Abstract
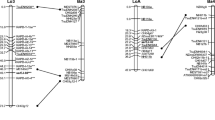
Two separate genetic linkage maps for Chinese silver birch based on inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) and amplified fragment-length polymorphism (AFLP) were constructed by a pseudo-testcross mapping strategy. Eighty F1 progenies were obtained from the cross between two parental trees with desirable traits (the paternal one selected from ‘Qinghai’ and the maternal one from ‘Wangqing’). A total of 46 ISSR primers and 31 AFLP primers were employed to generate 102 ISSR and 355 AFLP polymorphic markers in the F1 progenies. About 5.7% of all the markers displayed high segregation distortion with a P value below 0.01 and such markers were not used for map constructions. The paternal map consisted of 137 loci, spread over 13 groups and spanned 694.2 cM at an average distance of 5.1 cM between the markers, while in the maternal map, 147 loci were distributed in 14 groups covering a map distance about 949.62 cM at an average distance of 6.5 cM. These initial maps can serve as the basis for developing a more detailed genetic map.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arcade A, Anselin F, Faivre RP et al (2000) Application of AFLP, RAPD and ISSR markers to genetic mapping of European and Japanese larch. Theor Appl Genet 100:299–307. doi:10.1007/s001220050039
Barreneche T, Bodenes C, Lexer C et al (1998) A genetic linkage map of Quercus robur L. (pedunculate oak) based on RAPD, SCAR, microsatellite, minisatellite, isozyme and 5S rDNA markers. Theor Appl Genet 97:1090–1103. doi:10.1007/s001220050996
Beedanagari SR, Dove SK, Wood BW et al (2005) A first linkage map of pecan cultivars based on RAPD and AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 110:1127–1137. doi:10.1007/s00122-005-1944-5
Billotte N, Marseillac N, Risterucci AM (2005) Microsatellite-based high density linkage map in oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.). Theor Appl Genet 110:754–765. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1901-8
Boivin K, Deu M, Rami JF (1999) Towards a saturated sorghum map using RFLP and AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 98:320–328. doi:10.1007/s001220051076
Bradshaw HD Jr, Stettler RF (1994) Molecular genetics of growth and development in Populus. II. Segregation distortion due to genetic load. Theor Appl Genet 139:963–973
Casasoli M, Mattioni C, Cherubini M et al (2001) A genetic linkage map of European chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) based on RAPD, ISSR and isozyme markers. Theor Appl Genet 102:1190–1199. doi:10.1007/s00122-001-0553-1
Cavalcanti JJV, Wilkinson MJ (2007) The first genetic maps of cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.). Euphytica 157:131–143. doi:10.1007/s10681-007-9403-9
Cervera MT, Storme V, Ivens B et al (2001) Dense genetic linkage maps of three populus species (Populus deltoides, P. nigra and P. trichocarpa) based on AFLP and microsatellite markers. Genetics 158:787–809
Chagne D, Lalanne C, Madur D et al (2002) A high density genetic map of maritime pine based on AFLPs. Ann Sci 59:627–636. doi:10.1051/forest:2002048
Chakravarti A, Lasher LK, Reefer JE (1991) A maximum likelihood for estimating genome length using genetic linkage data. Genetics 128(1):175–182
Costa P, Pot D, Dubos C et al (2000) A genetic linkage map of Maritime pine based on AFLP, RAPD and protein markers. Theor Appl Genet 100:39–48. doi:10.1007/s001220050006
Dirlewanger E, Pronier V, Parvery C (1998) Genetic linkage map of peach (Prunus persica L. Batsch) using morphological and molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 97:888–895. doi:10.1007/s001220050969
Grattapaglia D, Sederoff R (1994) Genetic linkage maps of Eucalyptys grandis and Eucalyptys urophylla using a pseudotestcross mapping strategy and RAPD markers. Genetics 137:1121–1137
Hanley S, Barker JHA, Van Ooijen JW et al (2002) A genetic linkage map of willow (Salix viminalis) based on AFLP and microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 105:1087–1096. doi:10.1007/s00122-002-0979-0
Hulbert SH, Ilott TW, Legg EJ et al (1988) Genetic analysis of the fungus, Bremia lactucae, using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Genetics 120:947–958
Jiang J, Yang CP, Liu GF et al (1999) Trial of Betula platyphylla Suk. in seeding stage. J Northeast For Univ 27(6):1–3
Jiang J, Yang CP, Liu GF et al (2001) Analysis of genetic variation within and among Betula platyphylla provenances and provenance division using RAPD markers. Plant Res 21(1):126–130
Jiang TB, Li SC, Gao FL (2007) Genetic linkage map of Betula pendula Roth and Betula platyphylla Suk based on random amplified polymorphisms DNA markers. Hereditas Beijing 29(7):867–873. doi:10.1360/yc-007-0867
Kosambi DD (1994) The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Kubisiak TL, Nelson CD, Nance WL, Stine M (1995) RAPD linkage mapping in a longleaf pine × slash pine F1 family. Theor Appl Genet 90:1119–1127. doi:10.1007/BF00222931
La Rosa R, Angiolillo A, Guerrero C et al (2003) A first linkage map of olive (Olea europaea L.) cultivars using RAPD, AFLP, RFLP and SSR markers. Theor Appl Genet 106:1273–1282
Lanaud C, Risterucci AM, Ngoran AKJ et al (1995) A genetic linkage map of Theobroma cacao. Theor Appl Genet 91:987–993. doi:10.1007/BF00223910
Lanteri S, Acquadro A, Comino C et al (2006) A first linkage map of globe artichoke (Cynara cardunculus var. scolymus L.) based on AFLP, S-SAP, M-AFLP and microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 112:1532–1542. doi:10.1007/s00122-006-0256-8
