Abstract
Aims
Root functions are multiple and essential for the growth and survival of terrestrial plants. The aim of this work was to analyse the main trends in the variation of root traits, their coordination with leaf traits and their relationships with soil conditions.
Methods
We measured the variation of 27 fine root traits (five morphological, 20 chemical and two isotopic signatures) in trees of seven species of a mixed plantation in a metal-contaminated and remediated site of Southern Spain.
Results
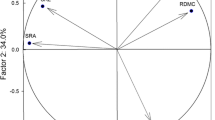
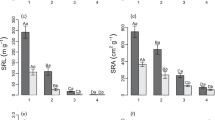
We found evidences supporting the existence of a root economics spectrum (RES). However, other dimensions were identified as being independent of the main RES: mainly the variation in the carbon concentration, the accumulation of trace elements associated with tolerance of metal-rich soils, and the fractionation of δ15N as a time-integrated trait of mycorrhizal-mediated nutrition. In general, roots and leaves were functionally coordinated, although most of the trace elements showed strong root-leaf discordance. The soil conditions interacted with the fine root traits in feedback processes. The ability of tree roots to accumulate trace elements and to reduce their translocation to leaves is a desirable trait for the phytoremediation of metal-contaminated soils.
Conclusions
Roots are multifunctional. Understanding the variations in the root traits of trees will help us to predict both the responses of forests to global changes, including soil contamination, and the provision of soil-based ecosystem services.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alameda D, Villar R (2012) Linking root traits to plant physiology and growth in Fraxinus angustifolia Vahl. seedlings under soil compaction conditions. Environ Exper Bot 79:49–57
Alameda D, Villar R, Iriondo JM (2012) Spatial pattern of soil compaction: trees´ footprint on physical properties. For Ecol Manag 283:128–137
Arduini I, Godbold DL, Onnis A (1994) Cadmium and copper change root growth and morphology of Pinus pinea and Pinus pinaster seedlings. Physiol Plantarum 92:675–680
Augusto L, Bonnaud P, Ranger J (1998) Impact of tree species on forest soil acidification. For Ecol Manag 105:67–78
Barceló J, Poschenrieder C (2004) Structural and ultrastructural changes in heavy metal exposed plants. In: Prasad MNV (ed) Heavy metal stress in plants, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin, pp 223–248
Bardgett RD, Mommer L, de Vries FT (2014) Going underground: root traits as drivers of ecosystem processes. Trends Ecol and Evol 29:692–699
Berthrong ST, Piñeiro G, Jobbagy EG, Jackson RB (2012) Soil C and N changes with afforestation of grasslands across gradients of precipitation and plantation age. Ecol Appl 22:76–86
Bolan NS, Park JH, Robinson B, Naidu R, Huh KY (2011) Phytostabilization. A green approach to contaminant containment. Adv Agron 112:145–204
Cernusak LA, Tcherkez G, Keitel C, Cornwell WK, Santiago LS, Knohl A, Barbour MM, Williams DG, Reich PB, Ellsworth DS, Dawson TE, Griffiths HG, Farquhar GD, Wright IJ (2009) Why are non-photosynthetic tissues generally 13C enriched compared with leaves in C3 plants? Review and synthesis of current hypotheses. Funct Plant Biol 36:199–213
Chagnon PL, Bradley RL, Maherali H, Klironomos JN (2013) A trait-based framework to understand life history of mycorrhizal fungi. Trends Plant Sci 18:484–491
Comas L, Becker S, Cruz VMV, Byrne PF, Dierig DA (2013) Root traits contributing to plant productivity under drought. Front Plant Sci 4:442
Craine JM, Brookshire ENJ, Cramer MD, Hasselquist NJ, Koba K, Marin-Spiotta E, Wang L (2015) Ecological interpretations of nitrogen isotope ratios of terrestrial plants and soils. Plant Soil 396:1–26
