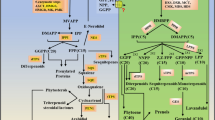
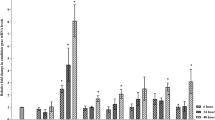
Abstract
Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades are highly conserved signaling modules downstream of receptors/sensors and play pivotal roles in signaling plant defense against pathogen attack. Extensive studies on Arabidopsis MPK4 have implicated that the MAP kinase is involved in multilayered plant defense pathways. In this study, we identified tobacco NtMPK2 as an ortholog of AtMPK4. Transgenic tobacco overexpressing NtMPK2 markedly enhances resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 (Pst DC3000) virulent and avirulent strains. Transcriptome analysis of NtMPK2-dependent genes shows that possibly the basal resistance system is activated by NtMPK2 overexpression. In addition to NtMPK2-mediated resistance, multiple pathways are involved in response to the avirulent bacteria based on analysis of Pst-responding genes, including SA and ET pathways. Notably, it is possible that biosynthesis of antibacterial compounds is responsible for inhibition of Pst DC3000 avirulent strain when programmed cell death processes in the host. Our results uncover that NtMPK2 positively regulate tobacco defense response to Pst DC3000 and improve our understanding of plant molecular defense mechanism.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahuja I, Kissen R, Bones AM (2012) Phytoalexins in defense against pathogens. Trends Plant Sci 17:73–90. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2011.11.002
Asai T et al (2002) MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature 415:977–983. doi:10.1038/415977a
Bednarek P, Pislewska-Bednarek M, Loren V, van Themaat E, Maddula RK, Svatos A, Schulze-Lefert P (2011) Conservation and clade-specific diversification of pathogen-inducible tryptophan and indole glucosinolate metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana relatives. New Phytol 192:713–726. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03824.x
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Broekaert WF, Delaure SL, De Bolle MF, Cammue BP (2006) The role of ethylene in host-pathogen interactions. Annu Rev Phytopathol 44:393–416. doi:10.1146/annurev.phyto.44.070505.143440
Browse J (2009) Jasmonate passes muster: a receptor and targets for the defense hormone. Annu Rev Plant Biol 60:183–205. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.043008.092007
Burow MD, Chlan CA, Sen P, Lisca A, Murai N (1990) High-frequency generation of transgenic tobacco plants after modified leaf disk cocultivation with Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Mol Biol Rep 8:124–139
Cameron RK, Dixon RA, Lamb CJ (1994) Biologically induced systemic acquired resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 5:715–725
Chen RE, Thorner J (2007) Function and regulation in MAPK signaling pathways: lessons learned from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773:1311–1340. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2007.05.003
Chen S, Songkumarn P, Liu J, Wang GL (2009) A versatile zero background T-vector system for gene cloning and functional genomics. Plant Physiol 150:1111–1121. doi:10.1104/pp.109.137125
Conesa A, Gotz S, Garcia-Gomez JM, Terol J, Talon M, Robles M (2005) Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 21:3674–3676. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti610
Corpet F (1988) Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical clustering. Nucleic Acids Res 16:10881–10890
Frei dit Frey N et al (2014) Functional analysis of Arabidopsis immune-related MAPKs uncovers a role for MPK3 as negative regulator of inducible defences. Genome Biol 15:R87. doi:10.1186/gb-2014-15-6-r87
Haas BJ et al (2013) De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat Protoc 8:1494–1512. doi:10.1038/nprot.2013.084
Han L, Li GJ, Yang KY, Mao G, Wang R, Liu Y, Zhang S (2010) Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 and 6 regulate Botrytis cinerea-induced ethylene production in Arabidopsis. Plant J 64:114–127. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04318.x
Ichimura K, Shinozaki K, Tena G, Sheen J, Henry Y (2002) Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plants: a new nomenclature. Trends Plant Sci 7:301–308
Ishihama N, Yamada R, Yoshioka M, Katou S, Yoshioka H (2011) Phosphorylation of the Nicotiana benthamiana WRKY8 transcription factor by MAPK functions in the defense response. Plant Cell 23:1153–1170. doi:10.1105/tpc.110.081794
