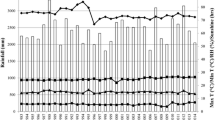
Abstract
Aims
Broad-leaved tree species are important group building tree species of typical zonal vegetation in subtropical China. Yet, the impacts of mixed broad-leaved plantations on microbial community and enzymatic stoichiometry are not well understood.
Methods
We evaluated soil microbial community structure and enzymatic stoichiometry using rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil samples of Machilus pauhoi from three forest plantation (pure M. pauhoi forest (CK), M. pauhoi with Cerasus campanulata mixed forest (MC), M. pauhoi with Manglietia glauca mixed forest (MM)) in subtropical China.
Results
P concentration of rhizosphere soil in MC was higher than that in CK, and soil TC, TN, SOC, DOC of non-rhizosphere soil in MC were higher than those in MM. Different mixed plantations had significant effects on G+/G−, being its value lower in MC than in CK and MM. The microbial P limitation in rhizosphere soil was higher than that in non-rhizosphere soil. The relative microbial C limitation did not change significantly amongst different treatment. Soil TC, TN, SOC and DOC are critical factors affecting the microbial community structure.
Conclusion
Mixing with Cerasus campanulata is more beneficial to reducing soil P deficiency and improving soil microbial community structure of young M. pauhoi afforestation in a mid-subtropical region of China.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai C, Liang G, Sun J, Wang X, Zhou W (2012) Responses of extracellular enzyme activities and microbial community in both the rhizosphere and bulk soil to long-term fertilization practices in a fluvo-aquic soil. Geoderma 173–174(2):330–338
Bååth E, Frostegard A, Pennanen T, Hannu F (1995) Microbial community structure and pH response in relation to soil or ganic matter quality in wood-ash fertilized, clear-cut or burned coniferous forest soils. Soil Biol Biochem 27:229–240
Bai Y, Zha X, Chen S (2020) Effects of the vegetation restoration years on soil microbial community composition and biomass in degraded lands in Changting County, China. J For Res 31(4):1295–1308
Bardgett RD (2005) The biology of soil: a community and ecosystem approach. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Brunel C, Gros R, Ziarelli F, Silva AMFD (2017) Additive or non-additive effect of mixing oak in pine stands on soil properties depends on the tree species in Mediterranean forests. Sci Total Environ 590–591:676–685
Carter MR (1993) Soil sampling and methods of analysis. The chemical rubber company press, Boca Raton
Cao ZP, Li DP, Han XM (2011) The fungal to bacterial ratio in soil food webs, and its measurement. Acta Ecol Sin 31(16):4741–4748
Chen YK, Tan XM, Li M et al (2021) Effects of mixture of valuable nitrogen-fixing tree species Dalbergia odorifera and second-generation Eucalyptus urophylla on structure and function of soil microbial community in subtropical China. Guihaia 41(9):1476–1485
Cornwell WK, Cornelissen JHC, Amatangelo K, Dorrepaal E, Eviner VT, Godoy O, Hobbie SE, HoorensB, Kurokawa H, Perez-Harguindeguy N, Quested HM, Santiago LS, Wardle DA, Wright IJ, Aerts R, Allison SD, van Bodegom P, Brovkin V, Chatain A, Callaghan TV, Diaz S, Garnier E, Gurvich DE, Kazakou E, Klein JA, Read J, Reich PB, Soudzilovskaia NA, Victoria Vaieretti M, Westoby M (2008) Plant species traits are the predominant control on litter decomposition rates within biomes worldwide. Ecol Lett 11:1065–1071
Cui YX, Bing HJ, Fang LC, Wu YH, Yu JL, Shen GT, Jiang M, Wang X, Zhang XC (2019) Diversity patterns of the rhizosphere and bulk soil microbial communities along an altitudinal gradient in an alpine ecosystem of the eastern tibetan Plateau. Geoderma 338:118–127