de la Riva EG, Pérez-Ramos IM, Tosto A, Navarro-Fernández CM, Olmo M, Marañón T, Villar R (2016a) Disentangling the relative importance of species occurrence, abundance and intraspecific variability in community assembly: a trait-based approach at the whole-plant level in Mediterranean forests. Oikos 125:354–363
de la Riva EG, Tosto A, Pérez-Ramos IM, Navarro-Fernández CM, Olmo M, Anten NPR, Marañón T, Villar R (2016b) A plant economics spectrum in Mediterranean forests along environmental gradients: is there coordination among leaf, stem and root traits? J Veg Sci 27:187–199
de la Riva EG, Olmo M, Poorter H, Ubera JL, Villar R (2016c) Leaf mass per area (LMA) and its relationship with leaf structure and anatomy in 34 Mediterranean woody species along a water availability gradient. PLoS One 11(2):e0148788
de la Riva EG, Marañón T, Pérez-Ramos IM, Navarro-Fernández CM, Olmo M, Villar R (2018a) Root traits across environmental gradients in Mediterranean woody communities: are they aligned along the root economics spectrum? Plant Soil 424:35–48
de la Riva EG, Villar R, Pérez-Ramos IM, Quero JL, Matías L, Poorter L, Marañón T (2018b) Relationships between leaf mass per area and nutrient concentrations in 98 Mediterranean woody species are determined by phylogeny, habitat and leaf habit. Trees 32:497–510
Dakora FD, Phillips DA (2002) Root exudates as mediators of mineral acquisition in low-nutrient environments. Plant Soil 245:35–47
Díaz S, Kattge J, Cornelissen JH, Wright IJ, Lavorel S, Dray S, Reu B, Kleyer M, Wirth C, Prentice IC, Garnier E, Bönisch G, Westoby M, Poorter H, Reich PB, Moles AT, Dickie J, Gillison AN, Zanne AE, Chave J, Wright SJ, Sheremet’ev SN, Jactel H, Baraloto C, Cerabolini B, Pierce S, Shipley B, Kirkup D, Casanoves F, Joswig JS, Günther A, Falczuk V, Rüger N, Mahecha MD, Gorné LD (2016) The global spectrum of plant form and function. Nature 529:167–171
Domínguez MT, Marañón T, Murillo JM, Schulin R, Robinson BH (2008) Trace element accumulation in woody plants of the Guadiamar Valley, SW Spain: a large scale phytomanagement case study. Environ Pollut 152:50–59
Domínguez MT, Madrid F, Marañón T, Murillo JM (2009) Cadmium availability in soil and retention in oak roots: potential for phytostabilization. Chemosphere 76:480–486
Erktan A, McCormack ML, Roumet C (2018) Frontiers in root ecology: recent advances and future challenges. Plant Soil 424:1–9
Fortunel C, Fine PV, Baraloto C (2012) Leaf, stem and root tissue strategies across 758 Neotropical tree species. Funct Ecol 26:1153–1161
Freschet GT, Cornelissen JH, Van Logtestijn RS, Aerts R (2010) Evidence of the ‘plant economics spectrum’ in a subarctic flora. J Ecol 98:362–373
Garnier E, Navas M-L, Grigulis K (2016) Plant functional diversity. University Press, Oxford
Geng Y, Wang L, Jin D, Liu H, He JS (2014) Alpine climate alters the relationships between leaf and root morphological traits but not chemical traits. Oecologia 175:445–455
Gil-Martínez M, López-García Á, Domínguez MT, Navarro-Fernández CM, Kjøller R, Tibbett M, Marañón T (2018) Ectomycorrhizal fungal communities and their functional traits mediate plant-soil interactions in trace element contaminated soils. Front Plant Sci 9:1682
Hobbie JE, Hobbie EA (2008) Natural abundance of N-15 in nitrogen limited forests and tundra can estimate nitrogen cycling through mycorrhizal fungi: a review. Ecosystems 11:815–830
Hobbie EA, Högberg P (2012) Nitrogen isotopes link mycorrhizal fungi and plants to nitrogen dynamics. New Phytol 196:367–382
Holdaway RJ, Richardson SJ, Dickie IA, Peltzer DA, Coomes DA (2011) Species-and community-level patterns in fine root traits along a 120000-year soil chronosequence in temperate rain forest. J Ecol 99:954–963
Houba VJG, Temminghoff EJM, Gaikhorst GA, Van Vark W (2000) Soil analysis procedures using 0.01M calcium chloride as extraction reagent. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 31:1299–1396
