Abstract
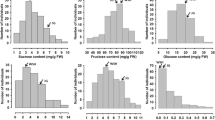
Sweetness is the most important trait for fruit breeding and is fundamentally determined by both total and individual sugar contents. We analyzed the contents of sucrose, fructose, glucose, and sorbitol in mature fruit in an F1 population derived from crossing modern Japanese pear cultivar ‘Akizuki’ and breeding line ‘373-55’. A genetic linkage map was constructed using simple sequence repeats (SSRs) and single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP). We identified two regions associated with individual sugar contents on linkage group (LG) 1 and LG 7. The percentages of the variance in sucrose, fructose, and glucose explained by the quantitative trait loci (QTLs) were 26.6, 15.9, and 18.5%, respectively, for the region on LG 1, and 22.2, 20.0, and 9.5%, respectively, for the region on LG 7. In both regions, genotypes associated with increases in sucrose were associated with decreases in both fructose and glucose. The 1.5-LOD support intervals of the QTLs on LGs 1 and 7 include SSRs within the regions flanking acid invertase genes PPAIV3 and PPAIV1, respectively. Because acid invertase is a key enzyme in the conversion of sucrose to hexose, these are promising candidates for genes underlying those QTLs and controlling individual sugar contents. We also found one region on LG 11 that explained 21.4% of the variation in total sugar content but was not significantly associated with variation for individual sugars. The information obtained in this study will accelerate research and breeding programs to improve fruit sweetness.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Byrne DH, Nikolic AN, Burns EE (1991) Variability in sugars, acids, firmness, and color characteristics of 12 peach genotypes. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 116:1004–1006
Celton JM, Tustin DS, Chagne D, Gardiner SE (2009) Construction of a dense genetic linkage map for apple rootstocks using SSRs developed from Malus ESTs and Pyrus genomic sequences. Tree Genet Genomes 5:93–107
Chen H, Song Y, Li L-T, Khan MA, Li X-G, Korban SS, Wu J, Zhang S-L (2015a) Construction of a high-density simple sequence repeat consensus genetic map for pear (Pyrus spp.). Plant Mol Biol Report 33:316–325
Chen J, Wang N, Fang LC, Liang ZC, Li SH, Wu BH (2015b) Construction of a high-density genetic map and QTLs mapping for sugars and acids in grape berries. BMC Plant Biol 15:28
Cirilli M, Bassi D, Ciacciulli A (2016) Sugars in peach fruit: a breeding perspective. Hortic Res 3:15067
Daccord N, Celton JM, Linsmith G, Becker C, Choisne N, Schijlen E, van de Geest H, Bianco L, Micheletti D, Velasco R, Di Pierro EA, Gouzy J, Rees DJG, Guérif P, Muranty H, Durel CE, Laurens F, Lespinasse Y, Gaillard S, Aubourg S, Quesneville H, Weigel D, van de Weg E, Troggio M, Bucher E (2017) High-quality de novo assembly of the apple genome and methylome dynamics of early fruit development. Nat Genet 49:1099–1106
Dirlewanger E, Moing A, Rothan C, Svanella L, Pronier V, Guye A, Plomion C, Monet R (1999) Mapping QTLs controlling fruit quality in peach (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch). Theor Appl Genet 98:18–31
Dondini L, Pierantoni L, Gaiotti F, Chiodini R, Tartarini S, Bazzi C, Sansavini S (2005) Identifying QTLs for fire-blight resistance via a European pear (Pyrus communis L.) genetic linkage map. Mol Breed 14:407–418
Doty T (1976) Fructose sweetness: a new dimension. Cereal Foods World 21:62–63
Etienne C, Rothan C, Moing A, Plomion C, Bodenes C, Svanella-Dumas L, Cosson P, Pronier V, Monet R, Dirlewanger E (2002) Candidate genes and QTLs for sugar and organic acid content in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch]. Theor Appl Genet 105:145–159