Cui YX, Zhang YL, Duan CJ, Wang X, Zhang XC, Ju WL, Chen HS, Yue SC, Wang YQ, Li SQ, Fang LC (2020) Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals microbial phosphorus limitation decreases the nitrogen cycling potential of soils in semi-arid agricultural ecosystems. Soil Tillage Res 197:104463
Cui YX, Bing HJ, Fang LC, Jiang M, Shen GT, Yu JL, Wang X, Zhu H, Wu YH, Zhang XC (2021) Extracellular enzyme stoichiometry reveals the carbon and phosphorus limitations of microbial metabolisms in the rhizosphere and bulk soils in alpine ecosystems. Plant Soil 458:7–20
Dai WW, Peng B, Liu J, Wang C, Wang X, Jiang P, Bai E (2021) Four years of litter input manipulation changes soil microbial characteristics in a temperate mixed forest. Biogeochemistry 154:371–383
Evans SE, Wallenstein MD (2012) Soil microbial community response to drying and rewetting stress: does historical precipitation regime matter? Biogeochemistry 109:101–116
Fang XM, Zhang XL, Chen FS, Zong YY, Bu WS, Wan SZ, Luo YQ, Wang HM (2019) Phosphorus addition alters the response of soil organic carbon decomposition to nitrogen deposition in a subtropical forest. Soil Biol Biochem 133:119–128
Fanin N, Kardol P, Farrell M, Nilsson MC, Gundale MJ, Wardle DA (2019) The ratio of Gram-positive to Gram-negative bacterial PLFA markers as an indicator of carbon availability in organic soils. Soil Biol Biochem 128:111–114
Fekete I, Lajtha K, Kotroczó Z, Várbíró G, Varga C, Tóth JA, Demeter I, Veperdi G, Berki I (2017) Long-term effects of climate change on carbon storage and tree species composition in a dry deciduous forest. Glob Chang Biol 23:3154–3168
Fu DG, Wu XN, Duan CQ, Zhao LQ, Li B (2020) Different life-form plants exert different rhizosphere effects on phosphorus biogeochemistry in subtropical mountainous soils with low and high phosphorus content. Soil Tillage Res 199:104516
Guo XP, Chen HYH, Meng MJ, Biswas SR, Ye LX, Zhang JC (2016) Effects of land use change on the composition of soil microbial communities in a managed subtropical forest. For Ecol Manag 373:93–99
Guo XF, Li HS, Chen HY (2017) The Effects of Biochar and Intercropping on the cd, cr and Zn Speciation in Soils and Plant Uptake by Machilus pauhoi Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 98:574–581
Hammesfahr U, Heuer H, Manzke B, Smalla K, Thiele-Bruhn S (2008) Impact of the antibiotic sulfadiazine and pig manure on the microbial community structure in agricultural soils. Soil Biol Biochem 40(7):1583–1591
Han SZ, Gao R, Li AP, Ma HL, Yin YF, Si YT, Chen SD, Zheng QR (2015) Soil microbial community structure of two types of forests in the mid-subtropics of China. Chin J Appl Ecol 26(7):2151–2158
Huang XM, Liu SR, Wang H, Hu ZD, Li ZG, You YM (2014) Changes of soil microbial biomass carbon and community composition through mixing nitrogen-fixing species with Eucalyptus urophylla in subtropical China. Soil Biol Biochem 73:42–48
Huang Y, Chen Y, Castro-Izaguirre et al (2018) Impacts of species richness on productivity in a large-scale subtropical forest experiment. Science 362:80–83
Ji L, Yang YC, Yang LX, Zhang DP (2020) Effect of land uses on soil microbial community structures among different soil depths in northeastern China. Eur J Soil Biol 99:103205
Jing X, Chen X, Fang JY, Ji CJ, Shen HH, Zheng CY, Zhu B (2020) Soil microbial carbon and nutrient constraints are driven more by climate and soil physicochemical properties than by nutrient addition in forest ecosystems. Soil Biol Biochem 141:107657