Jug A, Makeschin F, Rehfuess KE, Hofmann-Schielle C (1999) Short-rotation plantations of balsam poplars, aspen and willows on former arable land in the Federal Republic of Germany. III. Soil ecological effects. For Ecol Manag 121:85–99
Kabata-Pendias A (2011) Trace elements in soils and plants, 4th edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Kahle H (1993) Response of roots of trees to heavy metals. Environ Exper Bot 33:99–119
Kembel SW, Cahill JF (2011) Independent evolution of leaf and root traits within and among temperate grassland plant communities. PLoS One 6:e19992
Kong D, Ma C, Zhang Q, Li L, Chen X, Zeng H, Guo D (2014) Leading dimensions in absorptive root trait variation across 96 subtropical forest species. New Phytol 203:863–872
Kong D, Wang J, Wu H, Valverde-Barrantes OJ, Wang R, Zeng H et al (2019) Nonlinearity of root trait relationships and the root economics spectrum. Nature Comm 10:2203
Kramer-Walter KR, Bellingham PJ, Millar TR, Smissen RD, Richardson SJ, Laughlin DC (2016) Root traits are multidimensional: specific root length is independent from root tissue density and the plant economic spectrum. J Ecol 104:1299–1310
Krumins JA, Goodey NM, Gallagher F (2015) Plant–soil interactions in metal contaminated soils. Soil Biol Biochem 80:224–231
Ladanai S, Ågren GI, Olsson BA (2010) Relationships between tree and soil properties in Picea abies and Pinus sylvestris forests in Sweden. Ecosystems 13:302–316
Laliberté E (2017) Below-ground frontiers in trait-based plant ecology. New Phytol 213:1597–1603
Lambers H, Chapin FS, Pons TL (2008) Plant physiological ecology, 2nd edn., chapter 6 mineral nutrition. Springer, New York, pp 255–320
Li W, Jin C, Guan D, Wang Q, Wang A, Yuan F, Wu J (2015) The effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on plant root traits: a meta-analysis. Soil Biol Biochem 82:112–118
López-García Á, Gil-Martínez M, Navarro-Fernández CM, Kjøller R, Azcón-Aguilar C, Domínguez MT, Marañón T (2018) Functional diversity of ectomycorrhizal fungal communities is reduced by trace element contamination. Soil Biol Biochem 121:202–211
Madejón P, Marañón T, Murillo JM, Robinson B (2004) White poplar (Populus alba) as a biomonitor of trace elements in contaminated riparian forests. Environ Pollut 132:145–155
Madejón P, Marañón T, Murillo JM (2006) Biomonitoring of trace elements in the leaves and fruits of wild olive and holm oak trees. Sci Total Environ 355:187–203
Madejón P, Domínguez MT, Madejón E, Cabrera F, Marañón T, Murillo JM (2018a) Soil-plant relationships and contamination by trace elements: a review of twenty years of experimentation and monitoring after the Aznalcóllar (SW Spain) mine accident. Sci Total Environ 625:50–63
Madejón P, Domínguez MT, Gil-Martínez M, Navarro-Fernández CM, Montiel-Rozas MM, Madejón E, Murillo JM, Cabrera F, Marañón T (2018b) Evaluation of amendment addition and tree planting as measures to remediate contaminated soils: the Guadiamar case study (SW Spain). CATENA 166:34–43
Manaut N, Sanguin H, Ouahmane L, Bressan M, Thioulouse J, Baudoin E, Galiana A, Hafidi M, Prin Y, Duponnois R (2015) Potentialities of ecological engineering strategy based on native arbuscular mycorrhizal community for improving afforestation programs with carob trees in degraded environments. Ecol Eng 79:113–119
Maremmani A, Bedini S, Matoševic I, Tomei PE, Giovannetti M (2003) Type of mycorrhizal associations in two coastal nature reserves of the Mediterranean basin. Mycorrhiza 13:33–40
Martinez F, Lazo YO, Fernández-Galiano JM, Merino J (2002) Root respiration and associated costs in deciduous and evergreen species of Quercus. Plant Cell Environ 25:1271–1278
McCormack ML, Dickie I, Eissenstat DM, Fahey TJ, Fernandez CW, Guo D, Helmisaari HS, Hobbie EA, Iversen CM, Jackson RB, Leppälammi-Kujansuu J, Norby RJ, Phillips RP, Pregitzer KS, Pritchard SG, Rewald B, Zadworny M (2015) Redefining fine roots improves understanding of belowground contributions to terrestrial biosphere processes. New Phytol 207:505–518