Jin H, Axtell MJ, Dahlbeck D, Ekwenna O, Zhang S, Staskawicz B, Baker B (2002) NPK1, an MEKK1-like mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase, regulates innate immunity and development in plants. Dev Cell 3:291–297
Jones JD, Dangl JL (2006) The plant immune system. Nature 444:323–329. doi:10.1038/nature05286
Jones P et al (2014) InterProScan 5: genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 30:1236–1240. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu031
King EO, Ward MK, Raney DE (1954) Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescein. J Lab Clin Med 44:301–307
Kloek AP, Brooks DM, Kunkel BN (2000) A dsbA mutant of Pseudomonas syringae exhibits reduced virulence and partial impairment of type III secretion. Mol Plant Pathol 1:139–150. doi:10.1046/j.1364-3703.2000.00016.x
Li B, Dewey CN (2011) RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics 12:323. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-12-323
Li G, Meng X, Wang R, Mao G, Han L, Liu Y, Zhang S (2012) Dual-level regulation of ACC synthase activity by MPK3/MPK6 cascade and its downstream WRKY transcription factor during ethylene induction in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 8:e1002767. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002767
Liu Y, Zhang S (2004) Phosphorylation of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase by MPK6, a stress-responsive mitogen-activated protein kinase, induces ethylene biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:3386–3399. doi:10.1105/tpc.104.026609
Liu Y, Wang L, Cai G, Jiang S, Sun L, Li D (2013) Response of tobacco to the Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 is mainly dependent on salicylic acid signaling pathway. FEMS Microbiol Lett 344:77–85. doi:10.1111/1574-6968.12157
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Mao G, Meng X, Liu Y, Zheng Z, Chen Z, Zhang S (2011) Phosphorylation of a WRKY transcription factor by two pathogen-responsive MAPKs drives phytoalexin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 23:1639–1653. doi:10.1105/tpc.111.084996
Meng X, Zhang S (2013) MAPK cascades in plant disease resistance signaling. Annu Rev Phytopathol 51:245–266. doi:10.1146/annurev-phyto-082712-102314
Mudgett MB, Staskawicz BJ (1999) Characterization of the Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato AvrRpt2 protein: demonstration of secretion and processing during bacterial pathogenesis. Mol Microbiol 32:927–941
Muthamilarasan M, Prasad M (2013) Plant innate immunity: an updated insight into defense mechanism. J Biosci 38:433–449. doi:10.1007/s12038-013-9302-2
Nishihama R, Ishikawa M, Araki S, Soyano T, Asada T, Machida Y (2001) The NPK1 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase is a regulator of cell-plate formation in plant cytokinesis. Genes Dev 15:352–363. doi:10.1101/gad.863701
Petersen M et al (2000) Arabidopsis map kinase 4 negatively regulates systemic acquired resistance. Cell 103:1111–1120
Pitzschke A, Schikora A, Hirt H (2009) MAPK cascade signalling networks in plant defence. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:421–426. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2009.06.008
Remm M, Storm CE, Sonnhammer EL (2001) Automatic clustering of orthologs and in-paralogs from pairwise species comparisons. J Mol Biol 314:1041–1052. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2000.5197
Ren D, Liu Y, Yang KY, Han L, Mao G, Glazebrook J, Zhang S (2008) A fungal-responsive MAPK cascade regulates phytoalexin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:5638–5643. doi:10.1073/pnas.0711301105
Rogers EE, Glazebrook J, Ausubel FM (1996) Mode of action of the Arabidopsis thaliana phytoalexin camalexin and its role in Arabidopsis-pathogen interactions. Mol Plant Microbe Interact: MPMI 9:748–757
Sasaki K, Mitsuhara I, Seo S, Ito H, Matsui H, Ohashi Y (2007) Two novel AP2/ERF domain proteins interact with cis-element VWRE for wound-induced expression of the Tobacco tpoxN1 gene. Plant J 50:1079–1092. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03111.x
Seo S, Sano H, Ohashi Y (1999) Jasmonate-based wound signal transduction requires activation of WIPK, a tobacco mitogen-activated protein kinase. Plant Cell 11:289–298
Soyano T, Nishihama R, Morikiyo K, Ishikawa M, Machida Y (2003) NQK1/NtMEK1 is a MAPKK that acts in the NPK1 MAPKKK-mediated MAPK cascade and is required for plant cytokinesis. Genes Dev 17:1055–1067. doi:10.1101/gad.1071103
