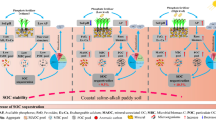
Abstract
Aims
Nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) have important roles in the terrestrial carbon (C) cycle. Nevertheless, the responses of microbial ecological functions involving C cycling in saline-sodic soils to N and P are barely known, particularly at the functional gene level.
Methods
The influence of N and P addition on C functional genes in saline-sodic soils was explored using a pot experiment. Eight treatments were conducted, namely: a control (CK), three N addition levels (NL, NM, and NH), three P addition levels (PL, PM, and PH), and combined N and P addition (NP).
Results
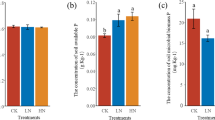
Results revealed that the total abundance of C functional genes was enhanced by the addition of N and P, promoting C fixation, degradation, and CH4 metabolism. The total gene abundance was the highest in NL among the three N addition treatments; however, the highest abundance was observed in PH among the three P addition treatments. Compared to CK, all treatments exerted greater effects on the abundance of genes related to recalcitrant C decomposition than on labile C decomposition. This was because increment in relative abundance of oligotrophic taxa was greater than that of copiotrophic taxa after the addition of N and P. Partial least squares path modeling analysis revealed that N and P addition regulated gene abundance by altering DOC, microbial diversity, and ESP, thereby directly influencing C mineralization.
Conclusions
Our results highlight that N and P stimulate the abundance of C functional genes via plant biomass and soil property traits in saline-sodic soils.







Similar content being viewed by others

Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ajwa HA, Dell CJ, Rice CW (1999) Changes in enzyme activities and microbial biomass of tallgrass prairie soil as related to burning and nitrogen fertilization. Soil Biol Biochem 31:769–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(98)00177-1
Aye NS, Butterly CR, Sale PWG, Tang C (2018) Interactive effects of initial pH and nitrogen status on soil organic carbon priming by glucose and lignocellulose. Soil Biol Biochem 123:33–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.04.027
Bodelier PLE, Steenbergh AK (2014) Interactions between CH4methane and the nitrogen cycle in light of climate change. Curr Opin Environ Sustain 9-10:26–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosust.2014.07.004
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Brookes PC, Chen Y, Chen L, Qiu G, Luo Y, Xu J (2017) Is the rate of mineralization of soil organic carbon under microbiological control? Soil Biol Biochem 112:127–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.05.003
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M et al (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.f.303
Chai H, Yu G, He N, Wen D, Li J, Fang J (2015) Vertical distribution of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in typical Chinese terrestrial ecosystems. Chin Geogr Sci 25:549–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-015-0756-z
Chang R, Li N, Sun X, Hu Z, Bai X, Wang G (2018) Nitrogen addition reduces dissolved organic carbon leaching in a montane forest. Soil Biol Biochem 127:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.09.006
Chen W, Zhou H, Wu Y, Wang J, Zhao Z, Li Y, Qiao L, Chen K, Liu G, Xue S (2020) Direct and indirect influences of long-term fertilization on microbial carbon and nitrogen cycles in an alpine grassland. Soil Biol Biochem 149:107922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2020.107922
Coskun D, Britto DT, Kronzucker HJ (2016) Nutrient constraints on terrestrial carbon fixation: the role of nitrogen. J Plant Physiol 203:95–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2016.05.016
Craine JM, Morrow C, Fierer N (2007) Microbial nitrogen limitation increases decomposition. Ecology 88:2105–2113. https://doi.org/10.1890/06-1847.1
Cruz AF, Hamel C, Hanson K, Selles F, Zentner RP (2009) Thirty-seven years of soil nitrogen and phosphorus fertility management shapes the structure and function of the soil microbial community in a Brown Chernozem. Plant Soil 315:173–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9742-x
Dong X, Li M, Lin Q, Li G, Zhao X (2019) Soil Na+ concentration controls salt-affected soil organic matter components in Hetao region China. J Soils Sediments 19:1120–1129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2127-8
Du XJ, Wang SY, Xu ZJ, Liu J, Gao ZD, Ren XQ, Ma K, Hu SW (2021) Response of soils properties and archaea community to saline-sodic soils under long-term rice-based cropping system. Arch Agron Soil Sci 2023 69(4):533–549. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2021.2013473
Elser JJ, Bracken MES, Cleland EE, Gruner DS, Harpole WS, Hillebrand H, Ngai JT, Seabloom EW, Shurin JB, Smith JE (2007) Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Lett 10:1135–1142. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01113.x