Mendez MO, Maier RM (2008) Phytoremediation of mine tailings in temperate and arid environments. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 7:47–59
Navarro-Fernández CM, Pérez-Ramos IM, de la Riva EG, Vera JR, Roumet C, Villar R, Marañón T (2016) Functional responses of Mediterranean plant communities to soil resource heterogeneity: a mycorrhizal trait-based approach. J Veg Sci 27:1243–1253
Newman GS, Hart SC (2006) Nutrient covariance between forest foliage and fine roots. For Ecol Manag 236:136–141
Olmo M, Lopez-Iglesias B, Villar R (2014) Drought changes the structure and elemental composition of very fine roots in seedlings of ten woody tree species. Implications for a drier climate. Plant Soil 384:113–129
Ouimette A, Guo D, Hobbie E, Gu J (2013) Insights into root growth, function, and mycorrhizal abundance from chemical and isotopic data across root orders. Plant Soil 367:313–326
Pérez-Harguindeguy N, Díaz S, Garnier E, Lavorel S, Poorter H, Jaureguiberry P, Bret-Harte MS, Cornwell WK, Craine JM, Gurvich DE, Urcelay C, Veneklaas EJ, Reich PB, Poorter L, Wright IJ, Ray P, Enrico L, Pausas JG, de Vos AC, Buchmann N, Funes G, Quétier F, Hodgson JG, Thompson K, Morgan HD, ter Steege H, van der Heijden MGA, Sack L, Blonder B, Poschlod P, Vaieretti MV, Conti C, Staver AC, Aquino S, Cornelissen JHC (2013) New handbook for standardised measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Aust J Bot 61:167–234
Pérez-Ramos IM, Roumet C, Cruz P, Blanchard A, Autran P, Garnier E (2012) Evidence for a ‘plant community economics spectrum’ driven by nutrient and water limitations in a Mediterranean rangeland of southern France. J Ecol 100:1315–1327
Phillips RP, Brzostek E, Midgley MG (2013) The mycorrhizal-associated nutrient economy: a new framework for predicting carbon–nutrient couplings in temperate forests. New Phytol 199:41–51
Poorter H, Villar R (1997) The fate of acquired carbon in plants: chemical composition and construction costs. In: Bazzaz FA, Grace J (eds) Plant resource allocation. Academic Press, New York, pp 39–72
Poorter H, Niinemets Ü, Poorter L, Wright IJ, Villar R (2009) Causes and consequences of variation in leaf mass per area (LMA): a meta-analysis. New Phytol 182:565–588
R Development Core Team (2018) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing
Reich PB (2014) The world-wide ‘fast–slow’ plant economics spectrum: a traits manifesto. J Ecol 102:275–301
Robinson D (2001) δ15N as an integrator of the nitrogen cycle. Trends Ecol Evol 16:153–162
Rodríguez-Eugenio N, McLaughlin M, Pennock D (2018) Soil pollution: a hidden reality. FAO, Rome
Roumet C, Birouste M, Picon-Cochard C, Ghestem M, Osman N, Vrignon-Brenas S, Cao K, Stokes A (2016) Root structure–function relationships in 74 species: evidence of a root economics spectrum related to carbon economy. New Phytol 210:815–826
Sariyildiz T, Anderson JM, Kucuk M (2005) Effects of tree species and topography on soil chemistry, litter quality, and decomposition in Northeast Turkey. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1695–1706
Sauer TA, Cambardella C, Brandle J (2007) Soil carbon and tree litter dynamics in a red cedar-scotch pine shelterbelt. Agrofor Syst 71:163–174
Seibt U, Rajabi A, Griffiths H, Berry JA (2008) Carbon isotopes and water use efficiency: sense and sensitivity. Oecologia 155:441–454
Smith SE, Read DJ (2008) Mycorrhizal symbiosis, 3rd edn. Academic, London
Soudzilovskaia NA, van der Heijden MG, Cornelissen JHC, Makarov MI, Onipchenko VG, Maslov MN, Akhmetzhanova AA, van Bodegom PM (2015) Quantitative assessment of the differential impacts of arbuscular and ectomycorrhiza on soil carbon cycling. New Phytol 208:280–293
Tjoelker MG, Craine JM, Wedin D, Reich PB, Tilman D (2005) Linking leaf and root trait syndromes among 39 grassland and savannah species. New Phytol 167:493–508