Kelly JJ, Favila E, Hundal LS, Marlin JC (2007) Assessment of soil microbial communities in surface applied mixtures of Illinois River sediments and biosolids. Appl Soil Ecol 36(2–3):176–183
Kooch Y, Bayranvand M (2017) Composition of tree species can mediate spatial variability of C and N cycles in mixed beech forests. For Ecol Manag 401:55–64
Kumar S, Garkoti SC (2022) Rhizosphere influence on soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity in banj oak, chir pine and banj oak regeneration forests in the central Himalaya. Geoderma 409:115626
Kuzyakov Y, Hill PW, Jones DL (2007) Root exudate components change litter decomposition in a simulated rhizosphere depending on temperature. Plant Soil 290(1–2):293–305
Landesman WJ, Dighton J (2010) Response of soil microbial community and the production of plant-available nitrogen to a two-year rainfall manipulation in the New Jersey Pinelands. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1751–1758
Li WQ, Wu ZJ, Zong YY, Wang GG, Chen FS, Liu YQ, Li JJ, Fang XM (2022a) Tree species mixing enhances rhizosphere soil organic carbon mineralization of conifers in subtropical plantations. For Ecol Manag 516:120238
Li WN, Luo YM, Huang ZY, Yang M (2022b) Effects of mixed young plantations of Parashorea chinensis on soil microbial functional diversity and carbon source utilization. Chin J Plant Ecol 46(9):1109–1124
Lin HY, Zhou JC, Zeng QX, Sun J, Xie H, Liu YY, Mei KC, Wu Y, Yuan XC, Wu JM, Su XC, Cheng DL (2022) Soil enzyme stoichiometry revealed the changes of soil microbial carbon and phosphorus limitation along an elevational gradient in a Pinus taiwanensis forest of Wuyi Mountains, Southeast China. Chin J Appl Ecol 33(1):33–41
Liu YB, Zhao LN, Wang ZR, Liu LC, Zhang P, Sun JY, Wang BY, Song G, Li XR (2018) Changes in functional gene structure and metabolic potential of the microbial community in biological soil crusts along a revegetation chronosequence in the Tengger Desert. Soil Biol Biochem 126:40–48
Liu YC, Tian HM, Li JR, Wang H, Liu SR, Liu XJ (2022) Reduced precipitation neutralizes the positive impact of soil warming on soil microbial community in a temperate oak forest. Sci Total Environ 806:150957
Lucas-Borja ME, Candel D, Jindo K, Moreno JL, Bastida F (2012) Soil microbial community structure and activity in monospecific and mixed forest stands, under Mediterranean humid conditions. Plant Soil 354:359–370
Ma SH, Chen GP, Tang WG, Xing AJ, Chen X, Xiao W, Zhou LH, Zhu JL, Li YD, Zhu B, Fang JY (2021) Inconsistent responses of soil microbial community structure and enzyme activity to nitrogen and phosphorus additions in two tropical forests. Plant Soil 460:453–468
Mo QF, Zou B, Li YW, Chen Y, Zhang WX, Mao R, Ding YZ, Wang J, Lu XK, Li XB, Tang JW, Li ZA, Wang FM (2015) Response of plant nutrient stoichiometry to fertilization varied with tissues in a tropical forest. Sci Rep 5:14605
Moorhead DL, Rinkes ZL, Sinsabaugh RL, Weintraub MN (2013) Dynamic relationships between microbial biomass, respiration, inorganic nutrients and enzyme activities: informing enzyme-based decomposition models. Front Microbiol 4(4):223
Myers RT, Zak DR, White DC, Peacock A (2001) Landscape-level patterns of microbial community composition and substrate use in upland forest ecosystems. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:359–367
Pereira APA, Durrer A, Gumiere T, Goncalves JLM, Robin A, Bouillet JP, Wang J, Verma JP, Singh BK, Cardoso EJBN (2019) Mixed Eucalyptus plantations induce changes in microbial communities and increase biological functions in the soil and litter layers. For Ecol Manag 433:332–342
Phillips RP, Fahey TJ (2008) The influence of soil fertility on rhizosphere effects in northern hardwood forest soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 72:453–461