Feng HJ, Wang SY, Gao ZD, Wang ZK, Pan H (2019) Effect of land use on the composition of bacterial and fungal communities in saline–sodic soils. Land Degrad Dev 30:1851–1860. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3386
Feng HJ, Wang SY, Gao ZD, Pan H, Zhuge YP, Ren XQ, Hu SW, Li CL (2021) Aggregate stability and organic carbon stock under different land uses integrally regulated by binding agents and chemical properties in saline-sodic soils. Land Degrad Dev 32:4151–4161. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.4019
Fierer N, Bradford MA, Jackson RB (2007) Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 88:1354–1364
Gai X, Liu H, Liu J, Zhai L, Yang B, Wu S, Ren T, Lei Q, Wang H (2018) Long-term benefits of combining chemical fertilizer and manure applications on crop yields and soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in North China plain. Agric Water Manag 208:384–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.07.002
Gray ND, McCann CM, Christgen B, Ahammad SZ, Roberts JA, Graham DW (2014) Soil geochemistry confines microbial abundances across an arctic landscape; implications for net carbon exchange with the atmosphere. Biogeochemistry 120:307–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-014-9997-7
Gupta SK, Sharma SK (1990) Response of crops to high exchangeable sodium percentage. Irrig Sci 11:173–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00189455
Hagedorn F, Spinnler D, Siegwolf R (2003) Increased N deposition retards mineralization of old soil organic matter. Soil Biol Biochem 35:1683–1692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2003.08.015
Hu A, Choi M, Tanentzap AJ, Liu J, Jang K-S, Lennon JT, Liu Y, Soininen J, Lu X, Zhang Y, Shen J, Wang J (2022a) Ecological networks of dissolved organic matter and microorganisms under global change. Nat Commun 13:3600. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-31251-1
Hu X, Gu H, Liu J, Wei D, Zhu P, Xa C, Zhou B, Chen X, Jin J, Liu X, Wang G (2022b) Metagenomics reveals divergent functional profiles of soil carbon and nitrogen cycling under long-term addition of chemical and organic fertilizers in the black soil region. Geoderma 418:115846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2022.115846
Jenkinson DS, Goulding K, Powlson DS (1999) Nitrogen deposition and carbon sequestration. Nature 400:629–629. https://doi.org/10.1038/23174
Johnson D, Leake JR, Lee JA, Campbell CD (1998) Changes in soil microbial biomass and microbial activities in response to 7 years simulated pollutant nitrogen deposition on a heathland and two grasslands. Environ Pollut 103:239–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(98)00115-8
Kim HS, Kim KR, Lee SH, Kunhikrishnan A, Kim WI, Kim KH (2018) Effect of gypsum on exchangeable sodium percentage and electrical conductivity in the Daeho reclaimed tidal land soil in Korea—a field scale study. J Soils Sediments 18:336–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1446-x
Li D, Wang Z, Tian H, He W, Geng Z (2017a) Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus contents in soils on taibai mountain and their ecological stoichiometry relative to elevation. Acta Pedol Sinica 54(1):160–170. https://doi.org/10.11766/trxb201604140096
Li H, Yang S, Xu Z, Ya Q, Li X, van Nostrand JD, He Z, Yao F, Han X, Zhou J, Deng Y, Jiang Y (2017b) Responses of soil microbial functional genes to global changes are indirectly influenced by aboveground plant biomass variation. Soil Biol Biochem 104:18–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.10.009
Li J, Wang G, Yan B, Liu G (2020) The responses of soil nitrogen transformation to nitrogen addition are mainly related to the changes in functional gene relative abundance in artificial Pinus tabulaeformis forests. Sci Total Environ 723:137679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137679
Liu L, Gundersen P, Zhang T, Mo J (2012) Effects of phosphorus addition on soil microbial biomass and community composition in three forest types in tropical China. Soil Biol Biochem 44:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.08.017
Liu Z, Shang HG, Han F, Zhang MR, Li Q, Zhou WZ (2021) Improvement of nitrogen and phosphorus availability by Pseudoalteromonas sp during salt-washing in saline-alkali soil. Appl Soil Ecol 168:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2021.104117
Luo M, Moorhead DL, Ochoa-Hueso R, Mueller CW, Ying SC, Chen J (2022) Nitrogen loading enhances phosphorus limitation in terrestrial ecosystems with implications for soil carbon cycling. Funct Ecol 36(11):2845–2858. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.14178
Ma B, Stirling E, Liu YH, Zhao KK, Zhou JZ, Singh BK, Tang CX, Dahlgren RA, Xu JM (2021) Soil biogeochemical cycle couplings inferred from a function-taxon network. Research 10:7102769. https://doi.org/10.34133/2021/7102769
Ma XY, Wang TX, Shi Z, Chiariello NR, Docherty K, Field CB, Gutknecht J, Gao Q, Gu YF, Guo X, Hungate BA, Lei JS, Niboyet A, Le Roux X, Yuan MT, Yuan T, Zhou JZ, Yang YF (2022) Long-term nitrogen deposition enhances microbial capacities in soil carbon stabilization but reduces network complexity. Microbiome 10:112. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-022-01309-9
