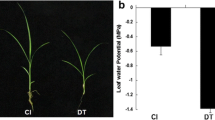
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, single-stranded, non-coding endogenous RNAs that play vital roles in the regulation of gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. Several studies of miRNAs in diploid and tetraploid Paulownia plants have been reported; however, miRNAs involved in response to drought stress have not yet been investigated. In this study, six small RNA libraries of Paulownia fortunei, two drought-treated and four controls, were built and then sequenced on an Illumina/Solexa GAIIx platform. A total of 30 conserved miRNAs and 88 novel miRNAs were identified in the sRNA libraries. Among them, 22 miRNAs in common were differentially expressed both in diploid and tetraploid P. fortunei under the drought stress. Degradome sequencing was used to identify the target genes of the miRNAs. Moreover, nine differentially expressed miRNAs and ten target genes were validated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). This study has provided data for further research into the molecular mechanisms associated with drought stress in diploid and autotetraploid P. fortunei plants.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addo-Quaye C, Eshoo TW, Bartel DP, Axtell MJ (2008) Endogenous siRNA and miRNA targets identified by sequencing of the Arabidopsis degradome. Curr Biol 18:758–762
Allen R, Li J, Alonso-Peral M, White R, Gubler F, Millar A (2010) MicroR159 regulation of most conserved targets in Arabidopsis has negligible phenotypic effects. Silence 1:1–18
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141701
Audic S, Claverie J-M (1997) The significance of digital gene expression profiles. Genome Res 7:986–995
Axtell MJ, Snyder JA, Bartel DP (2007) Common functions for diverse small RNAs of land plants. Plant Cell 19:1750–1769
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233
Brodersen P, Sakvarelidze-Achard L, Bruun-Rasmussen M, Dunoyer P, Yamamoto YY, Sieburth L, Voinnet O (2008) Widespread translational inhibition by plant miRNAs and siRNAs. Science 320:1185–1190. doi:10.1126/science.1159151
Combier JP et al (2006) MtHAP2-1 is a key transcriptional regulator of symbiotic nodule development regulated by microRNA169 in Medicago truncatula. Genes Dev 20:3084–3088. doi:10.1101/gad.402806
Conesa A, Götz S, García-Gómez JM, Terol J, Talón M, Robles M (2005) Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 21:3674–3676. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti610
Covarrubias AA, Reyes JL (2010) Post-transcriptional gene regulation of salinity and drought responses by plant microRNAs. Plant Cell Environ 33:481–489. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.02048.x
Dat J, Vandenabeele S, Vranova E, Van Montagu M, Inze D, Van Breusegem F (2000) Dual action of the active oxygen species during plant stress responses. Cell Mol Life Sci 57:779–795
Dong Y, Fan G, Zhao Z, Deng M (2014) Compatible solute, transporter protein, transcription factor, and hormone-related gene expression provides an indicator of drought stress in Paulownia fortunei. Funct Integr Genomic 14:479–491. doi:10.1007/s10142-014-0373-4
Fahlgren N et al (2010) MicroRNA gene evolution in Arabidopsis lyrata and Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 22:1074–1089. doi:10.1105/tpc.110.073999
Fan G, Cao Y, Zhao Z, Yang Z (2007a) Induction of autotereapioid of Paulownia Fortunei. Sci Silv Sin 43:31–35
Fan G, Yang Z, Cao Y, Zhang X (2007b) Induction of autotetraploid of Paulownia tomentosa (Thunb.) Steud. Plant Physiol Commun 43:109–111
Fan G, Zhai X, Niu S, Ren Y (2014) Dynamic expression of novel and conserved microRNAs and their targets in diploid and tetraploid of Paulownia tomentosa. Biochimie 102:68–77. doi: 1016/jbiochi.2014.02.008
Fan G, Zhai X, Wei Z, Yang Z (2010) Induction of autotetrapioid from the somatic cell of Paulownia tomentosa × P. fortunei and its in vitro plantlet regeneration. J Northeast Forest Univ 38:22–26
Fang Y, Xie K, Xiong L (2014) Conserved miR164-targeted NAC genes negatively regulate drought resistance in rice. J Exp Bot 65:2119–2135. doi:10.1093/jxb/eru072
German MA et al (2008) Global identification of microRNA-target RNA pairs by parallel analysis of RNA ends. Nat Biotechnol 26:941–946. doi:10.1038/nbt1417
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.08.016