Prober SM, Leff JW, Bates ST, Borer ET, Firn J, Harpole WS, Lind EM, Seabloom EW, Adler PB, Bakker JD (2015) Plant diversity predicts beta but not alpha diversity of soil microbes across grasslands worldwide. Ecol Lett 18:85–95
Qi DD, Feng FJ, Lu C, Fu YM (2022) C:N:P stoichiometry of different soil components after the transition of temperate primary coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forests to secondary forests. Soil Tillage Res 216:105260
Santana MC, Pereira A, Souza A et al (2021) Shifts on archaeal community structure in pure and mixed Eucalyptus grandis and Acacia mangium plantations. For Ecol Manag 492:119218
Shao WZ, Zhou XG, Wen YG et al (2022) Effects of mixing Eucalyptus and Castanopsis hystrix on soil hydrolytic enzyme activities and ecoenzymatic stoichiometry. Guihaia 42(4):543–555
Shi LJ, Wang HM, Fu XL, Kou L, Meng SW, Dai XQ (2020) Soil enzyme activities and their stoichiometry of typical plantations in mid-subtropical China. Chin J Appl Ecol 31(6):1980–1988
Singh J, Kumar S (2021) Responses of soil microbial community structure and greenhouse gas fluxes to crop rotations that include winter cover crops. Geoderma 385:114843
Sinsabaugh RL, Hill BH, Follstad Shah JJ (2009) Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial organic nutrient acquisition in soil and sediment. Nature 462:795–798
Sinsabaugh RL, Follstad Shah JJ (2012) Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and ecological theory. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 43:313–343
Steinbeiss S, Gleixner G, Antonietti M (2009) Effect of biochar amendment on soil carbon balance and soil microbial activity. Soil Biol Biochem 41(06):1301–1310
Swallow M, Quideau S, MacKenzie M, Kishchuk B (2009) Microbial community structure and function: the effect of silvicultural burning and topographic variability in northern Alberta. Soil Biol Biochem 41:770–777
Tan XP, Nie YX, Ma XM, Guo ZM, Liu Y, Tian X, Megharaj M, Shen WJ, He WX (2021) Soil chemical properties rather than the abundance of active and potentially active microorganisms control soil enzyme kinetics. Sci Total Environ 770:144500
Tian HQ, Chen GS, Zhang C, Melillo JM, Hall CAS (2010) Pattern and variation of C:N:P ratios in China’s soils: a synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry 98:139–151
Ushio M, Balser TC, Kitayama K (2013) Effects of condensed tannins in conifer leaves on the composition and activity of the soil microbial community in a tropical montane forest. Plant Soil 365:157–170
Wan XH, Huang ZQ, He ZM, Yu ZP, Wang MH, Davis MR, Yang YS (2015) Soil C:N ratio is the major determinant of soil microbial community structure in subtropical coniferous and broadleaf forest plantations. Plant Soil 387:103–116
Wang SY, Han XZ, Qiao YF, Wang SY, Li XH (2009) Efects of land uses and fertilization systems on soil enzyme activities and nutrients. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci 15(6):1311–1316
Waring BG, Weintraub SR, Sinsabaugh RL (2014) Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial nutrient acquisition in tropical soils. Biogeochemistry 117(1):101–113
Wen YG, Li HY, Zhou XG, Zhu HG, Li YC, Cai DX, Jia HY, Huang XM, You YM (2019) Effects of uneven-aged Pinus massoniana×Castanopsis hystrix mixed plantations on structural and functions of soil microbial community. Guangxi Sci 26(2):188–198
Xu H, Yu M, Cheng X (2021) Abundant fungal and rare bacterial taxa jointly reveal soil nutrient cycling and multifunctionality in uneven-aged mixed plantations. Ecol Ind 129(2):107932