Fernández-Fernández F, Harvey N, James C (2006) Isolation and characterization of polymorphic microsatellite markers from European pear (Pyrus communis L.). Mol Ecol Resour 6:1039–1041
Grattapaglia D, Sederoff R (1994) Genetic linkage maps of Eucalyptus grandis and Eucalyptus urophylla using a pseudo-testcross: mapping strategy and RAPD markers. Genetics 137:1121–1137
Guan Y, Peace C, Rudell D, Verma S, Evans K (2015) QTLs detected for individual sugars and soluble solids content in apple. Mol Breed 35:135
Guilford P, Prakash S, Zhu J, Rikkerink E, Gardiner S, Bassett H, Forster R (1997) Microsatellites in Malus x domestica (apple): abundance, polymorphism and cultivar identification. Theor Appl Genet 94:249–254
Hecke K, Herbinger K, Veberic R, Trobec M, Toplak H, Stampar F, Keppel H, Grill D (2006) Sugar-, acid- and phenol contents in apple cultivars from organic and integrated fruit cultivation. Eur J Clin Nutr 60:1136–1140
Hyun TK, Eom SH, Kim JS (2011) Genomic analysis and gene structure of the two invertase families in the domesticated apple (Malus x domestica Borkh.). Plant Omics 4:391–399
Iketani H, Yamamoto T, Katayama H, Uematsu C, Mase N, Sato Y (2010) Introgression between native and prehistorically naturalized (archaeophytic) wild pear (Pyrus spp.) populations in Northern Tohoku, Northeast Japan. Conserv Genet 11:115–126
Iketani H, Katayama H, Uematsu C, Mase N, Sato Y, Yamamoto T (2012) Genetic structure of East Asian cultivated pears (Pyrus spp.) and their reclassification in accordance with the nomenclature of cultivated plants. Plant Syst Evol 298:1689–1700
Illa E, Sargent DJ, Girona EL, Bushakra J, Cestaro A, Crowhurst R, Pindo M, Cabrera A, van der Knaap E, Iezzoni A, Gardiner S, Velasco R, Arus P, Chagne D, Troggio M (2011) Comparative analysis of rosaceous genomes and the reconstruction of a putative ancestral genome for the family. BMC Evol Biol 11
Ishimizu T, Inoue K, Shimonaka M, Saito T, Terai O, Norioka S (1999) PCR-based method for identifying the S-genotypes of Japanese pear cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 98:961–967
Iwata H, Hayashi T, Terakami S, Takada N, Sawamura Y, Yamamoto T (2013) Potential assessment of genome-wide association study and genomic selection in Japanese pear Pyrus pyrifolia. Breed Sci 63:125–140
Jung S, Cestaro A, Troggio M, Main D, Zheng P, Cho I, Folta KM, Sosinski B, Abbott A, Celton J-M (2012) Whole genome comparisons of Fragaria, Prunus and Malus reveal different modes of evolution between Rosaceous subfamilies. BMC Genomics 13:129
Kajiura I, Suzuki K, Yamazaki T (1975) Color chart for Japanese pear (Pyrus serotina var. culta Rehder). HortScience 10:257–258
Kajiura I, Yamaki S, Omura M, Akihama T, Machida Y (1979) Improvement of sugar content and composition in fruits, and classifications of East Asian pears by the principal component analysis of sugar compositions in fruits. Jpn J Breed 29:1–12
Kanayama Y (2017) Sugar metabolism and fruit development in the tomato. Hortic J 86:417–425
Katayama H, Adachi S, Yamamoto T, Uematsu C (2007) A wide range of genetic diversity in pear (Pyrus ussuriensis var. aromatica) genetic resources from Iwate, Japan revealed by SSR and chloroplast DNA markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:1573–1585
Kenis K, Keulemans J, Davey MW (2008) Identification and stability of QTLs for fruit quality traits in apple. Tree Genet Genomes 4:647–661
Kikuchi A (1948) Horticulture of fruit trees, vol 1. Yokendo, Tokyo
Kliewer WM (1966) Sugars and organic acids of Vitis vinifera. Plant Physiol 41:923–931
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugenics 12:172–175
Kotobuki K, Saito T, Machida Y, Sato Y, Abe K, Kurihara A, Ogata T, Terai O, Nishibata T, Kozono T, Fukuda H, Kihara T, Suzuki K (2002) New Japanese pear cultivar ‘Akizuki’. Bull Natl Inst Fruit Tree Sci 1:11–21 (In Japanese with English abstract)