Hao DC, Yang L, Xiao PG, Liu M (2012) Identification of Taxus microRNAs and their targets with high-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis. Physiol Plant 146:388–403. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.2012.01668.x
Huang SQ, Peng J, Qiu CX, Yang ZM (2009) Heavy metal-regulated new microRNAs from rice. J Inorg Biochem 103:282–287. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2008.10.019
Jackson JA, Tinsley RC (2003) Parasite infectivity to hybridising host species: a link between hybrid resistance and allopolyploid speciation? Int J Parasitol 33:137–144
Jovanović Ž, Stanisavljević N, Mikić A, Radović S, Maksimović V (2014) Water deficit down-regulates miR398 and miR408 in pea (Pisum sativum L.) Plant Physiol Biochem 83:26–31. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.07.008
Jover-Gil S, Candela H, Ponce MR (2005) Plant microRNAs and development. Int J Dev Biol 49:733–744. doi:10.1387/ijdb.052015sj
Koops P, Pelser S, Ignatz M, Klose C, Marrocco-Selden K, Kretsch T (2011) EDL3 is an F-box protein involved in the regulation of abscisic acid signalling in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 62:5547–5560. doi:10.1093/jxb/err236
Li WX et al (2008) The Arabidopsis NFYA5 transcription factor is regulated transcriptionally and posttranscriptionally to promote drought resistance. Plant Cell 20:2238–2251. doi:10.1105/tpc.108.059444
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−delta delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lv DK et al (2010) Profiling of cold-stress-responsive miRNAs in rice by microarrays. Gene 459:39–47. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2010.03.011
Meyers BC et al (2008) Criteria for annotation of plant microRNAs. Plant Cell 20:3186–3190. doi:10.1105/tpc.108.064311
Moskovitz J (2005) Methionine sulfoxide reductases: ubiquitous enzymes involved in antioxidant defense, protein regulation, and prevention of aging-associated diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1703:213–219. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2004.09.003
Nag A, King S, Jack T (2009) miR319a targeting of TCP4 is critical for petal growth and development in Arabidopsis. P Natl Acad Sci USA 106:22534–22539. doi:10.1073/pnas.0908718106
Nakabayashi R et al (2014) Enhancement of oxidative and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis by overaccumulation of antioxidant flavonoids. Plant J 77:367–379. doi:10.1111/tpj.12388
Ni Z, Hu Z, Jiang Q, Zhang H (2013) GmNFYA3, a target gene of miR169, is a positive regulator of plant tolerance to drought stress. Plant Mol Biol 82:113–129. doi:10.1007/s11103-013-0040-5
Nigam D, Kumar S, Mishra DC, Rai A, Smita S, Saha A (2015) Synergistic regulatory networks mediated by microRNAs and transcription factors under drought, heat and salt stresses in Oryza sativa spp. Gene 555:127–139. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2014.10.054
Niu S, Fan G, Xu E, Deng M, Zhao Z, Dong Y (2014a) Transcriptome/degradome-wide discovery of MicroRNAs and transcript targets in two Paulownia australis genotypes. PLoS One 9:e106736. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0106736
Niu S, Fan G, Zhao Z, Deng M, Dong Y (2014b) High-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis reveal microRNA differential expression profiles and their targets in Paulownia fortunei. Plant Cell Tiss Org 119:457–468. doi:10.1007/s11240-014-0546-9
Oh J, Kwon Y, Kim J, Noh H, Hong S-W, Lee H (2011) A dual role for MYB60 in stomatal regulation and root growth of Arabidopsis thaliana under drought stress. Plant Mol Biol 77:91–103. doi:10.1007/s11103-011-9796-7
Ramsey J, Schemske DW (2002) Neopolyploidy in flowering plants. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 33:589–639
Romero HM, Berlett BS, Jensen PJ, Pell EJ, Tien M (2004) Investigations into the role of the plastidial peptide methionine sulfoxide reductase in response to oxidative stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 136:3784–3794. doi:10.1104/pp.104.046656
Song JB, Gao S, Sun D, Li H, Shu XX, Yang ZM (2013) miR394 and LCR are involved in Arabidopsis salt and drought stress responses in an abscisic acid-dependent manner. BMC Plant Biol 13:210. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-13-210