Tripathi DK, Singh S, Gaur S, Singh S, Yadav V, Liu S, Singh VP, Sharma S, Srivastava P, Prasad SM, Dubey NK, Chauhan DK, Sahi S (2018) Acquisition and homeostasis of iron in higher plants and their probable role in abiotic stress tolerance. Front Environ Sci 5:86
Valverde-Barrantes OJ, Freschet GT, Roumet C, Blackwood CB (2017) A worldview of root traits: the influence of ancestry, growth form, climate and mycorrhizal association on the functional trait variation of fine-root tissues in seed plants. New Phytol 215:1562–1573
Villar R, Ruiz-Robleto J, De Jong Y, Poorter H (2006) Differences in construction costs and chemical composition between deciduous and evergreen woody species are small as compared to differences among families. Plant Cell Environ 29:1629–1643
Weemstra M, Mommer L, Visser EJ, Ruijven J, Kuyper TW, Mohren GM, Sterck FJ (2016) Towards a multidimensional root trait framework: a tree root review. New Phytol 211:1159–1169
Wisniewski L, Dickinson NM (2003) Toxicity of copper to Quercus robur (English oak) seedlings from a copper-rich soil. Environ Exp Bot 50:99–107
Withington JM, Reich PB, Oleksyn J, Eissenstat DM (2006) Comparisons of structure and life span in roots and leaves among temperate trees. Ecol Monogr 76:381–397
Wright IJ, Reich PB, Westoby M, Ackerly DD, Baruch Z, Bongers F, Cavender-Bares J, Chapin T, Cornelissen JHC, Diemer M, Flexas J, Garnier E, Groom PK, Gulias J, Hikosaka K, Lamont BB, Lee T, Lee W, Lusk C, Midgley JJ, Navas ML, Niinemets U, Oleksyn J, Osada N, Poorter H, Poot P, Prior L, Pyankov VI, Roumet C, Thomas SC, Tjoelker MG, Veneklaas EJ, Villar R (2004) The worldwide leaf economics spectrum. Nature 428:821–827
Zadworny M, McCormack ML, Żytkowiak R, Karolewski P, Mucha J, Oleksyn J (2017) Patterns of structural and defense investments in fine roots of scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) across a strong temperature and latitudinal gradient in Europe. Glob Chang Biol 23:1218–1231
Zhao N, Yu G, He N, Wang Q, Guo D, Zhang X, Wang R, Xu Z, Jiao C, Li N, Jia Y (2016) Coordinated pattern of multi-element variability in leaves and roots across Chinese forest biomes. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 25:359–367
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the European Union Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007–2013) (Grant No. 603498- RECARE), the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities (Grants No. CGL2014-52858-R-RESTECO, CGL2017-82254-R-INTARSU, and CGL2014-53236-R- ECO-MEDIT), and European FEDER funds. MG-M was supported by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (Grant No. BES-2015-073882), and MTD by the Universidad de Sevilla (Contrato de Acceso, V Plan Propio de Investigación). We thank J. M. Murillo and J.M. Alegre for their help in the field work, the IRNAS Analytical Service for multielement analyses of plants and soil, and the EBD-CSIC Laboratory of Stable Isotopes for determinations of δ15N and δ13C.
Author contribution statement
TM conceived the study, TM, CMNF and MTD conducted fieldwork, CMNF and PM measured morphological and chemical traits, TM, CMNF and MGM analysed the data, TM wrote the first draft, TM, CMNF, MGM, MTD, PM and RV participated in the interpretation, discussion and preparation of the final version.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Amandine Erktan.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1303 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marañón, T., Navarro-Fernández, C.M., Gil-Martínez, M. et al. Variation in morphological and chemical traits of Mediterranean tree roots: linkage with leaf traits and soil conditions. Plant Soil 449, 389–403 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04485-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04485-5