Li P, Fang GP, Sun CZ (1995) Wood characteristics of pulpwood. Chem Ind For Prod 15(Suppl):13–18
Lian L, Wei ZG, Yang CP (2007) Establishment and optimization of AFLP technical system for Betula Platyphylla. J Northeast For Univ 35(5):1–5
Luckaszewski P, Curtis CA (1993) Physical distribution of recombination in B-genome chromosomes of tetraploid wheat. Theor Appl Genet 85:121–127
Marques CM, Araujo JA, Ferreira JG et al (1998) AFLP genetic maps of Eucalyptus globulus and E. tereticornis. Theor Appl Genet 96:727–737. doi:10.1007/s001220050795
Melauku AG, Crispin W, Simon B et al (2001) An integrated restriction fragment length polymorphism-amplified fragment length polymorphism linkage map for cultivated sunflower. Genome 44(2):213–221. doi:10.1139/gen-44-2-213
Nikaido AM, Ujino T, Iwata H et al (2000) AFLP and CAPS linkage maps of Cryptomeria japonica. Theor Appl Genet 100:825–831. doi:10.1007/s001220051358
Nicholas KU, Kermit R, Shawn DM (2008) An AFLP linkage map for Douglas-fir based upon multiple full-sib families. Tree Genet Genomes 4:181–191. doi:10.1007/s11295-007-0099-8
Okogbenin E, Marin J, Fregene M (2006) An SSR-based molecular genetic map of cassava. Euphytica 147:433–440. doi:10.1007/s10681-005-9042-y
Pekkinen M, Varvio S, Kulju KKM et al (2005) Linkage map of birch, Betula pendula Roth, based on microsatellites and amplified fragment length polymorphisms. Genome 48(4):619–625. doi:10.1139/g05-031
Plomion C, O’Malley DM, Durel CE (1995) Genomic analysis in maritime pine (Pinus pinaster). Comparison of two RAPD maps using selfed and open-pollinated seeds of the same individual. Theor Appl Genet 90:1028–1034. doi:10.1007/BF00222917
Powell W, Machray G, Provan J (1996) Polymorphism revealed by simple sequence repeats. Trends Plant Sci 1:215–222
Remington DL, Whetten RW, Liu BH et al (1999) Construction of an AFLP genetic map with nearly complete genome coverage in Pinus taeda. Theor Appl Genet 98:1279–1292. doi:10.1007/s001220051194
Sankar AA, Moore GA (2001) Evaluation of inter-simple sequence repeat analysis for mapping in Citrus and extension of the genetic linkage map. Theor Appl Genet 102:206–214. doi:10.1007/s001220051637
Scalfi M, Troggio M, Piovani P et al (2004) A RAPD, AFLP and SSR linkage map, and QTL analysis in European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.). Theor Appl Genet 108:433–441. doi:10.1007/s00122-003-1461-3
Seefelder S, Ehrmaier H, Seigner E (2000) Male and female genetic linkage map of hops, Humulus lupulus. Plant Breed 119:249–255. doi:10.1046/j.1439-0523.2000.00469.x
Sewell MM, Sherman BK, Neale DB (1999) A consensus map for loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) construction and integration of individual linkage maps from two outbred three generation pedigrees. Genetics 151:321–330
Ukrainetz NK, Ritland K, Mansfield SD (2008) An AFLP linkage map for Douglas-fir based upon multiple full-sib families. Tree Genet Genomes 4:181–191. doi:10.1007/s11295-007-0099-8
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JoinMap 3.0, Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research, Wageningen, The Netherlands
Venkateswarlu M, Urs SR, Nath BS et al (2006) A first genetic linkage map of mulberry (Morus spp.) using RAPD, ISSR, and SSR markers and pseudotestcross mapping strategy. Tree Genet Genomes 3:15–24. doi:10.1007/s11295-006-0048-y
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: Software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78. doi:10.1093/jhered/93.1.77
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M et al (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414. doi:10.1093/nar/23.21.4407
Wang S, Bao Z, Pan J et al (2004) AFLP linkage map of an intraspecific cross in Chlamys farreri. J Shellfish Res 23:491–499
Wu RL, Han YF et al (2000) An integrated genetic map of Populus deltoides based on amplified fragment length polymorphisms. Theor Appl Genet 100(8):1249–1256. doi:10.1007/s001220051431
Yang C, Liu G, Wei Z (2004) Study on intensive breeding technique of accelerating Betula platyphylla flowering and seeding early. Scientia Silvae Sinicae 40(6):75–78
Yin TM, Wang XR, Andersson B et al (2003) Nearly complete genetic maps of Pinus sylvestris L. (Scots pine) constructed by AFLP marker analysis in a full-sib family. Theor Appl Genet 106:1075–1083
Zhang D, Zhang Z, Yang K et al (2004) Genetic mapping in (Populus tomentosa×Populus bolleana)and P. tomentosa Carr. using AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 108:657–662. doi:10.1007/s00122-003-1478-7
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Specific Basic Science-Technology project (2007FY110400-3), Provincial Key Technologies of Hei Longjiang (GA06B301-4), and National Natural Science Foundation. Special thanks to the Key Laboratory of Forest Tree Genetic Improvement and Biotechnology at Northeast Forestry University and Ministry of Education in China for hosting the research group and their critical comments in support of the research. Many thanks also go to Prof. Jiang Jing for her help and support in carrying out this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Z., Zhang, K., Yang, C. et al. Genetic Linkage Maps of Betula platyphylla Suk Based on ISSR and AFLP Markers. Plant Mol Biol Rep 28, 169–175 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-009-0138-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-009-0138-8