Magill AH, Aber JD (1998) Long-term effects of experimental nitrogen additions on foliar litter decay and humus formation in forest ecosystems. Plant Soil 203:301–311. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004367000041
Paul EA (2016) The nature and dynamics of soil organic matter: plant inputs, microbial transformations, and organic matter stabilization. Soil Biol Biochem 98:109–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.04.001
Paul LEB, Hendrikus JL (2004) Nitrogen as a regulatory factor of CH4 oxidation in soils and sediments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 47(3):265–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-6496(03)00304-0
Poeplau C, Herrmann AM, Kätterer T (2016) Opposing effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on soil microbial metabolism and the implications for soil carbon storage. Soil Biol Biochem 100:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.05.021
Rasul G, Appuhn A, Müller T, Joergensen RG (2006) Salinity-induced changes in the microbial use of sugarcane filter cake added to soil. Appl Soil Ecol 31:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2005.04.007
Reyon D, Tsai SQ, Khayter C, Foden JA, Sander JD, Joung JK (2012) FLASH assembly of TALENs for high-throughput genome editing. Nat Biotechnol 30:460–465. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2170
Setia R, Gottschalk P, Smith P, Marschner P, Smith J (2012) Soil salinity decreases global soil organic carbon stocks. Sci Total Environ 465:267–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.08.028
Shao H, Chu L, Lu H, Qi W, Chen X, Liu J, Kuang S, Tang B, Wong V (2019) Towards sustainable agriculture for the salt-affected soil. Land Degrad Dev 30:574–579. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3218
Shi BK, Zhang JM, Wang CL, Ma JY, Sun W (2018) Responses of hydrolytic enzyme activities in saline-alkaline soil to mixed inorganic and organic nitrogen addition. Sci Rep 8:4543. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-22813-9
Shrestha M, Shrestha PM, Frenzel P, Conrad R (2010) Effect of nitrogen fertilization on CH4methane oxidation, abundance, community structure, and gene expression of methanotrophs in the rice rhizosphere. ISME J 4:1545–1556. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2010.89
Song B, Niu S, Li L, Zhang L, Yu G (2014) Soil carbon fractions in grasslands respond differently to various levels of nitrogen enrichments. Plant Soil 384:401–412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2219-1
Sun RB, Guo XS, Wang DZ, Chu HY (2015) Effects of long-term application of chemical and organic fertilizers on the abundance of microbial communities involved in the nitrogen cycle. Appl Soil Ecol 95:171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2015.06.010
Swarup A (1985) Effect of exchangeable sodium percentage and presubmergence on yield and nutrition of rice under field conditions. Plant Soil 85:279–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02139632
Tahovská K, Choma M, Kaštovská E, Oulehle F, Bárta J, Šantrůčková H, Moldan F (2020) Positive response of soil microbes to long-term nitrogen input in spruce forest: results from Gårdsjön whole-catchment N-addition experiment. Soil Biol Biochem 143:107732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2020.107732
Trivedi P, Delgado-Baquerizo M, Trivedi C, Hu H, Anderson IC, Jeffries TC, Zhou J, Singh BK (2016) Microbial regulation of the soil carbon cycle: evidence from gene–enzyme relationships. ISME J 10:2593–2604. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2016.65
Ury EA, Wright JP, Ardón M, Bernhardt ES (2022) Saltwater intrusion in context: soil factors regulate impacts of salinity on soil carbon cycling. Biogeochemistry 157:215–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-021-00869-6
Veraart AJ, Steenbergh AK, Ho A, Kim SY, Bodelier PLE (2015) Beyond nitrogen: the importance of phosphorus for CH4 oxidation in soils and sediments. Geoderma 259-260:337–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.03.025
Wang ZP, Ineson P (2003) Methane oxidation in a temperate coniferous forest soil: effects of inorganic N. Soil Biol Biochem 35:427–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(02)00294-8
Wang Q, Garrity G, Tiedje J, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5264–5267. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00062-07
Wang R, Filley TR, Xu Z, Wang X, Li MH, Zhang Y, Luo W, Jiang Y (2014) Coupled response of soil carbon and nitrogen pools and enzyme activities to nitrogen and water addition in a semi-arid grassland of Inner Mongolia. Plant Soil 381:323–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2129-2
Wei X, Hu Y, Peng P, Zhu Z, Atere CT, O’Donnell AG, Wu J, Ge T (2017) Effect of P stoichiometry on the abundance of nitrogen-cycle genes in phosphorus-limited paddy soil. Biol Fertil Soils 53:767–776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-017-1221-1