Kunihisa M, Moriya S, Abe K, Okada K, Haji T, Hayashi T, Kim H, Nishitani C, Terakami S, Yamamoto T (2014) Identification of QTLs for fruit quality traits in Japanese apples: QTLs for early ripening are tightly related to preharvest fruit drop. Breed Sci 64:240–251
Li H (2011) A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics 27:2987–2993
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25:1754–1760
Li M, Feng F, Cheng L (2012) Expression patterns of genes involved in sugar metabolism and accumulation during apple fruit development. PLoS One 7:e33055
Liebhard R, Gianfranceschi L, Koller B, Ryder C, Tarchini R, Van de Weg E, Gessler C (2002) Development and characterisation of 140 new microsatellites in apple (Malus x domestica Borkh.). Mol Breed 10:217–241
Liebhard R, Kellerhals M, Pfammatter W, Jertmini M, Gessler C (2003) Mapping quantitative physiological traits in apple (Malus x domestica Borkh.). Plant Mol Biol 52:511–526
Martin M (2011) Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J 17:10–12
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly M, DePristo MA (2010) The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20:1297–1303
Moriguchi T, Ishizawa Y, Sanada T (1990a) Differences in sugar composition in Prunus persica fruit and the classification by the principal component analysis. J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 59:307–312
Moriguchi T, Sanada T, Yamaki S (1990b) Seasonal fluctuations of some enzymes relating to sucrose and sorbitol metabolism in peach fruit. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 115:278–281
Moriguchi T, Abe K, Sanada T, Yamaki S (1992) Levels and role of sucrose synthase, sucrose-phosphate synthase, and acid invertase in sucrose accumulation in fruit of Asian pear. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 117:274–278
Moriya S, Iwanami H, Kotoda N, Haji T, Okada K, Terakami S, Mimida N, Yamamoto T, Abe K (2012) Aligned genetic linkage maps of apple rootstock cultivar ‘JM7’ and Malus sieboldii ‘Sanashi 63’ constructed with novel EST–SSRs. Tree Genet Genomes 8:709–723
Nishio S, Hayashi T, Yamamoto T, Yamada M, Takada N, Kato H, Nishitani C, Saito T (2016a) Validation of molecular markers associated with fruit ripening day of Japanese pear (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai) using variance components. Sci Hortic 199:9–14
Nishio S, Takada N, Saito T, Yamamoto T, Iketani H (2016b) Estimation of loss of genetic diversity in modern Japanese cultivars by comparison of diverse genetic resources in Asian pear (Pyrus spp.). BMC Genet 17:81
Nishitani C, Terakami S, Sawamura Y, Takada N, Yamamoto T (2009) Development of novel EST-SSR markers derived from Japanese pear (Pyrus pyrifolia). Breed Sci 59:391–400
Okada K, Tonaka N, Moriya Y, Norioka N, Sawamura Y, Matsumoto T, Nakanishi T, Takasaki-Yasuda T (2008) Deletion of a 236 kb region around S4-RNase in a stylar-part mutant S4 sm-haplotype of Japanese pear. Plant Mol Biol 66:389–400
Ozaki K, Uchida A, Takabe T, Shinagawa F, Tanaka Y, Takabe T, Hayashi T, Hattori T, Rai AK, Takabe T (2009) Enrichment of sugar content in melon fruits by hydrogen peroxide treatment. J Plant Physiol 166:569–578
Pancoast HM, Junk WR (1980) Handbook of sugars. AVI Publishing Co., Westport, pp 387–389
Pangborn R (1963) Relative taste intensities of selected sugars and organic acids. J Food Sci 28:726–733
Quilot B, Wu BH, Kervella J, Genard M, Foulongne M, Moreau K (2004) QTL analysis of quality traits in an advanced backcross between Prunus persica cultivars and the wild relative species P. davidiana. Theor Appl Genet 109:884–897
Saito T (2016) Advances in Japanese pear breeding in Japan. Breed Sci 66:46–59