Su T et al (2011) Glutathione-indole-3-acetonitrile is required for camalexin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 23:364–380. doi:10.1105/tpc.110.079145
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729. doi:10.1093/molbev/mst197
Toshio M, Folke S (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Viana RA, Pinar M, Soto T, Coll PM, Cansado J, Perez P (2013) Negative functional interaction between cell integrity MAPK pathway and Rho1 GTPase in fission yeast. Genetics 195:421–432. doi:10.1534/genetics.113.154807
Vlot AC, Dempsey DA, Klessig DF (2009) Salicylic acid, a multifaceted hormone to combat disease. Annu Rev Phytopathol 47:177–206. doi:10.1146/annurev.phyto.050908.135202
Wang Z, Mao H, Dong C, Ji R, Cai L, Hao F, Liu S (2009) Overexpression of Brassica napus MPK4 enhances resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in oilseed rape. MPMI 22:235–244. doi:10.1094/mpmi
Wei CF et al (2007) A Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 mutant lacking the type III effector HopQ1-1 is able to cause disease in the model plant Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant J 51:32–46. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03126.x
Whalen MC, Innes RW, Bent AF, Staskawicz BJ (1991) Identification of Pseudomonas syringae pathogens of Arabidopsis and a bacterial locus determining avirulence on both Arabidopsis and soybean. Plant Cell 3:49–59. doi:10.1105/tpc.3.1.49
Wink M (1988) Plant breeding: importance of plant secondary metabolites for protection against pathogens and herbivores. Theor Appl Genet: TAG 75:225–233
Xin XF, He SY (2013) Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000: a model pathogen for probing disease susceptibility and hormone signaling in plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol 51:473–498. doi:10.1146/annurev-phyto-082712-102321
Xu J, Zhang S (2015) Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in signaling plant growth and development. Trends Plant Sci 20:56–64. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2014.10.001
Ye J et al (2006) WEGO: a web tool for plotting GO annotations. Nucleic Acids Res 34:W293–W297. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl031
Zeng Q, Chen JG, Ellis BE (2011) AtMPK4 is required for male-specific meiotic cytokinesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 67:895–906. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04642.x
Zhang S, Klessig DF (2001) MAPK cascades in plant defense signaling. Trends Plant Sci 6:520–527
Zhang Z et al (2012) Disruption of PAMP-induced MAP kinase cascade by a Pseudomonas syringae effector activates plant immunity mediated by the NB-LRR protein SUMM2. Cell Host Microbe 11:253–263. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2012.01.015
Zhang X, Cheng T, Wang G, Yan Y, Xia Q (2013) Cloning and evolutionary analysis of tobacco MAPK gene family. Mol Biol Rep 40:1407–1415. doi:10.1007/s11033-012-2184-9
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2012CB114600) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. XDJK2013C043).
Author’s contribution
XZ and QX designed the project. XZ, GW, JG, MN and WL performed the experimental analysis. XZ performed the bioinformatics analysis and wrote the manuscript. All of the authors have read the manuscript and approved the submission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
The primer sequences used in this study (DOC 41 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Statistics of sequencing and de novo assembly (DOC 33 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 1
Screening of NtMPK2-OX T1 generation transgenic lines using Hygromycin antibiotics (PNG 196 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
H2O2 accumulation in WT and TG19 tobacco (JP2 2758 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
QRT-PCR validation of differentially expressed genes (JPEG 32 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 4
QRT-PCR analysis of 4 selected genes (JPEG 57 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Wang, G., Gao, J. et al. Functional analysis of NtMPK2 uncovers its positive role in response to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 in tobacco. Plant Mol Biol 90, 19–31 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0391-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0391-1