Xie WJ, Chen QF, Wu LF, Yang HJ, Xu JK, Zhang YP (2020) Coastal saline soil aggregate formation and salt distribution are affected by straw and nitrogen application: a 4-year field study. Soil Till Res 198:8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.104535
Xu H, Qu Q, Li G, Liu G, Geissen V, Ritsema CJ, Xue S (2022) Impact of nitrogen addition on plant-soil-enzyme C–N–P stoichiometry and microbial nutrient limitation. Soil Biol Biochem 170:108714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2022.108714
Yang C, Lv D, Jiang S, Lin H, Sun J, Li K, Sun J (2021) Soil salinity regulation of soil microbial carbon metabolic function in the Yellow River Delta. China Sci Total Environ 790:148258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148258
Yu LL, Luo SS, Xu X, Gou YG, Wang JW (2020) The soil carbon cycle determined by GeoChip 50 in sugarcane and soybean intercropping systems with reduced nitrogen input in South China. Appl Soil Ecol 155:14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103653
Yuan Y, Gao S, Dai XQ, Chen FS, Wang HM (2021) Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on soil aggregation and its associated organic carbon. Chem Ecol 37(7):603–615. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2021.1936512
Zaehle S (2013) Terrestrial nitrogen - carbon cycle interactions at the global scale. Proc R Soc B-Biol Sci 368:9. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2013.0125
Zhang Q, Wang YP, Pitman AJ, Dai YJ (2011a) Limitations of nitrogen and phosphorous on the terrestrial carbon uptake in the 20th century. Geophys Res Lett 38. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011GL049244
Zhang T, Zhu W, Mo J, Liu L, Dong S (2011b) Increased phosphorus availability mitigates the inhibition of nitrogen deposition on CH4 uptake in an old-growth tropical forest, southern China. Biogeosciences 8:2847–2847. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-8-2847-2011
Zhang XM, Wei HW, Chen QS, Han XG (2014) The counteractive effects of nitrogen addition and watering on soil bacterial communities in a steppe ecosystem. Soil Biol Biochem 72:26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.01.034
Zhang JF, Sayer EJ, Zhou JG, Li YW, Li YX, Li ZA, Wang FM (2021) Long-term fertilization modifies the mineralization of soil organic matter in response to added substrate. Sci Total Environ 798:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149341
Zhao QQ, Bai JH, Lu QQ, Zhang GL (2007) Effects of salinity on dynamics of soil carbon in degraded coastal wetlands: implications on wetland restoration. Phys Chem Earth 97:12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2016.08.008
Zhao GY, Liu JS, Wang Y, Dou JX, Dong XY (2009) Effects of elevated CO2 concentration and nitrogen supply on biomass and active carbon of freshwater marsh after two growing seasons in Sanjiang plain, Northeast China. J Environ Sci 21:1393–1399. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1001-0742(08)62431-6
Zhao QQ, Bai JH, Wang X, Zhang W, Huang YJ, Wang LL, Gao YC (2020) Soil organic carbon content and stock in wetlands with different hydrologic conditions in the Yellow River Delta, China. Ecohydrol Hydrobiol 20:537–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecohyd.2019.10.008
Zheng MH, Zhang T, Liu L, Zhang W, Lu XK, Mo JM (2016) Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus additions on soil methane uptake in disturbed forests. J Geophys Res-Biogeosci 121:3089–3100. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016jg003476
Zheng B, Zhu Y, Sardans J, Peñuelas J, Su J (2018) QMEC: a tool for high-throughput quantitative assessment of microbial functional potential in C, N, P, and S biogeochemical cycling. Sci China-Life Sci 61:1451–1462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-018-9364-7
Zhou J, Guan D, Zhou B, Zhao B, Ma M, Qin J, Jiang X, Chen S, Cao F, Shen D, Li J (2015) Influence of 34-years of fertilization on bacterial communities in an intensively cultivated black soil in Northeast China. Soil Biol Biochem 90:42–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.07.005
Funding
This work was supported by “Double First-Class” project of the Ministry of Education of China (2022 AC019), National Natural Science Foundation of China (42007076), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR2020QD116).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Xuejun Du, Yanning Ge, Yun Zhang. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Xuejun Du. Hao Hu, Yiying Zhang, Ziye Yang and Yuling Song revised the manuscript. Xueqin Ren, Shuwen Hu and Haojie Feng contributed substantially to the study design and supervised the field and laboratory personnel. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Luca Bragazza.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 606 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Du, X., Ge, Y., Zhang, Y. et al. Responses of soil carbon cycling microbial functional genes to nitrogen and phosphorus addition in saline-sodic soils. Plant Soil 490, 261–277 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06070-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06070-y