Salazar JA, Ruiz D, Campoy JA, Sánchez-Pérez R, Crisosto CH, Martínez-García PJ, Blenda A, Jung S, Main D, Martínez-Gómez P (2014) Quantitative trait loci (QTL) and Mendelian trait loci (MTL) analysis in Prunus: a breeding perspective and beyond. Plant Mol Biol Report 32:1–18
Shulaev V, Sargent DJ, Crowhurst RN, Mockler TC, Folkerts O, Delcher AL, Jaiswal P, Mockaitis K, Liston A, Mane SP (2011) The genome of woodland strawberry (Fragaria vesca). Nat Genet 43:109–116
Silfverberg-Dilworth E, Matasci C, Van de Weg W, Van Kaauwen M, Walser M, Kodde L, Soglio V, Gianfranceschi L, Durel C, Costa F (2006) Microsatellite markers spanning the apple (Malus x domestica Borkh.) genome. Tree Genet Genomes 2:202–224
Tamura F (2006) Japanese pear. In: Jpn Soc Hort Sci (ed) Horticulture in Japan 2006. Shoukadoh Publication, Kyoto, pp. 50–58
Terakami S, Shoda M, Adachi Y, Gonai T, Kasumi M, Sawamura Y, Iketani H, Kotobuki K, Patocchi A, Gessler C, Hayashi T, Yamamoto T (2006) Genetic mapping of the pear scab resistance gene Vnk of Japanese pear cultivar Kinchaku. Theor Appl Genet 113:743–752
Terakami S, Adachi Y, Iketani H, Sato Y, Sawamura Y, Takada N, Nishitani C, Yamamoto T (2007) Genetic mapping of genes for susceptibility to black spot disease in Japanese pears. Genome 50:735–741
Terakami S, Kimura T, Nishitani C, Sawamura Y, Saito T, Hirabayashi T, Yamamoto T (2009) Genetic linkage map of the Japanese pear ‘Housui’ identifying three homozygous genomic regions. J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 78:417–424
Terakami S, Nishitani C, Kunihisa M, Shirasawa K, Sato S, Tabata S, Kurita K, Kanamori H, Katayose Y, Takada N, Saito T, Yamamoto T (2014) Transcriptome-based single nucleotide polymorphism markers for genome mapping in Japanese pear (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai). Tree Genet Genomes 10:853–863
van Dyk MM, Soeker MK, Labuschagne IF, Rees DJG (2010) Identification of a major QTL for time of initial vegetative budbreak in apple (Malus x domestica Borkh.). Tree Genet Genomes 6:489–502
Van Ooijen J (2006) JoinMap 4. Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations. Kyazma BV, Wageningen
Van Ooijen J (2009) MapQTL® 6, Software for the mapping of quantitative trait in experiment populations of diploid species. Kyazma B V, Wageningen
Velasco R, Zharkikh A, Affourtit J, Dhingra A, Cestaro A, Kalyanaraman A, Fontana P, Bhatnagar SK, Troggio M, Pruss D, Salvi S, Pindo M, Baldi P, Castelletti S, Cavaiuolo M, Coppola G, Costa F, Cova V, Dal Ri A, Goremykin V, Komjanc M, Longhi S, Magnago P, Malacarne G, Malnoy M, Micheletti D, Moretto M, Perazzolli M, Si-Ammour A, Vezzulli S, Zini E, Eldredge G, Fitzgerald LM, Gutin N, Lanchbury J, Macalma T, Mitchell JT, Reid J, Wardell B, Kodira C, Chen Z, Desany B, Niazi F, Palmer M, Koepke T, Jiwan D, Schaeffer S, Krishnan V, Wu C, Chu VT, King ST, Vick J, Tao Q, Mraz A, Stormo A, Stormo K, Bogden R, Ederle D, Stella A, Vecchietti A, Kater MM, Masiero S, Lasserre P, Lespinasse Y, Allan AC, Bus V, Chagné D, Crowhurst RN, Gleave AP, Lavezzo E, Fawcett JA, Proost S, Rouzé P, Sterck L, Toppo S, Lazzari B, Hellens RP, Durel CE, Gutin A, Bumgarner RE, Gardiner SE, Skolnick M, Egholm M, Van de Peer Y, Salamini F, Viola R (2010) The genome of the domesticated apple (Malus × domestica). Nat Genet 42:833–841
Verde I, Bassil N, Scalabrin S, Gilmore B, Lawley CT, Gasic K, Micheletti D, Rosyara UR, Cattonaro F, Vendramin E, Main D, Aramini V, Blas AL, Mockler TC, Bryant DW, Wilhelm L, Troggio M, Sosinski B, Aranzana MJ, Arús P, Iezzoni A, Morgante M, Peace C (2013) The high-quality draft genome of peach (Prunus persica) identifies unique patterns of genetic diversity, domestication and genome evolution. Nat Genet 45:487–494
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78
Wu J, Gao H, Zhao L, Liao X, Chen F, Wang Z, Hu X (2007) Chemical compositional characterization of some apple cultivars. Food Chem 103:88–93