Yi XG, Yu XQ, Chen J, Zhang M, Liu SW, Zhu H, Li M, Duan YF, Chen L, Wu L, Zhu S, Sun ZS, Liu XH, Wang XR (2020) The genome of chinese flowering cherry (Cerasus serrulata) provides new insights into Cerasus species. Hortic Res 7:165
Zelles L (1999) Fatty acid patterns of phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides in the characterisation of microbial communities in soil: a review. Biol Fertil Soils 29:111–129
Zhang ZF, Zhou XY (2011) GC/MS analysis on Benzene/Alcohol extractives of Manglietia Glauca Leavies for biomedicine engineering. Adv Mater Res 213:475–478
Zhang QF, Xie JS, Lyu MK, Xiong DC, Wang J, Chen YM, Li YQ, Wang MH, Yang YS (2017) Short-term effects of soil warming and nitrogen addition on the N:P stoichiometry of Cunninghamia lanceolata in subtropical regions. Plant Soil 411:395–407
Zhang XX, Yang LM, Chen Z, Li YQ, Lin YY, Zheng XZ, Chu HY, Yang YS (2018) Patterns of ecoenzymatic stoichiometry on types of forest soils form different parent materials in subtropical areas. Acta Ecol Sin 38(16):5828–5836
Zhang YL, Sun CX, Chen ZH, Zhang GN, Chen LJ, Wu ZJ (2019) Stoichiometric analyses of soil nutrients and enzymes in a Cambisol soil treated with inorganic fertilizers or manures for 26 years. Geoderma 353:382–390
Zhang WW, Liu W, He SW, Chen QC, Han JG, Zhang QF (2021a) Mixed plantations of Metasequoia glyptostroboides and Bischofia polycarpa change soil fungal and archaeal communities and enhance soil phosphorus availability in Shanghai, China. Ecol Evol 11:7239–7249
Zhang HJ, Wang SJ, Zhang JX, Tian CJ, Luo SS (2021b) Biochar application enhances microbial interactions in mega-aggregates of farmland black soil. Soil Tillage Res 213:105145
Zhang ZQ, Peng WX, Duan CJ, Zhu XZ, Wu H, Zhang XC, Fang LC (2022) Microplastics pollution from different plastic mulching years accentuate soil microbial nutrient limitations. Gondwana Res 108:91–101
Zhong QL, Cheng DL, Hu SZ, He LZ, Tang CC, Wen YX, Qiu JF, Li XH (2009) Chlorophyll content and net photosynthetic rate of Machilus pauhoi and M. leptophylla. Chin J Appl Ecol 20(02):271–276
Zhou LH, Liu SS, Shen HH, Zhao MY, Xu LC, Xing AJ, Fang JY (2020) Soil extracellular enzyme activity and stoichiometry in China’s forests. Funct Ecol 34:1461–1471
Zhu YZ, Li YY, Han JG, Yao HY (2019) Effect on changes in water status on soil microbes and their response mechanism: a review. Chin J Appl Ecol 30(12):4323–4332
Zi HB, Xiang ZY, Wang GX, Ade LJ, Wang CT (2017) Profile of soil microbial community under different stand types in Qinghai Province. Sci Silvae Sinicae 53(3):21–32
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31971643, 41601008, 32071555), Forestry department of Fujian Province (2021FKJ29), the General Program of Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (2018J01737), the Industry-University Cooperation Project of Fujian Science and Technology Department (2020N5008, 2019N5009), and Special Funding Project of Fujian Provincial Department of Finance (SC-299). JP and JS acknowledge the financial support from the the Spanish Government grant PID2019-110521GB-I00, the Fundación Ramón Areces grant CIVP20A6621, and the Catalan Government grant SGR 2017−1005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Jiayin Pang.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 843 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, C., Chang, Y., Penuelas, J. et al. Mixing Machilus pauhoi with Cerasus campanulata improves soil P availability and changes the soil G+/G- in a mid-subtropical region of China. Plant Soil 486, 409–424 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-05878-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-05878-y