Abstract
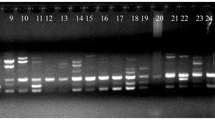
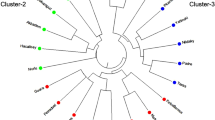
Genetic diversity was evaluated by sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) and simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers among 45 lemons (Citrus limon (L.) Burm. f.), five citrons (Citrus medica L.), four rough lemons (Citrus jambhiri Lush), and two Citrus volkameriana accessions. Twenty-one SRAP primer combinations produced a total of 141 (77%) polymorphic fragments with an average of 6.7 fragments per primer combinations whereas 13 SSR primers produced a total of 26 (76%) polymorphic fragments with an average of 2.0 per primer. The unweighted pair-group method arithmetic average analysis as assessed with combined SRAP and SSR data demonstrated that the accessions had a similarity range from 0.65 to 1.00. Rough lemons and C. volkameriana accessions were relatively closely related. In lemon group, accessions from hybrid origin were distant from the others. We also applied principal components analysis (PCA) for a better presentation of relation among the accessions studies. Using PCA, 88.7% of the total variation in the original dimensions could be represented by just the two dimensions defined by the first two PCs. Although nearly all accessions could be distinguished, there was a low level of genetic diversity detected among lemon cultivars.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abkenar AA, Isshiki S, Matsumoto R (2008) Comparative analysis of organelle DNAs acid citrus grown in Japan using PCR-RFLP method. Genet Resour Crop Evol 55:487–492
Aka-Kacar Y, Demirel A, Tuzcu O, Yesiloglu T, Ulas M, Yildirim B (2005) Preliminary results on fingerprinting of lemon genotypes tolerant to ‘mal secco’ disease by RAPD markers. Biologia 60:295–300
Albanese G, Renis M, Reforgito Recupero G (1992) RFLP analysis of different lemon cultivars. Proc Int Soc Citriculture 1:208–209
Baraket G, Chatti K, Saddoud O, Abdelkarim AB, Mars M, Trifi M, Hannachi AS (2010) Comparative assessment of SSR and AFLP markers for evaluation of genetic diversity and conservation of Fig, Ficus carica L., genetic resources in Tunisia. Plant Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11105-010-0217-x
Barkley NA, Roose ML, Krueger RR, Federici CT (2006) Assessing genetic diversity and population structure in a citrus germplasm collection utilizing simple sequence repeat markers (SSRs). Theor Appl Genet 112:1519–1531
Barrett HC, Rhodes AM (1976) A numerical taxonomic study of affinity relationships in cultivated Citrus and its close relatives. Syst Bot 1:105–136
Bernet GP, Mestre PF, Pina JA, Asins MJ (2004) Molecular discrimination of lemon cultivars. Hortscience 39:165–169
Bourguiba H, Krichen L, Audergon JM, Khadari B, Trifi-Farah N (2010) Impact of mapped SSR markers on the genetic diversity of apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) in Tunisia. Plant Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11105-010-0189-x
Capparelli R, Viscardi M, Amoroso MG, Blaiotta G, Bianco M (2004) Inter-simple sequence repeat markers and flow cytometry for the characterization of closely related Citrus limon germplasms. Biotechnol Lett 26:1295–1299
Corazza-Nunes MJ, Machado MA, Nunes WMC, Cristofani M, Targon MLPN (2002) Assessment of genetic variability in grapefruits (Citrus paradisi Macf.) and pummelos (C. maxima Burm. Merr.) using RAPD and SSR markers. Euphytica 126:169–176
Cottin R (2002) Citrus of the World, A Citrus Directory Version 2. SRA INRA-CIRAD, France
Cristofani-Yaly M, Novelli VM, Bastinel M, Machado MA (2010) Transferability and level of heterozygosity of microsatellite markers in Citrus species. Plant Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11105-010-0241-x
Deng ZN, Gentile A, Domina F, Nicolosi E, Tribulato E (1995) Selecting lemon protoplasts for insensitivity to Phoma tracheiphila toxin and regenerating tolerant plants. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 120:902–905
Dice LR (1945) Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 26:297–302
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Federici CT, Fang DQ, Scora RW, Roose ML (1998) Phylogenetic relationships within the genus Citrus (Rutaceae) and related genera as revealed by RFLP and RAPD analysis. Theor Appl Genet 96:812–822
Gomes S, Martins-Lopes P, Lopes J, Guedes-Pinto H (2009) Assessing genetic diversity in Olea europaea L. using ISSR and SSR markers. Plant Mol Biol Rep 27:365–373
Gulsen O, Roose ML (2000) The origin of Interdonato lemon inferred from cpRFLP, SSR, isozyme and ISSR markers. Proc Int Soc Citriculture 1:158–159
Gulsen O, Roose ML (2001a) Lemons: diversity and relationships with selected Citrus genotypes as measured with nuclear genome markers. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 126:309–317
Gulsen O, Roose ML (2001b) Chloroplast and nuclear genome analysis of the parentage of lemons. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 126:210–215