Wu J, Wang Z, Shi Z, Zhang S, Ming R, Zhu S, Khan MA, Tao S, Korban SS, Wang H, Chen NJ, Nishio T, Xu X, Cong L, Qi K, Huang X, Wang Y, Zhao X, Wu J, Deng C, Gou C, Zhou W, Yin H, Qin G, Sha Y, Tao Y, Chen H, Yang Y, Song Y, Zhan D, Wang J, Li L, Dai M, Gu C, Wang Y, Shi D, Wang X, Zhang H, Zeng L, Zheng D, Wang C, Chen M, Wang G, Xie L, Sovero V, Sha S, Huang W, Zhang S, Zhang M, Sun J, Xu L, Li Y, Liu X, Li Q, Shen J, Wang J, Paull RE, Bennetzen JL, Wang J, Zhang S (2013) The genome of the pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.). Genome Res 23:396–408
Wu J, Li LT, Li M, Khan MA, Li XG, Chen H, Yin H, Zhang SL (2014) High-density genetic linkage map construction and identification of fruit-related QTLs in pear using SNP and SSR markers. J Exp Bot 65:5771–5781
Yamaki S (2010) Metabolism and accumulation of sugars translocated to fruit and their regulation. J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 79:1–15
Yamaki S, Moriguchi T (1989) Seasonal fluctuation of sorbitol-related enzymes and invertase activities accompanying maturation of Japanese pear (Pyrus serotina Rehder var. culta Rehder) fruit. J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 57:602–607
Yamamoto T, Kimura T, Shoda M, Imai T, Saito T, Sawamura Y, Kotobuki K, Hayashi T, Matsuta N (2002) Genetic linkage maps constructed by using an interspecific cross between Japanese and European pears. Theor Appl Genet 106:9–18
Yamamoto T, Kimura T, Terakami S, Nishitani C, Sawamura Y, Saito T, Kotobuki K, Hayashi T (2007) Integrated reference genetic linkage maps of pear based on SSR and AFLP markers. Breed Sci 57:321–329
Yamamoto T, Terakami S, Takada N, Nishio S, Onoue N, Nishitani C, Kunihisa M, Inoue E, Iwata H, Hayashi T, Itai A, Saito T (2014) Identification of QTLs controlling harvest time and fruit skin color in Japanese pear (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai). Breed Sci 64:351–361
Zhang R, Wu J, Li X, Khan MA, Chen H, Korban SS, Zhang S (2013) An AFLP, SRAP, and SSR genetic linkage map and identification of QTLs for fruit traits in pear (Pyrus L.). Plant Mol Biol Report 31:678–687
Acknowledgments
We are deeply indebted to all the people involved in the Japanese pear breeding program at the Institute of Fruit Tree and Tea Science, NARO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary Fig. 1
Distributions of individual sugars in an F1 population derived from crossing ‘Akizuki’ and ‘373-55’ (PDF 383 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Linkage maps of ‘Akizuki’, ‘373-55’, and their integrated map. “CP” indicates that the integrated LG maps were built using the cross-pollination mode of JoinMap v. 4.1. Markers with segregation distortion are identified by asterisks (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001) (PDF 380 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
Significant QTLs for sucrose (SUC), fructose (FRU), glucose (GLU), sorbitol (SOR), and total sugar content (TSC). “CP” indicates that the integrated maps were built using the cross-pollination mode of JoinMap v. 4.1. Marker loci and significant QTLs are shown to the right of the linkage groups. Boxes and range lines indicate 1-LOD and 1.5-LOD support intervals, respectively. Markers with segregation distortion are identified by asterisks (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001) (PDF 1995 kb)
ESM 1
(XLSX 101 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishio, S., Saito, T., Terakami, S. et al. Identification of QTLs Associated with Conversion of Sucrose to Hexose in Mature Fruit of Japanese Pear. Plant Mol Biol Rep 36, 643–652 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-018-1106-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-018-1106-y