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B: Struct. Crystallogr. Cryst. Chem., 1977, 33(1), p 30–36. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0567740877002556
S. Fürtauer, D. Li, D. Cupid, and H. Flandorfer, The Cu–Sn Phase Diagram, Part I: New Experimental Results, Intermetallics, 2013, 34, p 142–147.
Y. Watanabe, Y. Fujinaga, and H. Iwasaki, Lattice Modulation in the Long-Period Superstructure of Cu3Sn, Acta Crystallogr. B, 1983, 39(3), p 306–311. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0108768183002451
S. Lidin, and A.-K. Larsson, A Survey of Superstructures in Intermetallic NiAs-Ni2In-type Phases, J. Solid State Chem., 1995, 118(2), p 313–322. https://doi.org/10.1006/jssc.1995.1350
A. Gangulee, G.C. Das, and M.B. Bever, An X-ray Diffraction and Calorimetric Investigation of the Compound Cu6Sn5, Metallurgical Trans., 1973, 4(9), p 2063–2066.
L. Kaufman, Coupled Phase Diagrams and Thermochemical Data for Transition Metal Binary Systems-III, Calphad, 1978, 2(2), p 117–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/0364-5916(78)90031-7
M. Hasebe, and T. Nishizawa, Calculation of Phase Diagrams of the Iron-Copper and Cobalt-Copper Systems, Calphad, 1980, 4(2), p 83–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/0364-5916(80)90026-7
J. Kubišta, and J. Vřešt’ál, Thermodynamics of the Liquid Co-Cu System and Calculation of Phase Diagram, J. Phase Equilibria, 2000, 21(2), p 125–129. https://doi.org/10.1361/105497100770340165
M.A. Turchanin, and P.G. Agraval, Phase Equilibria and Thermodynamics of Binary Copper Systems with 3d-Metals v. Copper-Cobalt System, Powder Metallurgy and Metal Ceram., 2007, 46(1–2), p 77–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-007-0013-9
M.A. Turchanin, L.A. Dreval, A.R. Abdulov, and P.G. Agraval, Mixing Enthalpies of Liquid Alloys and Thermodynamic Assessment of the Cu-Fe-Co System, Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 2011, 50(1–2), p 98–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-011-9307-z
Y. Yu, X.J. Liu, Z.P. Jiang, C.P. Wang, R. Kainuma, and K. Ishida, Thermodynamics and Liquid Phase Separation in the Cu–Co–Nb Ternary Alloys, J. Mater. Res., 2011, 25(9), p 1706–1717. https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2010.0223
A.T. Dinsdale, SGTE Data for Pure Elements, Calphad, 1991, 15(4), p 317–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/0364-5916(91)90030-N
O. Redlich, and A. Kister, Algebraic Representation of Thermodynamic Properties and the Classification of Solutions, Ind. Eng. Chem., 1948, 40(2), p 345–348.
L.B. Liu, C. Andersson, and J. Liu, Thermodynamic Assessment of the Sn-Co Lead-Free Solder System, J. Electron. Mater., 2004, 33(9), p 935–939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-004-0019-8
G.P. Vassilev, and K.I. Lilova, Contribution to the Thermodynamics of the Co-Sn System, Arch. Metall. Mater., 2006, 51(3), p 365–375.
V. Jedličková, A. Zemanová, and A. Kroupa, The Thermodynamic Assessment of the Co-Sn System, J. Phase Equilib. Diffus., 2019, 40(1), p 21–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-018-0687-3
K.W. Moon, W.J. Boettinger, U.R. Kattner, F.S. Biancaniello, and C.A. Handwerker, Experimental and Thermodynamic Assessment of Sn-Ag-Cu Solder Alloys, J. Electron. Mater., 2000, 29(10), p 1122–1136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-000-0003-x
J. Miettinen, Thermodynamic Description of the Cu-Al-Sn System in the Copper-Rich Corner, Metall. and Mater. Trans. A., 2002, 33(6), p 1639–1648. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-002-0173-7
X.J. Liu, C.P. Wang, I. Ohnuma, R. Kainuma, and K. Ishida, Experimental Investigation and Thermodynamic Calculation of the Phase Equilibria in the Cu-Sn and Cu-Sn-Mn Systems, Metallurgical and Mater. Trans. A, 2004, 35(6), p 1641–1654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-018-0687-3
W. Gierlotka, S.W. Chen, and S.K. Lin, Thermodynamic Description of the Cu-Sn System, J. Mater. Res., 2007, 22(11), p 3158–3165. https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2007.0396
J. Miettinen, Thermodynamic Description of the Cu-Fe-Sn System at the Cu-Fe Side, Calphad, 2008, 32(3), p 500–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.calphad.2008.06.003
M. Li, Z.M. Du, C.P. Guo, and C.R. Li, Thermodynamic Optimization of the Cu-Sn and Cu-Nb-Sn Systems, J. Alloy. Compd., 2009, 477(1–2), p 104–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.09.141
D. Li, P. Franke, S. Furtauer, D. Cupid, and H. Flandorfer, The Cu-Sn Phase Diagram part II: New Thermodynamic Assessment, Intermetallics, 2013, 34, p 148–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2012.10.010
H.Q. Dong, V. Vuorinen, X.M. Tao, T. Laurila, and M. Paulasto-Krockel, Thermodynamic Reassessment of Au-Cu-Sn Ternary System, J. Alloy. Compd., 2014, 588, p 449–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.11.041
B. Sundman, H.L. Lukas, and S.G. Fries, Computational Thermodynamics: The Calphad Method. Cambridge University Press, New York, 2007.
H. Flandorfer, U. Saeed, C. Luef, A. Sabbar, and H. Ipser, Interfaces in Lead-Free Solder Alloys: Enthalpy of Formation of Binary Ag–Sn, Cu–Sn and Ni–Sn Intermetallic Compounds, Thermochim. Acta, 2007, 459(1–2), p 34–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2007.04.004
O.J. Kleppa, Heat of Formation of Solid and Liquid Binary Alloys of Copper with Cadmium, Indium, Tin and Antimony at 450°, J. Phys. Chem., 1956, 60(7), p 852–858. https://doi.org/10.1021/j150541a005
S. Ramos De Debiaggi, C. Deluque Toro, G.F. Cabeza, and A. Fernández Guillermet, Ab Initio Comparative Study of the Cu–In and Cu–Sn Intermetallic Phases in Cu–In–Sn Alloys, J. Alloys and Compounds, 2012, 542, p 280–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.06.138
A. Jain, P.S. Ong, G. Hautier, W. Chen, W.D. Richards, S. Dacek, S. Cholia, D. Gunter, D. Skinner, G. Ceder, and K. Persson, Commentary: The Materials Project: A Materials Genome Approach to Accelerating Materials Innovation, APL Mater., 2013, 1, p 1011002. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4812323
Acknowledgment
The financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52171024 and 51871186) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Materials Genome Initiative: 2017YFB0701700) are gratefully acknowledged. The authors thank the support from the High-Performance Computing Center of Central South University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, D., Wang, J. & Yan, N. Thermodynamic Modeling of the Co-Cu-Sn Ternary System. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 43, 214–228 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-022-00953-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-022-00953-w