He X, Li W, Liang GL, Ji K, Guo QG, Yuan WM, Zhou GZ, Chen KS, Van de Weg WE, Gao ZS (2010) Genetic diversity and identity of Chinese loquat cultivars/Accessions (Eriobotrya japonica) using apple SSR markers. Plant Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11105-010-0218-9
Herrero R, Asins MJ, Carbonell AE, Navarro L (1996) Genetic diversity in the orange subfamily Aurantioideae. I. Intraspecies and intragenus genetic variability. Theor Appl Genet 92:599–609
Hodgson RW (1967) Horticultural varieties of citrus. In: Reuther W, Webber HJ, Batchelor LD (eds) The Citrus industry, vol 1. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 431–591
Kahn TL, Krueger RR, Gumpf DJ, Roose ML, Arpaia ML, Batkin TA, Bash JA, Bier OJ, Clegg MT, Cockerham ST et al (2001) Citrus genetic resources in California: Analysis and recommendations for long-term conservation. Report No. 22. University of California Division of Agriculture and Natural Resources, Genetic Resources Conservation Program, Davis, CA, USA
Li G, Quiros CF (2001) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 103:455–461
Luro F, Laigret F, Bove JM, Ollitrault P (1992) Application of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) to Citrus genetic and taxonomy. Proc Int Soc Citriculture 1:225–228
Mantel N (1967) The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res 27:209–220
Marak CK, Laskar MA (2010) Analysis of phenetic relationship between Citrus indica Tanaka and a few commercially important citrus species by ISSR markers. Sci Hortic 124:345–348
Morton CM, Grant M, Blackmore S (2003) Phylogenic relationships of the Aurantioideae inferred from chloroplast DNA sequence data. Am J Bot 90:1463–1469
Nicolosi E, Deng ZN, Gentile A, La Malfa S, Continella G, Tribulato E (2000) Citrus phylogeny and genetic origin of important species as investigated by molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 100:1155–1166
Pang XM, Hu CG, Deng XX (2007) Phylogenetic relationship within Citrus and related genera as inferred from AFLP markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:429–436
Rohlf FJ (2000) NTSYS-pc, numerical taxonomy and multivarite analysis system, version 2.11. Exeter, Setauket, New York
Scora RW (1975) On the history and origin of Citrus. Bull Torrey Bot Club 102:369–375
Scora RW (1988) Biochemistry, taxonomy and evolution of modern cultivated Citrus. In: Goren RK, Mendel K (eds) Proc 6th Int Citrus Cong, vol 1. Margraf, Weikersheim, pp 277–289
Siragusa M, De Pasquale F, Abbate L, Martorana L, Tusa N (2008) The genetic variability of sicilian lemon germplasm revealed by molecular marker fingerprints. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 133:242–248
Smith JSC, Chin ECL, Shu H, Smith OS, Wall SJ, Senior ML, Mitchel SE, Kresorich S, Tiegle J (1997) An evaluation of the utility of SSR loci as molecular markers in maize (Zea mays L.): comparisons with data from RFLPs and pedigree. Theor Appl Genet 95:163–173
Swingle WT, Reece PC (1967) The botany of citrus and its wild relatives. In: Reuther W, Webber HJ, Batchelor LD (eds) The Citrus industry, vol 1. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 389–390
Tanaka T (1977) Fundamental discussion of Citrus classification. Stud Citrol 14:1–6
Torres AM, Soost RK, Diedenhofen U (1978) Leaf isozymes as genetic markers in Citrus. Am J Bot 65:869–881
Tuzcu O, Kaplankiran M, Yesiloglu T, Erkilic A (1992) Preliminary results on breeding lemon cultivars tolerant to ‘mal secco’ (Phoma tracheiphila Kanc. Et Ghik.) disease in Turkey. Derim 9:99–107 (in Turkish)
Uzun A, Yesiloglu T, Aka-Kacar Y, Tuzcu O, Gulsen O (2009a) Genetic diversity and relationships within Citrus and related genera based on sequence related amplified polymorphism markers (SRAPs). Sci Hortic 121:306–312
Uzun A, Gulsen O, Kafa G, Seday U (2009b) Field performance and molecular diversification of lemon selections. Sci Hortic 120:473–478
Uzun A, Yesiloglu T, Aka-Kacar Y, Tuzcu O, Gulsen O (2009c) Determination of genetic diversity in rough lemon genotypes with SRAP markers. Alatarım 8:8–14 (in Turkish)
Uzun A, Gulsen O, Kafa G, Seday U, Tuzcu O, Yesiloglu T (2009d) Characterization for yield, fruit quality, and molecular profiles of lemon genotypes tolerant to ‘mal secco’ disease. Sci Hortic 122:556–561
Acknowledgements
The authors thanks to Scientific and Technological Research Council (TUBITAK), General Directorate of Agricultural Research of Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, and Scientific Research Project Unit of University of Cukurova, Adana, Turkey for funding and supporting.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uzun, A., Yesiloglu, T., Polat, I. et al. Evaluation of Genetic Diversity in Lemons and Some of Their Relatives Based on SRAP and SSR Markers. Plant Mol Biol Rep 29, 693–701 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-010-0277-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-010-0277-y