Sorin C et al (2014) A miR169 isoform regulates specific NF-YA targets and root architecture in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 202:1197–1211. doi:10.1111/nph.12735
Sunkar R, Zhou X, Zheng Y, Zhang W, Zhu JK (2008) Identification of novel and candidate miRNAs in rice by high throughput sequencing. BMC Plant Biol 8:25. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-8-25
Taylor JS, Raes J (2004) Duplication and divergence: the evolution of new genes and old ideas. Annu Rev Genet 38:615–643. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.38.072902.092831
Vogt W (1995) Oxidation of methionyl residues in proteins: tools, targets, and reversal. Free Radic Biol Med 18:93–105
Wang YG, An M, Zhou SF, She YH, Li WC, Fu FL (2014) Expression profile of maize microRNAs corresponding to their target genes under drought stress. Biochem Genet 52:474–493. doi:10.1007/s10528-014-9661-x
Wang M, Wang Q, Zhang B (2013) Response of miRNAs and their targets to salt and drought stresses in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) Gene 530:26–32. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2013.08.009
Wang Y, Zhao Z, Deng M, Liu R, Niu S, Fan G (2015) Identification and functional analysis of MicroRNAs and their targets in Platanus acerifolia under lead (Pb) stress. Int J Mol Sci 16:7098–7111
Warpeha KM et al (2007) The GCR1, GPA1, PRN1, NF-Y signal chain mediates both blue light and abscisic acid responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 143:1590–1600. doi:10.1104/pp.106.089904
Yang J et al (2014) Identification of miR159s and their target genes and expression analysis under drought stress in potato. Comput Biol Chem 53:204–213. doi:10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2014.09.009
Zhang X, Liu R, Fan G, Zhao Z, Deng M (2013) Study on the physiological response of tetraploid Paulownia to drought. J Henan Agr Univ 47:543–551
Zhang X et al (2011) Over-expression of microRNA169 confers enhanced drought tolerance to tomato. Biotechnol Lett 33:403–409. doi:10.1007/s10529-010-0436-0
Zhao M, Ding H, Zhu J-K, Zhang F, Li W-X (2011) Involvement of miR169 in the nitrogen-starvation responses in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 190:906–915. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03647.x
Zhou M, Li D, Li Z, Hu Q, Yang C, Zhu L, Luo H (2013) Constitutive expression of a miR319 gene alters plant development and enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic creeping bentgrass. Plant Physiol 161:1375–1391. doi:10.1104/pp.112.208702
Zhou ZS, Song JB, Yang ZM (2012) Genome-wide identification of Brassica napus microRNAs and their targets in response to cadmium. J Exp Bot 63:4597–4613
Zhou X, Wang G, Zhang W (2007) UV-B responsive microRNA genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Syst Biol 3. doi:10.1038/msb4100143
Zhu J-K (2002) Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:247–273. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.53.091401.143329
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Joint Funds of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (U1204309), the Fund of the Transformation Project of the National Agricultural Scientific and Technological Achievement of China (2012GB2D000271), the Central Financial Forestry Science Promotion Project (GTH [2012]01), the Fund of the Science Key Program of Department of Henan Education (12A220003), the Fund of the Technology Innovation Team Project of Zhengzhou (121PCXTD515), the Fund of the Science and Technology Key Project of Henan Education Department (14A220001), and the Fund of Zhongyuan Scholarship Foundation of Henan Province (122101110700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Data Archiving Statement
The raw sequence data are available at the NIH Short Read Archive database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih. gov/sra) under the accession number SRP062453 (alias: PRJNA293002).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, G., Niu, S., Li, X. et al. Functional Analysis of Differentially Expressed MicroRNAs Associated with Drought Stress in Diploid and Tetraploid Paulownia fortunei . Plant Mol Biol Rep 35, 389–398 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-017-1031-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-017-1031-5